
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
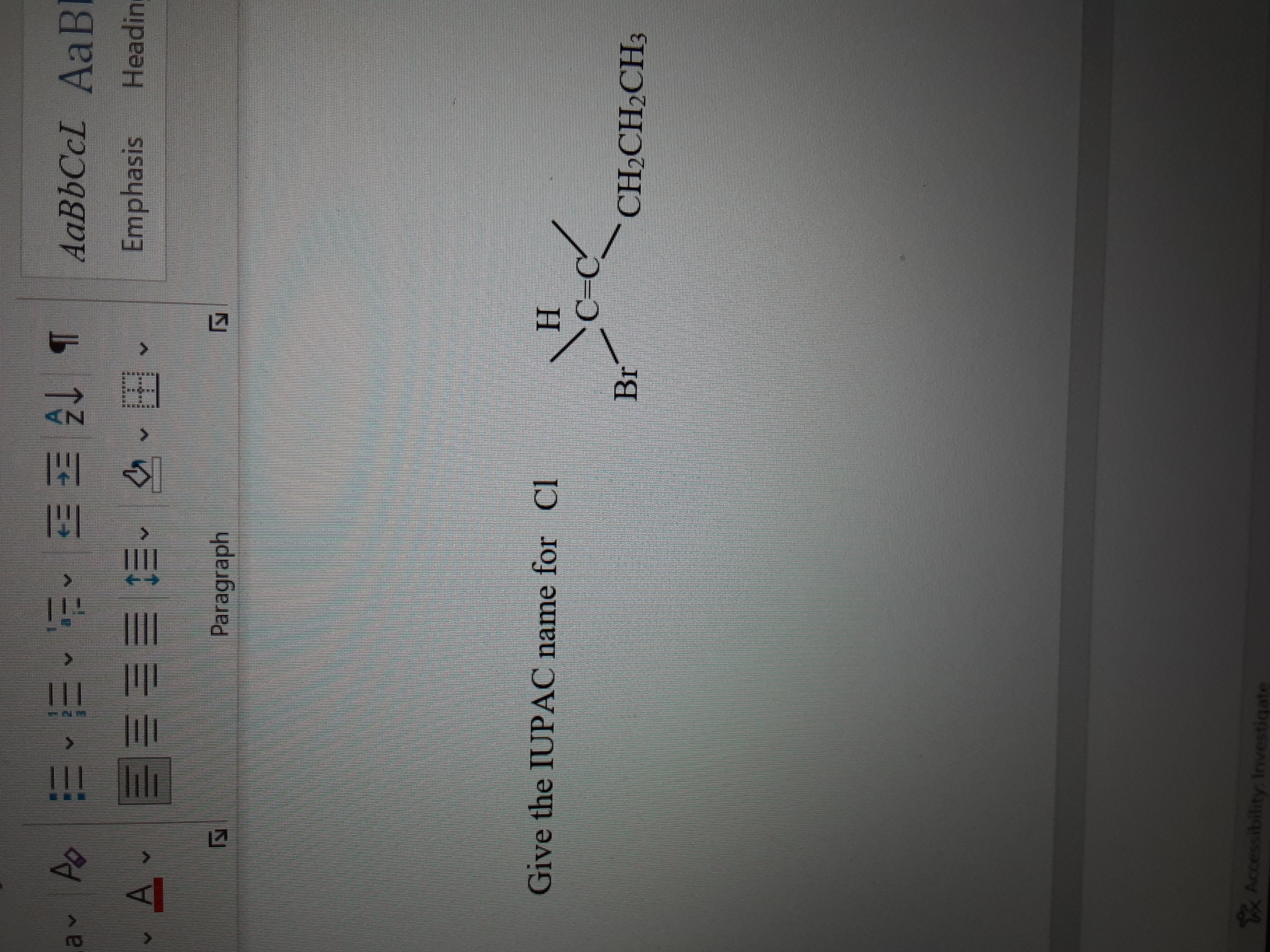
Transcribed Image Text:**Title: Understanding IUPAC Nomenclature for Organic Compounds**
**Objective:**
To determine the IUPAC name for the given chemical compound.
**Chemical Structure:**
The diagram presents a structural formula of an organic compound with the following elements:
1. A carbon-carbon double bond is denoted by "C=C".
2. A hydrogen atom (H) is bonded to the first carbon.
3. A bromine atom (Br) is bonded to the first carbon.
4. A chlorine atom (Cl) is referenced in the question for naming but not shown connected in the image.
5. An ethyl group (CH₂CH₂CH₃) is attached to the second carbon.
**Explanation:**
The structure shown is a monosubstituted alkene with a bromine atom and an ethyl group attached to the carbon atoms involved in a double bond.
**Steps to Determine the IUPAC Name:**
1. **Identify the Longest Carbon Chain:**
- The longest chain that contains the double bond has two carbon atoms; hence, it is an ethene base.
2. **Number the Carbon Atoms:**
- Number the carbon atoms in the main chain starting from the end nearest a substituent. The double bond should get the lowest possible number.
3. **Identify and Name the Substituents:**
- At the first carbon (C-1), there is a bromine atom, and on C-2, there is an ethyl group.
4. **Combine the Components into the Compound Name:**
- The compound name is based on substituents and their positions. Since bromine is not explicitly prioritized over chlorine in the structure provided (i.e., based on alphabetical order without further information where Cl should be), assume only the visible substituents are to be named:
The compound can be named:
- 1-Bromo-2-chloropropene if chlorine is assumed as being part of the structure, replacing the CH₂ component in the question.
- 1-Bromo-1-propene if chlorine is not connected as shown.
**Conclusion:**
This provides an understanding of how to approach determining the IUPAC nomenclature, examining structural elements and naming conventions for clarity in organic chemistry education.
**Note:**
The relevant placement of chlorine should be clarified in practice for accurate naming.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- CH CH OCH,CH, CH₂CH₂CH₂CH, 1) NaOH, H₂O 2) H₂O*. A CH₂ CH₂-CH₂CH₂CH,CH, malonarrow_forwardDraw a perspective representation of the most stable conformation of 3-methylhexane. Draw the molecule on the canvas by choosing buttons from the Tools (for bonds and charges), Atoms, and Templates toolbars. 0 + 7 C Akri C H 12D EXP CONT Marvin JS by ChemAxon 1 H CI P UNOS Jarrow_forwardneed asap pleasearrow_forward
- Give a complete name using IUPACarrow_forwardWhat is the systematic name of the product P of this chemical reaction? ☐ CH3 CH2 CH2 CH2 C-OH + NaOH P + H2Oarrow_forwardb) a) b) Identify the functional group for each organic compound below and give the IUPAC name the compound. 0 CH3CH₂CH₂CH₂C-O-CH₂CH3 CH3-C=CH2 CH₂ CH3 mature Functional group_ Name: Functional group_ Name:arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY