
World of Chemistry, 3rd edition
3rd Edition
ISBN: 9781133109655
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Choose a chemical reaction that is used in industry, research, or nature. DO NOT USE the photosynthesis process or the cellular respiration process. Photosynthesis and cellular respiration are not single chemical reactions ; they are each a series of chemical reactions.
For the reaction that you choose:
1) Write the balanced chemical equation for the reaction (include the phases).
2) What is/are the reactant(s)?
3) What is/are the product(s)?
4) Why is this reaction important in either industry, research, or nature?
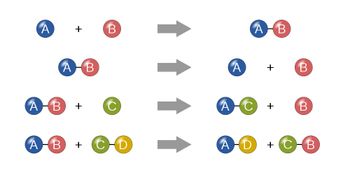
Transcribed Image Text:The image illustrates four different types of chemical reactions using a visual representation of molecules composed of colored spheres labeled with letters.
1. **Synthesis Reaction:**
- Left Side: A single blue sphere labeled "A" and a single red sphere labeled "B" are shown separately with a plus sign between them.
- Right Side: The spheres "A" and "B" are shown connected together.
- Description: This diagram represents a synthesis reaction where two or more simple substances combine to form a more complex compound (A + B → AB).
2. **Decomposition Reaction:**
- Left Side: A molecule composed of a blue sphere "A" and a red sphere "B" connected together.
- Right Side: The spheres "A" and "B" are separate with a plus sign between them.
- Description: This diagram shows a decomposition reaction where a complex molecule breaks down into simpler parts (AB → A + B).
3. **Single Replacement Reaction:**
- Left Side: A molecule with a blue sphere "A" and red sphere "B" connected, along with a separate green sphere "C".
- Right Side: The blue sphere "A" is now connected to the green sphere "C" with the red sphere "B" shown separately.
- Description: This diagram illustrates a single replacement reaction where one element replaces another in a compound (AB + C → AC + B).
4. **Double Replacement Reaction:**
- Left Side: Two molecules: one with a blue sphere "A" and red sphere "B" connected, and another with green sphere "C" and yellow sphere "D" connected.
- Right Side: The blue sphere "A" is now connected to the yellow sphere "D", and the green sphere "C" is connected to the red sphere "B".
- Description: This diagram depicts a double replacement reaction in which components of two compounds exchange places to form two new compounds (AB + CD → AD + CB).
These illustrations provide a clear visual representation of basic chemical reactions, helping to understand how atoms or groups of atoms rearrange during chemical processes.
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1
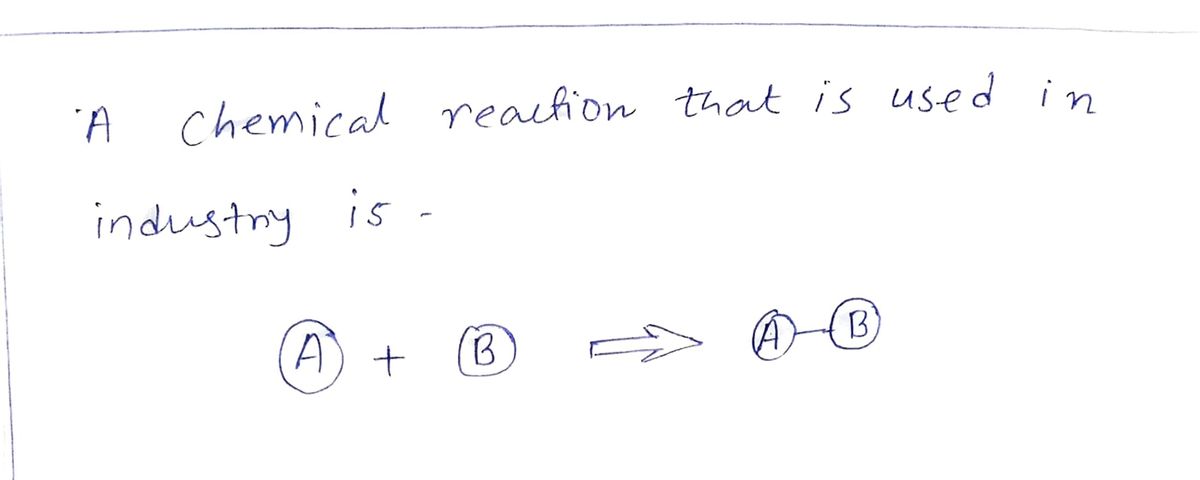
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Write a chemical equation representing the decomposition of water into two gaseous products. What are the products?arrow_forwardTable 6.1 lists some clues that a chemical reaction has occurred. However, these events do not necessarily prove the existence of a chemical change. Give an example for each of the clues that is not a chemical reaction but a physical change.arrow_forwardCarbon monoxide reacts with oxygen to form carbon dioxide at a temperature at which all species are in the gas phase. A tiny sample of the pre-reaction mixture is shown in the following diagram, in which purple spheres represent oxygen atoms and green spheres represent carbon atoms. Draw the product mixture. Give a written description of your reasoning.arrow_forward
- list at least three quantities that must be conserved in chemical reactions.arrow_forwardConsider the following particulate-level representation of a chemical equation: The white spheres represent hydrogen atoms, the black sphere represents a carbon atom, and the red spheres represent oxygen atoms. a Write a balanced chemical equation representing this reaction. b Write a word description of the reaction on the particulate and molar levels.arrow_forwardCarbon dioxide from the atmosphere weathers, or dissolves, limestone (CaCO3) by the reaction CaCO3(s)+CO2(g)+H2O(l)Ca2(aq)+2HCO3(aq) Obtain H for this reaction. See Table 6.2 for the data.arrow_forward
- A weighed sample of a metal is added to liquid bromine and allowed to react completely. The product substance is then separated from any leftover reactants and weighed. This experiment is repeated with several masses of the metal but with the same volume of bromine. This graph indicates the results. Explain why the graph has the shape that it does.arrow_forwardMany over-the-counter antacid tablets are now formulated using calcium carbonate as the active ingredient, which enables such tablets to also be used as dietary calcium supplements. As an antacid for gastric hyperacidity, calcium carbonate reacts by combining with hydrochloric acid found in the stomach, producing a solution of calcium chloride, converting the stomach acid to water, and releasing carbon dioxide gas (which the person suffering from stomach problems may feel as a “burp”). Write the unbalanced chemical equation for this process.arrow_forwardIf you’ve ever left bread in a toaster too long, you know that the bread eventually burns and turns black. What evidence is there that this represents a chemical process?arrow_forward
- An experiment is conducted in which varying amounts of solid iron are added to a fixed volume of liquid bromine. The product of the reaction is a single compound, which can be separated from the product mixture and weighed. The graph shows the relationship between the mass of iron in each trail versus the mass of the product compound. Explain why the group has a positive slope for low masses of iron and a zero slope when the mass of iron added becomes larger.arrow_forwardThe element carbon undergoes many inorganic reactions, as well as being the basis for the field of organic chemistry. Write balanced chemical equations for the reactions of carbon described below. l type='a'> Carbon burns in an excess of oxygen (for example. in the air) to produce carbon dioxide. If the supply of oxygen is limited, carbon will still burn but will produce carbon monoxide rather than carbon dioxide. molten lithium metal is treated with carbon, lithium car bide, Li2C2 , is produced. i>Iron(II) oxide reacts with carbon above temperatures of about 700 °C to produce carbon monoxide gas and molten elemental iron. i>Carbon reacts with fluorine gas at high temperatures to make carbon tetrafluoride.arrow_forwardApply Describe the reaction of aqueous solutions of sodium sulfide and copper(ll) sulfate, producing the precipitate copper(ll) sulfide.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co World of ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780618562763Author:Steven S. ZumdahlPublisher:Houghton Mifflin College Div
World of ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780618562763Author:Steven S. ZumdahlPublisher:Houghton Mifflin College Div Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Living By Chemistry: First Edition TextbookChemistryISBN:9781559539418Author:Angelica StacyPublisher:MAC HIGHER
Living By Chemistry: First Edition TextbookChemistryISBN:9781559539418Author:Angelica StacyPublisher:MAC HIGHER Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning

World of Chemistry, 3rd edition
Chemistry
ISBN:9781133109655
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Matter and Change
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078746376
Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl Wistrom
Publisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co

World of Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780618562763
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl
Publisher:Houghton Mifflin College Div

Introductory Chemistry: A Foundation
Chemistry
ISBN:9781337399425
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Living By Chemistry: First Edition Textbook
Chemistry
ISBN:9781559539418
Author:Angelica Stacy
Publisher:MAC HIGHER

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:9781285199047
Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:Cengage Learning