
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
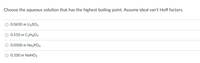
Transcribed Image Text:Choose the aqueous solution that has the highest boiling point. Assume ideal van't Hoff factors.
0.0650 m Li2S04
0.510 m C3H8O3
O 0.0500 m Na3PO4
0.100 m NaNO3
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1
Boiling point elevation:
The formula used here is,
∆Tb = i × Kb × m
Tb(solution) - Tb°(water) = i × Kb × m
Where,
Tb°(water) = boiling point of pure water
Tb(solution) = freezing point of solution
i = van't Hoff factor
Kb = boiling point elevation constant
m = molality of solution
Note:
Boiling point of pure water (Tb°(water)) = 100 °C
Boiling point elevation constant (Kb)water = 0.52 °C/m
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 6 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Determine mass percent of a solution of sucrose (C,H,O1) prepared by dissolving 3.245 g of C12H20 in 73.5 g of water.arrow_forwardWhich of the following solutions has the lowest boiling point? All the solutes are nonvolatile and assume ideal van't Hoff factors. 0.100 m Li,SO4 0.100 m C3H8O3 0.100 m NANO3 0.100 m Na3P04 They all have the same boiling point.arrow_forward1. A solution is prepared by dissolving 12 grams of turmeric powder in 350 grams of water. Calculate the mass percent of each component of the solution. 2. 30 grams of ethyl alcohol (C2H$OH) is dissolved in 75 grams of water. Calculate the mole fraction of ethyl alcohol and water in the solution. 3. A solution is prepared by dissolving 51.30 g of NH,Cl (ammonium chloride) into enough water to make 600 mL of solution. Calculate its molarity. 4. Calculate the molality of a solution prepared from 30.25 grams of NaOH (sodium hydroxide) in 5.00 kilograms of water. 5. If a beaker contains 2.0 moles of water. How many grams of water are the beaker?arrow_forward
- Calculate the vapor pressure at 85.0°C of a solution prepared by dissolving 0.450 mol of liquid dibromoethane (C2H4B12, P° = 127 torr) in 1.80 mol of liquid dibromopropane (C3H6Br2, p° = 173 torr). %3D torrarrow_forwardFeCl₃ has a van't Hoff factor of i = 3.40. What is the concentration of particles in a 0.501 M solution of FeCl₃?arrow_forwardThe vapor pressure of pure water is 23.80 torr at 25.00ºC. Determine the vapor pressure of an aqueous solution containing 45.00 g of glucose (a non-volatile, nonelectrolyte; molar mass = 180.2 g/mol) dissolved in 100.0 g of water. Group of answer choices 793.3 torr 0.9708 torr 23.11 torr 24.15 torr 20.18 torr 22.78 torr64arrow_forward
- A solution is made by dissolving 41.3 g urea (CH4N20), a nonelectrolyte, in 275 g water. Calculate the vapor pressure of this solution at 25°C and 45°C. vapor pressure of water 25°C 23.8 torr 45°C 71.9 torr vapor pressure at 25°C = torr vapor pressure at 45°C = torrarrow_forwardA solution is prepared by adding 25 g of C6H12O6 of glucose to 100 g of water. The resulting solution is 75 ml. Calculate the mole fraction.arrow_forwardChoose the aqueous solution below with the lowest freezing point. All solutions are made of nonvolatile solutes. 0.200 m C6H12O6 0.200 m Al2(SO4)3 0.200 m K3PO4 0.200 m Ca(ClO4)2 These all have the same freezing pointarrow_forward
- Find the mass of urea (CH4N2O)(CH4N2O) needed to prepare 51.0 gg of a solution in water in which the mole fraction of urea is 7.68×10−2arrow_forwardCalculate the freezing point of a 0.383 m solution of a nonelectrolyte. The freezing point of the pure solvent is 5.45 °C and Kf is equal to 6.70 °C/marrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY