
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
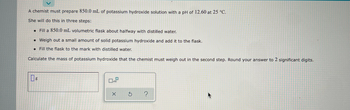
Transcribed Image Text:A chemist must prepare 850.0 mL of potassium hydroxide solution with a pH of 12.60 at 25 °C.
She will do this in three steps:
• Fill a 850.0 mL volumetric flask about halfway with distilled water.
• Weigh out a small amount of solid potassium hydroxide and add it to the flask.
.
Fill the flask to the mark with distilled water.
Calculate the mass of potassium hydroxide that the chemist must weigh out in the second step. Round your answer to 2 significant digits.
6.0
0x10
X
Ś
?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A chemist must prepare 900.0 mL of sodium hydroxide solution with a pH of 13.40 at 25 °C. He will do this in three steps: • Fill a 900.0 mL volumetric flask about halfway with distilled water. • Weigh out a small amount of solid sodium hydroxide and add it to the flask. • Fill the flask to the mark with distilled water. Calculate the mass of sodium hydroxide that the chemist must weigh out in the second step. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. Ox10arrow_forwardA chemist must prepare 800.0 mL of potassium hydroxide solution with a pH of 12.30 at 25 °C. He will do this in three steps: ⚫ Fill a 800.0 mL volumetric flask about halfway with distilled water. • Weigh out a small amount of solid potassium hydroxide and add it to the flask. • Fill the flask to the mark with distilled water. Calculate the mass of potassium hydroxide that the chemist must weigh out in the second step. Round your answer to 2 significant digits.arrow_forwardA stock solution of hydrochloric acid has a concentration of 0.1200M. It is diluted by transferring 10.00 mL to a 100mL volumetric flask using a volumetric pipette. Based on calculations it is found the pH is 1.92. Using the solution that was diluted, prepare a solution with a pH of 2.912. What volume of the diluted solution should you dilute to 100.00 mL to make this solution?arrow_forward
- Rate data have been determined at a particular temperature for the overall reaction 2NO + 2H2 → N2 + 2H2O in which all reactants and products are gases. Trial Run Initial [NO] Initial [H 2] Initial Rate ( M•s1) 1 0.10 M 0.20 M 0.0150 2 0.10 M 0.30 M 0.0225 3 0.20 M 0.20 M 0.0600 What would be the initial rate of the reaction if the initial molar concentration of NO = 0.30 M and the initial molar concentration of H 2 = 0.10 M? О а. 0.068 Мes-1 O b.0.10 Mos-1 O c. 0.040 M•s-1 O d. 0.022 Mos-1 O e. 0.22 Mos-1arrow_forwardA chemist dissolves 158. mg of pure potassium hydroxide in enough water to make up 130. mL of solution, Calculate the pH of the solution. (The temperature of the solution is 25 °C.) Round your answer to 3 significant decimal places.arrow_forwardA chemist dissolves 815. mg of pure barium hydroxide in enough water to make up 110. mL of solution. Calculate the pH of the solution. (The temperature of the solution is 25 °C.) Be sure your answer has the correct number of significant digits. 0 x10 ×arrow_forward
- A chemist must prepare 800.0 mL of potassium hydroxide solution with a pH of 12.90 at 25 °C. She will do this in three steps: • Fill a 800.0 mL volumetric flask about halfway with distilled water. Weigh out a small amount of solid potassium hydroxide and add it to the flask. • Fill the flask to the mark with distilled water. Calculate the mass of potassium hydroxide that the chemist must weigh out in the second step. Round your answer to 2 significant digits.arrow_forwardA chemist dissolves 204. mg of pure barium hydroxide in enough water to make up 170. mL of solution. Calculate the pH of the solution. (The temperature of the solution is 25 °C.) Round your answer to 3 significant decimal places. 0 x10 X Śarrow_forwardA chemist must prepare 400.0 mL of hydrochloric acid solution with a pH of 1.20 at 25 °C. He will do this in three steps: • Fill a 400.0 mL volumetric flask about halfway with distilled water. • Measure out a small volume of concentrated (8.0M) stock hydrochloric acid solution and add it to the flask. • Fill the flask to the mark with distilled water. Calculate the volume of concentrated hydrochloric acid that the chemist must measure out in the second step. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. |mL x10arrow_forward
- Consider the following data on some weak acids and weak bases: name hydrofluoric acid hydrocyanic acid acid 0.1 M C₂H5NHBr 0.1 M NH4CI 0.1 M NaI solution 0.1 M NaF formula HF HCN Ka 6.8 × 10 4.9 × 10 Use this data to rank the following solutions in order of increasing pH. In other words, select a '1' next to the solution that will have the lowest pH, a '2' next to the solution that will have the next lowest pH, and so on. 10 pH choose one ✓ choose one ✓ choose one ✓ base choose one ✓ name formula Kb ammonia NH3 1.8 × 10 pyridine CHN 1.7 x 10 9arrow_forwardA chemist dissolves 715. mg of pure sodium hydroxide in enough water to make up 110. mL of solution. Calculate the pH of the solution. (The temperature of the solution is 25 °C.) Round your answer to 3 significant decimal places.arrow_forwardA chemist must prepare 700.0 mL of sodium hydroxide solution with a pH of 12.30 at 25 °C. She will do this in three steps: • Fill a 700.0 mL volumetric flask about halfway with distilled water. • Weigh out a small amount of solid sodium hydroxide and add it to the flask. • Fill the flask to the mark with distilled water. Calculate the mass of sodium hydroxide that the chemist must weigh out in the second step. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. Ox10arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY