
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
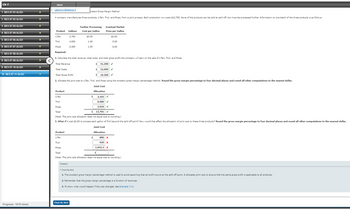
Transcribed Image Text:Ch 7
1. BEX.07.01.ALGO
eBook
Learning Objective 5
Instant Gross Margin Method
A company manufactures three products, L-Ten, Triol, and Pioze, from a joint process. Each production run costs $12,700. None of the products can be sold at split-off, but must be processed further. Information on one batch of the three products is as follows:
2. BEX.07.02.ALGO
3. BEX.07.03.ALGO
Further Processing
Product
Gallons
Cost per Gallon
Eventual Market
Price per Gallon
4. BEX.07.04.ALGO
L-Ten
3,700
$0.50
$2.00
5. BEX.07.05.ALGO
Triol
4,000
1.00
5.00
6. BEX.07.07.ALGO
Pioze
2,300
1.50
6.00
7. BEX.07.08.ALGO
Required:
1. Calculate the total revenue, total costs, and total gross profit the company will earn on the sale of L-Ten, Triol, and Pioze.
8. BEX.07.09.ALGO
9. BEX.07.10.ALGO
10. BEX.07.11.ALGO
Total Revenue
Total Costs
$ 41,200 ✔
$
22,000
✓
-
19,200 ✓
Total Gross Profit
2. Allocate the joint cost to L-Ten, Triol, and Pioze using the constant gross margin percentage method. Round the gross margin percentage to four decimal places and round all other computations to the nearest dollar.
Product
L-Ten
Triol
Joint Cost
Allocation
2,102 v
6,680
Pioze
Total
3,919 ✔
$
12,701 ✔
(Note: The joint cost allocation does not equal due to rounding.)
3. What if it cost $2.00 to process each gallon of Triol beyond the split-off point? How would that affect the allocation of joint cost to these three products? Round the gross margin percentage to four decimal places and round all other computations to the nearest dollar.
Joint Cost
Allocation
Product
L-Ten
Triol
Pioze
Total
$
880 X
620 x
1,642.2 x
ક
(Note: The joint cost allocation does not equal due to rounding.)
Feedback
▼ Check My Work
1. The constant gross margin percentage method used to avoid assuming that all profit occurs at the split-off point. allocates joint cost to ensure that the same gross profit is applicable to all products.
2. Remember that the gross margin percentage is a function of revenues.
3. To show what would happen if the cost changed, see Example 7.11.
Check My Work
Progress: 10/10 items
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- eBook Joint Cost Allocation-Net Realizable Value Method Pure lemonade Show Me How Strawberry lemonade Raspberry lemonade Lily's Lemonade Stand makes three types of lemonade: pure, raspberry, and strawberry. The lemonade is produced through a joint mixing process that costs a total of $30 per batch. One batch produces 32 cups of pure lemonade, 21 cups of strawberry lemonade, and 21 cups of raspberry lemonade. After the split-off point, all three lemonades can be sold for $0.80 per cup, but strawberry and raspberry lemonade can be processed further by adding artificial coloring and flavoring and sold for $0.95 and $1.00 per cup, respectively. It is estimated that these additional processing costs are $0.75 and $1.80 per batch for strawberry and raspberry lemonade, respectively. Allocate the joint costs of production to each product using the net realizable value method. Joint Product Totals Allocation cator=&inprogress=false Check My Work 2 more Check My Work uses remaining. I B Updat…arrow_forwardProblem: Module 6 Textbook Problem 6 Learning Objective: 6-3 Make appropriate outsourcing decisions Perez Electronics currently produces the shipping containers it uses to deliver the electronics products it sells. The monthly cost of producing 9.200 containers follows. Unit-level materials Unit-level labor Unit-level overhead Product-level costs Allocated facility-level costs $5,400 6,800 4,100 9,600 27,900 "One-third of these costs can be avoided by purchasing the containers. Russo Container Company has offered to sell comparable containers to Perez for $2.80 each.. Required a. Calculate the total relevant cost. Should Perez continue to make the containers? b. Perez could lease the space it currently uses in the manufacturing process. If leasing would produce $11,700 per month, calculate the total avoidable costs. Should Perez continue to make the containers? a Total relevant cost Should Perez continue to make the containers? b. Total avoidable cost Should Perez continue to make the…arrow_forwardI want to know how to do those last two, please!arrow_forward
- HELP ASAP *arrow_forwardProblem: Module 6 Textbook Problem 6 Learning Objective: 6-3 Make appropriate outsourcing decisions Benson Electronics currently produces the shipping containers it uses to deliver the electronics products it sells. The monthly cost of producing 9,400 containers follows. Unit-level materials Unit-level labor Unit-level overhead Product-level costs* Allocated facility-level costs $ 6,600 6,300 4,000 9,900 26,400 *One-third of these costs can be avoided by purchasing the containers. Russo Container Company has offered to sell comparable containers to Benson for $2.80 each. Required a. Calculate the total relevant cost. Should Benson continue to make the containers? b. Benson could lease the space it currently uses in the manufacturing process. If leasing would produce $12,400 per month, calculate the total avoidable costs. Should Benson continue to make the containers? a. Total relevant cost Should Benson continue to make the containers? b. Total avoidable cost Should Benson continue to…arrow_forwardCD Only CD With Instructional Materials Estimated Demand 43,000 Units 43,000 Units Est. Sales Price $27.000 $54.00 Est. Cost per unit Dir. Materials $2.50 $2.75 Dir. Labor $3.00 $6.00 Var. Manufacturing OH $3.00 $6.25 Fixed Man. OH $3.00 $3.00 Unit Man. Cost $11.50 $18.00 Additional Development Cost $125,000 Based on the given data, compute the increase or decrease in profit that would result if instructional materials were added to the CD's.…arrow_forward
- Problem 04-4A Evaluating product line costs and prices using ABC LO P3 Bright Day Company produces two beverages, Hi-Voltage and EasySlim. Data about these products follow. Hi-Voltage EasySlim Production volume 12,000 bottles 260,000 bottles Liquid materials 1,600 gallons 33,000 gallons Dry materials 1,120 pounds 12,000 pounds Bottles 12,000 bottles 260,000 bottles Labels 3 labels per bottle 2 label(s) per bottle Machine setups 1,000 setups 800 setups Machine hours 200 MH 3,450 MH Additional data from its two production departments follow. Department Driver Cost Mixing department Liquid materials Gallons $ 1,384 Dry materials Pounds 5,904 Utilities Machine hours 1,460 Bottling department Bottles Units $ 163,200 Labeling Labels per bottle 16,680 Machine setup Setups 27,000 Required:1 & 2. Determine the cost of each product line using ABC. What is the cost per bottle for Hi-Voltage and…arrow_forwardhelparrow_forwardPlease do not give solution in image format thankuarrow_forward
- Aa 16.arrow_forwardProblem: Module 5 Textbook Problem 5 Learning Objective: 5-5 Prepare an income statement using the contribution margin approach Estrada Corporation produced 220,000 watches that it sold for $19 each. The company determined that fixed manufacturing cost per unit was $9 per watch. The company reported a $1,100,000 gross margin on its financial statements. Required Determine the variable cost per unit, the total variable product cost, and the total contribution margin. Variable cost per unit Total variable product cost Total contribution marginarrow_forwardUS Kimmel, Accounting, 7e Help | System Announcements CALCULATOR PRINTER VERSION BACK NEXT Exercise 21-11 a-b Chen Company's Small Motor Division manufactures a number of small motors used in household and office appliances. The Household Division of Chen then assembles and packages such items as blenders and juicers. Both divisions are free to buy and sell any of their components internally or externally. The following costs relate to small motor LN233 on a per unit basis. Fixed cost per unit $4.65 Variable cost per unit $11.20 Selling price per unit $35.10 Assuming that the Small Motor Division has excess capacity, compute the minimum acceptable price for the transfer of small motor LN233 to the Household Division. (Round answer to 2 decimal places, e.g. 10.50.) Minimum transfer price 24 per unit Assuming that the Small Motor Division does not have excess capacity, compute the minimum acceptable price for the transfer of the small motor to the Household Division. (Round answer to 2…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education