
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
13th Edition
ISBN: 9780133923605
Author: Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Acertain electric circuit has a resistor and a capacitor. The capacitor is initially charged to 100 V. When the power supply is detached, the capacitor voltage decays with time, as the following data table shows. Find a functional description of the capacitor voltage v as a function of time t. Plot the function and the data on the same plot.
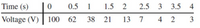
Transcribed Image Text:Time (s)
0.5
1
1.5
2.5
3 3.5 4
Voltage (V)
100 62
38
21
13 7
4 2
3
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, electrical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Inductance and Capacitancearrow_forwardA 10-9.F capacitor (1 nanofarad) is charged to 50 V and then disconnected. One can model the charge leakage of the capacitor with a RC circuit with no voltage source and the resistance of the air between the capacitor plates. On a cold dry day, the resistance of the air gap is 3× 1018 2, on a humid day, the resistance is 6 × 10° 2. How long will it take the capacitor voltage to dissipate to half its original value on each day? ... On the dry day, it will take seconds.arrow_forwardA 10-µF (C1) and a 15-µF (C2) capacitor are connected in series to a 230-V, 60-Hz source. Determine the value of the voltage drop across each capacitor.arrow_forward
- The current through a 220 μF capacitor is given below. Use Ohm’s Law to find the voltage. Convert to polar form, find the impedance and complete the math, then convert back to the waveform at i1 = 1.5sin(2500t + 30°) mA and i2 = 4.7sin(200t – 40°) mAarrow_forwardA thin metallic foil is placed between the plates of a flat capacitor parallel to them. How does this affect capacity? What if you join a plate with a wire?arrow_forward2. The capacitor in the following figure .......arrow_forward
- An inductor is constructed by winding a coil of 100 turns around a magnetic core. The core is a cylinder with radius 0.5 cm and the core material has relative permeability of 1000. The coil covers a length of 10 cm. Determine the resulting inductance. Enter your answer in mH rounded to two decimal places.arrow_forwardInductors are fundamental components in electronics and electrical circuits. They are passive devices that store energy in the form of a magnetic field when crossed by an electric current. Inductors consist of a wire wound around a core, often made of iron or another ferromagnetic material. The storage of magnetic energy in inductors is expressed in terms of inductance, measured in henries (H). What is the value of inductive reactance (XL) in ΩΩ, exhibited by the inductor in the circuit below?arrow_forward1) Propose and draw a circuit of a resistive current divider in halfarrow_forward
- Using the series circuit in Figure 3 consisting of a voltage source V, the resistor R and the fully uncharged capacitor C, how to find the value of the capacitance C considering as known data the time constant of the circuit T and the value of the resistor R? V ww Rarrow_forwardFind the equivalent inductance as seen from the terminals shown in the figure.arrow_forwardA resistor R and a capacitor C are connected in series across a 400 V variable ac supply. When the frequency is 40 Hz, it draws 10 A current, and when the frequency is 50 Hz, it draws 15 A current. Find R and C.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780133923605
Author:Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher:PEARSON

Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9781337900348
Author:Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780073373843
Author:Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Fundamentals of Electric Circuits
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028229
Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew Sadiku
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780134746968
Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan Riedel
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Electromagnetics
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028151
Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.
Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,