
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
thumb_up100%

Transcribed Image Text:WPS Office
ASSIGNMENT 2.pdf
+
Sign in
O Go Premium
= Menu v
Home
Insert
Comment
Edit
Page
Protect
Tools
1. The photoelectric threshold wavelength of a tungsten surface is 270 nm. Calculate the
maximum kinetic energy (in eV) of the electrons ejected from this tungsten surface by
ultraviolet radiation of frequency 1.45 x 1015 Hz.
K
2. What would the min. work function for a metal have to be for visible light (380–750 nm)
to eject photoelectrons?
B
3. The cathode-ray tubes that generated the picture in early color televisions were sources of
X-rays. If the acceleration voltage in a television tube is 15 kV, what are the shortest-
wavelength x-rays produced by the television?
4. (a) What is the minimum potential difference between the filament and the target of an x-
ray tube if the tube is to produce x-rays with a wavelength of 0.16 nm? (b) What is the
shortest wavelength produced in an x-ray tube operated at 30 kV?
3E
5. A laser produces light of wavelength 620 nm in an ultrashort pulse. What is the minimum
duration of the pulse if the minimum uncertainty in the energy of the photons is 1%?
6. An x-ray with a wavelength of 0.1 nm collides with an electron that is initially at rest. The
x-ray's final wavelength is 0.119 nm. What is the final kinetic energy of the electron?
7. An ultrashort pulse has a duration of 7.2 fs and produces light at a wavelength of 522 nm.
What are the momentum and momentum uncertainty of a single photon in the pulse?
8. (a) An electron moves with a speed of 4.5 x 106 m/s. What is its de Broglie wavelength?
(b) A proton moves with the same speed. Determine its de Broglie wavelength.
9. An electron has a de Broglie wavelength of 2.79 Å. Determine (a) the magnitude of its
momentum and (b) its kinetic energy (in joules and in electron volts).
1/2
> >I
BD 00
1- O O
98% -
4:53 PM
Transcribed Image Text:WPS Office
ASSIGNMENT 2.pdf
+
Sign in
O Go Premium
= Menu v
Home
Insert
Comment
Edit
Page
Protect
Tools
K
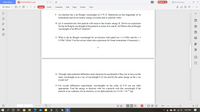
9. An electron has a de Broglie wavelength of 2.79 Å. Determine (a) the magnitude of its
momentum and (b) its kinetic energy (in joules and in electron volts).
10. (a) A nonrelativistic free particle with mass m has kinetic energy K. Derive an expression
for the de Broglie wavelength of the particle in terms of m and K. (b) What is the de Broglie
wavelength of an 800-eV electron?
B
11. What is the de Broglie wavelength for an electron with speed (a) v = 0.469c and (b) v =
0.958c? (Hint: Use the correct relativistic expression for linear momentum if necessary.)
1.
3E
12. Through what potential difference must electrons be accelerated if they are to have (a) the
same wavelength as an x ray of wavelength 0.22 nm and (b) the same energy as the x ray
in part (a)?
13. For crystal diffraction experiments, wavelengths on the order of 0.23 nm are often
appropriate. Find the energy in electron volts for a particle with this wavelength if the
particle is (a) a photon; (b) an electron; (c) an alpha particle (m =6.64 × 10-27 kg).
1/2
> >I
BO 00
98% -
4:53 PM
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Learning Goal: To understand the Bohr model of the hydrogen atom. In 1913 Niels Bohr formulated a method of calculating the different energy levels of the hydrogen atom. He did this by combining both classical and quantum ideas. In this problem, we go through the steps needed to understand the Bohr model of the atom. Part A Consider an electron with charge -e and mass m orbiting in a circle around a hydrogen nucleus (a single proton) with charge +e. In the classical model, the electron orbits around the nucleus, being held in orbit by the electromagnetic interaction between itself and the protons in the nucleus, much like planets orbit around the sun, being held in orbit by their gravitational interaction. When the electron is in a circular orbit, it must meet the condition for circular motion: The magnitude of the net force toward the center, F, is equal to mv²/r. Given these two pieces of information, deduce the velocity of the electron as it orbits around the nucleus. Express your…arrow_forwardAnswer all parts pleasearrow_forwardShow all working explaining detaillly each steparrow_forward
- Question in the Picturesarrow_forwardExplain the steps to find the answer. Show which equation you are using and why you are using it. Also a small reflection about the problem. Thanks.arrow_forwardThe dark-adapted eye can supposedly detect one photon of light of wavelength 500 nm. Suppose that 100 such photons enter the eye each second. Part A Estimate the intensity of the light. Assume that the diameter of the eye's pupil is 0.50 cm. Express your answer in watts per square meter. Templates Symbols undo redo Teset keyboard shortcuts help I= W/m² ܬܘܝܐarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON