
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
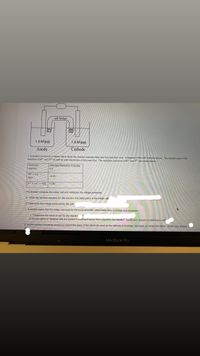
Transcribed Image Text:salt bridge
1.0 M (aq)
1.0 M (aq)
Anode
Cathode
1. A student constructs a voltaic cell to study the reaction between M(s) and X(s) and their ions. A diagram of the cell is shown above. The student uses 1.0 M
solutions of M2* and X3+ as well as solid electrodes of M(s) and X(s). The reduction reactions of M2+ and X3+ are shown below.
Reduction
Standard Reduction Potential
reaction
(V)
M2+ + 2 e-
-0.35
M(s)
X3+ + 3 e- X(s) +1.80
The student connects the voltaic cell and measures the voltage produced.
a*. Write the net-ionic equation for the reaction that takes place in the voltaic cell
b*.Determine the voltage produced by the cell (
C. A student states that the voltaic cell must be thermodynamically unfavorable since a voltage was produced.
i. * Determine the value of AG° for the reactior
ii. Do you agree or disagree with the student's slatement about thermodynamic favorability? Justify your answer by referring to AG°
d. As the reaction proceeds would you expect the mass of the electrode used as the cathode to increase, decrease, or remain the same. Justify your answer.
pte
MacBook Pro
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Consider an electrochemical cell made up of Au Au* and Co²+ | Co³+ half-cells. Part 1 of 2 Write the equation for the cell reaction that occurs under standard-state conditions. Be sure to include the physical state of each species in the reaction. Part 2 of 2 E = ローロ V 00 Calculate the standard emf of a cell that uses the Au Au and Co²+ | Co³+ half-cell reaction at 25 °C. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. Note: Reference the Standard reduction potentials at 25 °C table for additional information. 09 Sarrow_forwardA voltaic electrochemical cell is constructed using the following reaction. The half-cell components are separated by a salt bridge. Br2(1) + Mn(s) 2Br"(aq) + Mn2+(aq) Write the reactions that take place at the anode and at the cathode, the direction in which the electrons migrate in the external circuit, and the direction the anions in the salt bridge migrate. Use smallest possible integer coefficients. If a box is not needed, leave it blank. Enter the reaction that takes place at the anode. Include state symbols: Enter the reaction that takes place at the cathode. Include state symbols: In the external circuit, electrons migrate the Mn electrode the Br2 electrode. Anions migrate the salt bridge the Br2 compartment.arrow_forwardThe half-reaction occurring at the cathode during electrolysis of an aqueous copper(II) iodide solution isarrow_forward
- A galvanic cell is powered by the following redox reaction: 2 Br,(1) + N,H,(aq) + 4OH (aq) 4 Br (aq) + N,(g) + 4 H,O(1) Answer the following questions about this cell. If you need any electrochemical data, be sure you get it from the ALEKS Data tab. Write a balanced equation for the half-reaction that takes place at the cathode. ローロ e Write a balanced equation for the half-reaction that takes place at the anode. Calculate the cell voltage under standard conditions. E - Round your answer to 2 decimal places. のarrow_forwardMnO4– + Sn ----> MnO2 + Sn2+ A) Identify the half-reaction that occurs at the cathode. B) Identify the oxidizing agent and anode. C) standard cell potential? D) What will be the potential of a cell constructed using 57.0 g MnO2, 1.57 M MnO4–, 14.8 g Pt, 12.5 g Sn and 0.87 M Sn2+ at pH 2.5?arrow_forward(ii) State which species is the oxidising agent.arrow_forward
- Consider the following half-reactions and their standard reduction potentials then give the standard line (cell) notation for a voltaic cell built on these half reactions. Mn2*(aq) + 2 e Mn(s) E° = -1.18 V Fe(aq) +3 e Fe(s) E° = -0.036 V A. Fe(s) | Fe3t(aq, 1.0 M) || Mn (s) | Mn 2*(aq. 1.0 M) B. Mn (s) | Mn 2*(aq, 1.0 M) | | Fe(s) | Fe(aq. 1.0 M) C. Fe(s) | Fe3t(aq. 1.0 M) || Mn2*(aq, 1.0 M) | Mn(s) D. Mn (s) | Mn 2*(aq. 1.0 M) || Fe(aq, 1.0 M) | Fe(s)arrow_forwardA galvanic cell is powered by the following redox reaction: 2 NO(g) + 2 H₂O(l) + Zn²+ (aq) Answer the following questions about this cell. If you need any electrochemical data, be sure you get it from the ALEKS Data tab. + 2H¹ (aq) + Zn(s) 2 HNO₂(aq) + Write a balanced equation for the half-reaction that takes place at the cathode. Write a balanced equation for the half-reaction that takes place at the anode. Calculate the cell voltage under standard conditions. Round your answer to 2 decimal places. 0 0 E = -OV ローロ e X ¹0 c.arrow_forwardPlease don't provide handwritten solution .....arrow_forward
- 5. A more complex example where other atoms are involved. Balance the following reaction in basic solution. r (aq) + MnO4 (aq) MnO, (s)+ BrO;" (aq) TABLE 19.1 Standard Electrode Potentials at 25 °C Reduction Half-Reaction E'(V) F + 20 H,0,(aq) + 2 H(aq)+2 e 2F(aq) 2.87 Stronger oxidizing agent Weaker 2 H,0 - PBSO (s) +2 H,0) -Mn0(s)+ 2 H,0) Mn (aq) 4 H,O) - Auts) 1.78 reducing agent PO,(s) + 4 H"(ag) + S0,2-(aq) + 2 e 1.69 Mno, (aq)+ 4 H'(aq) 3 e Mno, (aa) + 8 H (aq)+5 e Au (aq)+3e PbO,(s)+ 4 H(aa) + 2 e Cl,(g) + 2 e" 1.68 1.51 1.50 1.46 - P (ag) + 2 HO - 2a(aq) 1.36 1.33 Cr0, (aq) + 14 H'(ag) + 6 e 0+ 4 H (aq) + 4 e MnO(s)+4 H'(aq) +2 e 10, (aq) 6 H'(aq) + 5e Br+2e vo, (aq) + 2 H'(aq) + e NO, (aq) + 4 H°(aq) + 3e CIO+e 2 C"(aq) + 7 H,On - 2 H,O1) 1.23 Mn (aq) + 2 HyOV) 121 ulae) + 3 H,0() 2 Br (ag) - vo"(aq) +H,00 - NO + 2 H,O0 - CIO, (aa) - Agis) 1.20 1.09 1.00 0.96 0.95 Ag"(aa) + e 0.80 Fe (aq) + O+2 H'(aq)+2e - Fe*(aq) 0.77 - H,O,(ag) 0.70 Mn0, Taa) + e Mn0 (aa) 0.56 8) + 2 e…arrow_forward(c) A galvanic cell is constructed using the following two half-cells at 25°C and 1 atm. The concentration of each species is given in the half-cell equation. Fe* (aq, 1.10 mol dm³) +3e → Fe2+ (aq, 0.86 mol dm³) E° = +0.77 V Ag* (aq, 1.35 mol dm³) + e → Ag(s) E° = +0.88 Varrow_forward3) Draw a picture of the galvanic cell represented by the line notation below and then write the reduction half-reactions for each electrode. Also identify the anode and cathode for each half cell. Pt (s) | Fe3+ (aq), Fe2+ (aq) || Cr2O72-(aq), Cr3+ (aq), HA (aq) | Pt (s)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY