
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Suppose you place 0.245 kg of 20.5°C water in a 0.45 kg aluminum pan with a temperature of 143°C, and 0.0085 kg of the water evaporates immediately, leaving the remainder to come to a common temperature with the pan.
| What would be the final temperature, in degrees Celsius, of the pan and water? The heat of vaporization of water is Lv = 2256 kJ/kg. You may neglect the effects of the surroundings and the heat required to raise the temperature of the vaporized water. | |||
|
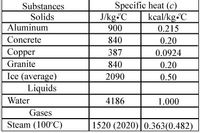
Transcribed Image Text:Substances
Solids
Aluminum
Specific heat (c)
J/kg.C
900
kcal/kg C
0.215
Concrete
840
0.20
Copper
387
0.0924
Granite
840
0.20
Ice (average)
Liquids
2090
0.50
Water
4186
1.000
Gases
Steam (100°C)
1520 (2020) 0.363(0.482)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The world's deepest gold mine, which is located in South Africa, is over 5.1 km deep. Every day, the mine transfers enough energy by heat to the mine's cooling systems to melt 348114 kg of ice at 0.0 degrees Celsius. If the energy output from the mine is increased by 9.6 percent, to what final temperature will the 348114 kg of ice-cold water be heated? Latent Heat of fusion of Ice-3.33 × 105 J/kg Specific heat capacity of Water = 4186J/(kg. °C)arrow_forwardA 0.0725 kg ice cube at −30.0°C is placed in 0.557 kg of 35.0°C water in a very well insulated container. What is the final temperature? The latent heat of fusion of water is 79.8 kcal/kg, the specific heat of ice is 0.50 kcal/(kg · °C), and the specific heat of water is 1.00 kcal/(kg · °C).arrow_forwardIn a physics lab, students are conducting an experiment to learn about the heat capacity of different materials. The first group is instructed to add a number of 1.50 g pellets made of lead, at a temperature of 92.0°C, to 305 g of water at 16.0°C. A second group is given the same number of 1.50 g pellets as the first group, but these are now aluminum pellets. Assume that no heat is lost to or gained from the surroundings for either group. (a) If the final equilibrium temperature of the lead pellets and water is 25.0°C, how many whole pellets did the first group use in the experiment? The specific heat of lead is 0.0305 kcal/(kg · °C). pellets (b) Will the final equilibrium temperature for the second group be higher, lower, or the same as for the first group? The specific heat of aluminum is 0.215 kcal/(kg · °C). O higher O lower O the same (c) What is the equilibrium temperature of the aluminum and water mixture for the second group? °Carrow_forward
- An aluminum wire is wrapped in rubber insulation. Both are subject to thermal expansion, with the following coefficients of linear expansion: alphaa=24· 10−6 1/C and alphar=8· 10−5 1/C . If the wire and insulation are the same length of 1.85m at a temperature of20.00°C, what is the difference in length (in MILLIMETERS) between the copper wire and the rubber insulation when heated up to a temperature of 189.00°C? Express a magnitude only (no negatives!). ______mm (MILLIMETERS!)arrow_forwardA heavy pot made of copper has a mass of 2.07 kg (including the lid) and is heated in an oven to a temperature of 155 °C. You pour 0.10 kg of water at 25.6 °C into the pot and quickly close the lid so that no steam can escape. We assume that no heat is lost to the surrounding. For copper, Ccopper 390 J/(kg.K) = For water, Cwater = 4190 J/(kg.K), Lv = 2256 kJ/kg, Lƒ = 333 kJ/kg. What is the final mass of steam in the pot? garrow_forwardEstimate the temperature change you expect in this air. Let the volume of your room be 38 m3. Heat capacity of air is 1000 J/kg⋅∘C.arrow_forward
- A heavy pot made of copper has a mass of 2.24 kg (including the lid) and is heated in an oven to a temperature of 154 °C. You pour 0.12 kg of water at 26.0 °C into the pot and quickly close the lid so that no steam can escape. We assume that no heat is lost to the surrounding. For copper, Ccopper 390 J/(kg.K) For water, Cwater 4190 J/(kg.K), L, = 2256 kJ/kg, L; = 333 kJ/kg. %3D What is the final mass of steam in the pot? onarrow_forwardA closed box is filled with dry ice at a temperature of -81.3 oC, while the outside temperature is 21.5 oC. The box is cubical, measuring 0.392 m on a side, and the thickness of the walls is 4.40 × 10-2 m. In one day, 3.93 × 106 J of heat is conducted through the six walls. Find the thermal conductivity of the material from which the box is made.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON