
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
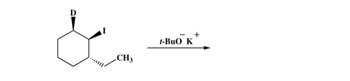
Transcribed Image Text:CH3
+
t-BuO K
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- C2. Chemistry ....arrow_forwardUse the following information to answer Questions 6-9: A sample of NH4NO3 with a mass of 5.0 g is dissolved in 40.1 g of deoinized water in a calorimeter. The initial temperature of the water is 21.2 oC. The final temperature of the solution is 15.4 oC. The calorimeter constant = 25.2 J/oC. If qH2O = -910 J and qcal = -130 J for 5.0 g of NH4NO3, calculate the heat of solution in J per gram of NH4NO3.arrow_forwardHow would you answer this question?arrow_forward
- Concentrated sulfuric acid is 18.0 M. What volume is needed to prepare 1.0 L of 6.0 M sulfuric acid solution? Report your answer with 2 SFarrow_forward2. Given the following data: P4(s) + 6CI2(g) →> 4PCI3(g) AHrxn = 1225.6 kJ %3D P4(s) + 502(g) →> P4O10(s) AHrxn = -2967.3 kJ %3D PCI3(g) + Cl2(g)→ PCI5(g) AHrxn = -84.2 kJ %3D PCI3(g) + %02(g) → CI3PO(g) AHrxn = -285.7 kJ %3D Calculate AH for the reaction P4O10(s) + 6PCI5(g) → 10C13PO(g)arrow_forwardUse the set of three reactions shown below to answer the questions that follow.2NO(g) + O2(g) → 2NO2(g) ΔH = -116 kJ2N2(g) + 5O2(g) + 2H2O(l) → 4HNO3(aq) ΔH = -256 kJN2(g) + O2(g) → 2NO(g) ΔH = +183 kJ If 35.5 g of NO g is reacted with excess oxygen, how much heat energy is produced?arrow_forward
- Please answer these 2 for mearrow_forwardA 90.0 g piece of metal, initially at 98.6°C, is placed into 120.0 g of water initially at 24.3°C. If the final temperature of the water is 34.0°C, what is the specific heat of the metal? (The specific heat of water is 4.18 J/g. °C).arrow_forwardORT SHEET Heat of Neutralization EXPERIMENT elemsboomfchg lom 12 A. Heat Capacity of Calorimeter 1. Temp. of calorimeter and water before mixing 2. Temp. of warm water °C 22.0 39,0 30.3 3. Maximum temp. determined from your curve °C 4. Heat lost by warm water (temp decrease x °C 50.0 g x 4.184 J/K-g) = 02), 5. Heat gained by cooler water (temp. increase x 50.0 g x 4.184 J/K-g) = 30,3 22.0)x 13626J s0.0gmpi S0.0gy 6. Heat gained by the calorimeter [(4) – (5)] = 7. Heat capacity of calorimeter: heat gained by the calorimeter temperature increase J/K 3. Heat of Neutralization of HCl-NaOH 22.2 22.2. °C . Temp. of calorimeter and NaOH Temp. of HCI AT determined from your curve after adding HC1 °C to the NaOH Heat gained by solution (temperature increase x ON 100 g x 4.184 J/K-g) = 9977.8J %3D Heat gained by calorimeter (temperature increase x heat capacity of calorimeter) = J %3D Total joules released by reaction [(3) + (4)] = Tight O 2018 Pearson Education, Inc.arrow_forward
- HBr 50°Carrow_forwardDid I do this conversion correctly? (My answer is highlighted in red)arrow_forwardWhich of the following collisions will initiate the reaction? The energy of the collision is written in kJ beside the possible orientation of the molecules. 130 kJ Reactants Activation Energy 100 kJ Products 15 kJ Reaction Progress Potential Energy [kJ]arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY