
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
- Calculate the ΔH (in kcal/mol) for the reactions (use table above):
a) H2 + O2 → 2 H2O
b) CH4 + 2 O2 → CO2 + 2 H2O
c) 6 CO2 + 6 H2O → C6H16O6 + 6 O2
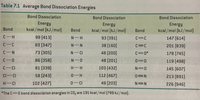
Transcribed Image Text:Table 7.1 Average Bond Dissociation Energies
Bond Dissociation
Bond Dissociation
Bond Dissociation
Energy
kcal/mol (kJ/mol)
Energy
kcal/mol (kJ/mol)
Energy
Bond
Bond
Bond
kcal/mol (kJ/mol)
C-H
99 (413)
N-H
93 (391)
C=C
147 (614)
C C
83 (347)
N-N
38 (160)
C=C
201 (839)
C-N
73 (305)
N-CI
48 (200)
C=0*
178 (745)
C-0
86 (358)
N-0
48 (201)
119 (498)
0=0
C- CI
81 (339)
H-H
103 (432)
N=0
145 (607)
CI-CI
58 (243)
0-H
112 (467)
0=N
213 (891)
H-CI
102 (427)
0-CI
49 (203)
N=N
226 (946)
*The C=0 bond dissociation energies in CO2 are 191 kcal/mol (799 kJ/mol).
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The reaction that was on the screen when you started and its derivative demonstrate that the reaction enthalpy, ΔH, changes sign when a process is reversed. Consider the reaction H2O(l)→H2O(g), ΔH =44.0kJ What will ΔH be for the reaction if it is reversed?arrow_forwardIn the reaction below, how much heat is required for the creation of 38.2 g HBr? H2 + Br2 → 2 HBr ΔH = 72.80 kJ/molarrow_forwardDd.101.arrow_forward
- Classify each as exothermic or endothermic AND explain why. N2O4(g) + 19 kcal → 2 NO2(g) H2O(g) + CO(g) → H2(g) + CO2(g) + 10 kcalarrow_forwardcan you please solve part c and darrow_forwardIn the reaction shown below, the change in enthalpy, AH, will be H H H H H 63 kcal/mol + + H-CI 103 kcal/mol 166 kcal/mol 101 kcal/mol Mi H H CI 84 + kcal/mol 185 kcal/mol kcal/mol.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY