
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
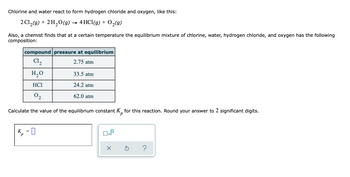
Transcribed Image Text:Chlorine and water react to form hydrogen chloride and oxygen, like this:
2 Cl₂(g) + 2H₂O(g) → 4 HCl(g) + O₂(g)
Also, a chemist finds that at a certain temperature the equilibrium mixture of chlorine, water, hydrogen chloride, and oxygen has the following
composition:
compound pressure at equilibrium
C1₂
2.75 atm
H₂O
HC1
02
Calculate the value of the equilibrium constant K for this reaction. Round your answer to 2 significant digits.
K
=
4,-0
33.5 atm
24.2 atm
62.0 atm
☐
x10
?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Mercury(II) oxide decomposes to form mercury and oxygen, like this: 2 HgO(s)→2 Hg(1)+O2(g) At a certain temperature, a chemist finds that a 3.3 L reaction vessel containing a mixture of mercury(II) oxide, mercury, and oxygen at equilibrium has the following composition: compound amount HgO 19.5 g Hg 14.6 g O2 0, 17.4 g Calculate the value of the equilibrium constant K, for this reaction. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. K_ = 0 x10arrow_forwardPicturearrow_forwardNitrogen and water react to form nitrogen monoxide and hydrogen, like this: N2(9) + 2 H,O(g) 2 NO(g) + 2 H2(g) → Also, a chemist finds that at a certain temperature the equilibrium mixture of nitrogen, water, nitrogen monoxide, and hydrogen has the following composition: compound pressure at equilibrium N2 92.2 atm H,O 76.1 atm NO 19.3 atm H2 33.6 atm Calculate the value of the equilibrium constant K, for this reaction. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. K = 0arrow_forward
- Hydrogen and chlorine react to form hydrogen chloride, like this: H,(g) + Cl,(g) 2 HCl(g) Also, a chemist finds that at a certain temperature the equilibrium mixture of hydrogen, chlorine, and hydrogen chloride has the following composition: compound concentration at equilibrium 0.86 M Cl, 0.30 M HC1 1.9 M Calculate the value of the equilibrium constant K for this reaction. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. K = 0arrow_forwardHydrogen chloride decomposes to form hydrogen and chlorine, like this: 2 HCl(g) - H2(9) + Cl,(9) Also, a chemist finds that at a certain temperature the equilibrium mixture of hydrogen chloride, hydrogen, and chlorine has the following composition: compound concentration at equilibrium HC1 0.49 M H, 1.9M Cl, 0.10M Calculate the value of the equilibrium constant K, for this reaction. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. K̟ = 0arrow_forwardAt a certain temperature, the equilibrium constant K for the following reaction is 0.0017: CO(g)+ H₂O(g) CO₂(g) + H₂(g) Use this information to complete the following table. Suppose a 27. L reaction vessel is filled with 1.5 mol of CO and 1.5 mol of H₂0. What can you say about the composition of the mixture in the vessel at equilibrium? What is the equilibrium constant for the following reaction? Be sure your answer has the correct number of significant digits. CO,(9)+H,(9) CO(g)+H,O(g) What is the equilibrium constant for the following reaction? Be sure your answer has the correct number of significant digits. 2 CO(g) + 2H₂O(g) 2 CO₂(g)+2H₂(9) There will be very little CO and H₂O. There will be very little CO₂ and H₂. Neither of the above is true. K = 0arrow_forward
- Nitrogen and hydrogen react to form ammonia, like this: N,(g) + 3 H,(g) → 2 NH,(g) Also, a chemist finds that at a certain temperature the equilibrium mixture of nitrogen, hydrogen, and ammonia has the following composition: compound pressure at equilibrium N2 82.3 atm H2 38.7 atm NH3 73.0 atm Calculate the value of the equilibrium constant K for this reaction. Round your answer to 2 significant digits.arrow_forwardA chemist is studying the following equilibirum, which has the given equilibrium constant at a certain temperature: 2 NO(g) + Cl₂(g) 2 NOC1 (g) K₂ = 1. x 10 -6 He fills a reaction vessel at this temperature with 13. atm of nitrogen monoxide gas and 17. atm of chlorine gas. Use this data to answer the questions in the table below. Can you predict the equilibrium pressure of NOCI, using only the tools available to you within ALEKS? If you said yes, then enter the equilibrium pressure of NOCI at right. Round your answer to 1 significant digit. O yes O no atm 0 X S BEEN 000 Ararrow_forwardAt a certain temperature, the equilibrium constant K for the following reaction is 0.0087: NO₂(g) + CO(g) → NO(g) + CO₂(g) Use this information to complete the following table. Suppose a 29. L reaction vessel is filled with 0.27 mol of NO₂ and 0.27 mol of CO. What can you say about the composition of the mixture in the vessel at equilibrium? What is the equilibrium constant for the following reaction? Round your answer to 2 significant digits. NO(g) + CO₂(g) NO₂(g) +CO(g) What is the equilibrium constant for the following reaction? Round your answer to 2 significant digits. 2 NO₂(g)+2CO(g) 2NO(g)+2CO₂(g) There will be very little NO₂ and Co. There will be very little NO and CO₂. Neither of the above is true. K = 0 0 0 x10 X ?arrow_forward
- Calcium oxide and carbon dioxide react to form calcium carbonate, like this: CaO(s)+CO2(g)→CaCO3(s) At a certain temperature, a chemist finds that a 4.4 L reaction vessel containing a mixture of calcium oxide, carbon dioxide, and calcium carbonate at equilibrium has the following composition: compound amount Cao 31.2 g CO2 16.8 g CACO3 32.3 g Calculate the value of the equilibrium constant K̟ for this reaction. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. K = [| Submit A Continue MacBook Air F10arrow_forward#3arrow_forwardMercury and oxygen react to form mercury(II) oxide, like this: 2 Hg(1)+O2(g)→2 HgO(5) At a certain temperature, a chemist finds that a 3.6 L reaction vessel containing a mixture of mercury, oxygen, and mercury(II) oxide at equilibrium has the following composition: compound amount Hg 9.7 g O2 21.8 g HgO 10.2 g Calculate the value of the equilibrium constant K̟ for this reaction. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. K_ = 0arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY