
Biochemistry
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781319114671
Author: Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.
Publisher: W. H. Freeman
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
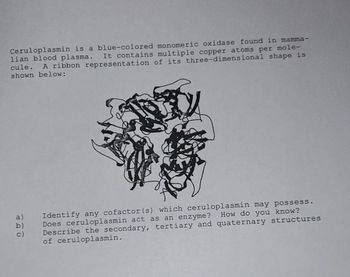
Transcribed Image Text:Ceruloplasmin is a blue-colored monomeric oxidase found in mamma-
lian blood plasma. It contains multiple copper atoms per mole-
cule. A ribbon representation of its three-dimensional shape is
shown below:
a)
b)
c)
Identify any cofactor(s) which ceruloplasmin may possess.
How do you know?
Does ceruloplasmin act as an enzyme ?
Describe the secondary, tertiary and quaternary structures
of ceruloplasmin.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- A) illustrate in molecular detail how hemoglobin's reduced oxygen affinity is caused by protonation of the histidine side chain. b) what is the pKa of the histidine side-chain ionizable group expected to have?|arrow_forwardThe effect of ATP on the allosteric enzyme PFK-1 is shown below. For a given concentration of fructose 6-phosphate, the PFK-1 activity increases with increasing concentrations of ATP, but a point is reached beyond which increasing the concentration of ATP inhibits the enzyme. (a) Explain how ATP can be both a substrate and an inhibitor of PFK-1. How is the enzyme regulated by ATP? (b) In what ways is glycolysis regulated by ATP levels? (c) The inhibition of PFK-1 by ATP is diminished when the ADP concentration is high, as shown in the illustration. How can this observation be explained? *A graph is included for this question*arrow_forwardWhat term best describes the isomeric relationship between alpha-D- glucopyranose and alpha-L-glucopyranose? A) structural isomers B) enantiomers C) epimers D) diastereoisomers, but not epimers E) not isomersarrow_forward
- Which of the following statements regarding the nitrogenous base guanine is FALSE? A) ALL of these statements are TRUE B) the enol form of guanine base-pairs with thymine C) guanine undergoes a tautomeric shift between a keto and an enol form D) the keto form of guanine base-pairs with cytosine E) an alcohol (-OH) group is present in guanine's enol form, but absent in the keto form F) guanine’s keto form is more stable than its enol formarrow_forwardthere are A-D questions to this picture set up. A) What enzyme catalyzes this reaction? B) What is Delta G, please answer in Joules, K=19 C) If concentration of Glucose-1_Phosphate is 48.82 uM at equalibrium, what is the concentration of Glucose-6-phosphate in uM? D) If the reaction is NOT at equalibrium, what is delta G at 25C if the concentration of Glucose-1-phosphate is 15.04 uM and concentration of Glucose -6-phosphate is 1.62 mM? please answer in Joules and in significant figures. *note, 10^3uM in 1 mM Thank you!!arrow_forwardGlucose-6- phosphatase catalyzes the following reaction: glucose – 6-phosphate + H2O = glucose + phosphate. Glucose-6- phosphatase would be classified as a(n) a) kinase b) hydrolase c) lyase d) oxidoreductase If ∆G for a biochemical reaction has a positive value, this means: a) the reaction will proceed very rapidly b) the reaction will proceed very slowly c) the reaction will generate heat d) The reaction requires energy input to proceed. Which thermodynamic parameter do enzymes change? A) entropy b) activation energy c) enthalpy d) all of these Enzymes have which effect on the chemical equilibrium of a biochemical reaction? A) the equilibrium shifts to favor products b) the equilibrium shifts to favor reactants c) The equilibrium does not shift, but gets there faster d) a new equilibrium is formedarrow_forward
- Cottage cheese and many other cheeses are produced by adding the enzyme rennin to milk, producing curds and whey. a) Design an experiment to determine the pH at which rennin is most effective. How will you measure the results? b) What are tests that can be used to detect protein, sugars, and fats? How can these tests to determine the chemical makeup of curds and whey?arrow_forwarda) At what pH will you try to bind lysozyme to a cation exchanger? b) Is it possible to perform this binding even at a different pH than the one you mentioned in section a? Explain your answer. c) Is it possible to bind lysozyme to an anion exchanger as well? If so, at what pH?arrow_forwardHypoglycin A, an amino acid derivative found in unripened lychee, is an acutely toxic compound that produces seizures, coma, and sometimes death in undernourished children when ingested on an empty stomach. (a) Draw the neutral, positively charged, and negatively charged forms of hypoglycin A. (b) Which form predominates at pH = 1, 6, and 11? (c) What is the structure of hypoclycin A at its isoelectric point?arrow_forward
- You are studying the tripep de Lys-Val-Thr. a) Could you use the absorbance at 280 nm to determine the concentra on of this tripep de? Briefly explain your answer. b) Show how the charge of this pep de would change at different pHs.arrow_forwardProvide the precise chemical description (anomer, isomer, and ring form) of the mono-saccharide subunits that are forming the tri-saccharide sugar molecule. Note the indicated numbering of the carbon atoms for the middle and the right subunit. Research the generic name of the tri-saccharide once you have identified the mono-saccharide subunits. Left subunit: Middle subunit: Right subunit: Name of sugar: b) Provide the precise chemical description of the two bonds that connect the sugar subunits?arrow_forwardConsider a short peptide with the sequence M-C-Q-L-Y-P-E-D-K. List the ionizable groups in this peptide, and the net charge of the whole peptide at pH a) 1.5, b) 7.0, and c)12.0.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781319114671Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.Publisher:W. H. Freeman
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781319114671Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.Publisher:W. H. Freeman Lehninger Principles of BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781464126116Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. CoxPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Lehninger Principles of BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781464126116Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. CoxPublisher:W. H. Freeman Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...BiochemistryISBN:9781118918401Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. PrattPublisher:WILEY
Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...BiochemistryISBN:9781118918401Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. PrattPublisher:WILEY BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...BiochemistryISBN:9780134015187Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. PetersonPublisher:PEARSON
Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...BiochemistryISBN:9780134015187Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. PetersonPublisher:PEARSON

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781319114671
Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781464126116
Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. Cox
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781118918401
Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. Pratt
Publisher:WILEY

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781305961135
Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougal
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781305577206
Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...
Biochemistry
ISBN:9780134015187
Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. Peterson
Publisher:PEARSON