
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approach
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781305079250
Author: Mark S. Cracolice, Ed Peters
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
desired Mg mass =0.0340g
"Atmospheric pressure (mmHg): 733.59
Trial 1 and Trial 2 values separated by commas:
Mass of Mg (g): 0.038, 0.031
Temperature (°C): 20.2 (both trials)
Vapor pressure of water (mmHg): 17.86 (both trials)
Volume of gas (mL): 42.95, 35.80
need calculations for table.
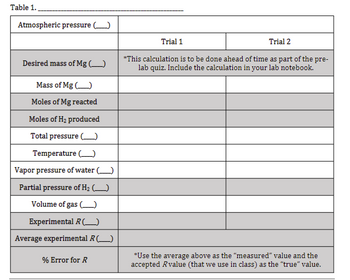
Transcribed Image Text:Table 1.
Atmospheric pressure (______)
Desired mass of Mg (_____)
Mass of Mg()
Moles of Mg reacted
Moles of H₂ produced
Total pressure (
Temperature (
Vapor pressure of water (_____)
Partial pressure of H₂ (____)
Volume of gas
Experimental R (_____)
Average experimental R (______)
% Error for R
Trial 1
Trial 2
*This calculation is to be done ahead of time as part of the pre-
lab quiz. Include the calculation in your lab notebook.
*Use the average above as the "measured" value and the
accepted Rvalue (that we use in class) as the "true" value.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Follow-up Questions
Read through expert solutions to related follow-up questions below.
Follow-up Question
can you show the expermiental r calculations in detail
Solution
by Bartleby Expert
Follow-up Questions
Read through expert solutions to related follow-up questions below.
Follow-up Question
can you show the expermiental r calculations in detail
Solution
by Bartleby Expert
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Solve like the example attached. Apply the significant figure rule to your final answer.arrow_forwardFor a gaseous sample, Pressure (P) and quantity (n) are inversely related directly related No answer text provided. O No answer text provided.arrow_forwardSolve correctly please. (Gpt/ai wrong answer not allowed)arrow_forward
- ited .doc C The stopcock connecting a 2.00 L bulb containing nitrogen gas at a pressure of 636 mm Hg, and a 2.00 L bulb containing methane gas at a pressure of 446 mm Hg, is opened and the gases are allowed to mix. Assuming that the temperature remains constant, what is the final pressure in the system? Submit Answer $ 4 R F 95 % Retry Entire Group F5 [Review Topics] [References] Use the References to access important values f needed for this question. T G 6 B MacBook Air Y 9 more group attempts remaining H & 7 U N mm Hg 8 1 M ( 9 K F9 O ) P Previous Email Instructor Next Save and Exit [ Show All 1 Xarrow_forwardFinding vapor pressure / Partial pressure and moles using the Data collectionarrow_forwardCompare, at the same temperature and pressure, equal volumes of H2 and O2 as to the following: massmass O2 = (insert answer) times mass of H2 density density O2 =(insert answer) times the density of H2arrow_forward
- my fault. I am talking about question 30. I am guessing that when looking at Density questions of gases, D= m/v Since ideal gases have no volume, is it true that the volume is assumed always to be the container? # 30 is tougharrow_forwardcollege.com/course.html?courseld3 154322748HepID=2b3e48e6520860bfd5591538a4a5a27b#10001 Search... y alosles are o USAonline: IMS 460-801F2 ay ceTripAdvisor (MC 13 on Temperature, Changes in Energy, and Gases Item 22 A Review | Constants Use molar volume to solve the following problems at STP. Part C Ne Find the number of grams of neon contained in 11.4 L gas. AZ4 Request Answer Submit Part D Find the number of moles of H, in 1820 mL H, gas. ΗΑΣ. P Pearson GLAYA Contact Us Permissions Privacy Policy Terms of Use Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education Inc. All rights reserved. hp hp dts Studio Sound f12 f1o f9 f8 f7 +1 f6 fs f4 & 23 3. 6. 8. 7. 6. 4. P. Y. R %24arrow_forwardAnswer both 1 &2 .if u answer only 1st quesion I will downvotearrow_forward
- Test Tube #1: Pure KCIO3 Sample 1. Determine the weight of KCIO3 heated. 2. Determine the weight of oxygen gas lost using the constant weight obtained from repeated heatings. 3. Based on the values obtained above, determine the experimental percent of oxygen in KCIO3 HINT: Percentage is defined as the "part" of interest divided by the total times 100. Determine the theoretical percent oxygen present in KCIO3 using stoichiometry. 4. 5. Based on the values obtained from #3 and #4, determine the percent error of percent oxygen.arrow_forwardRichards and Willard determined the molar mass of lithium and collected the following data. Experiment Molar Mass, g/mol 1 6.9391 2 6.9407 3 6.9409 4 6.9399 5 6.9407 6 6.9391 7 6.9406 a. Find the mean molar mass determined by these workers. b. Find the median molar mass. c. Assuming that the currently accepted value for the molar mass of lithium is the true value (state your reference), calculate the absolute error and the percent relative error of the mean value determined by Richards and Willard.arrow_forwardConvert : 60 grams of O, --> _Moles of O,. (Use 32.00 grams = 1 mole of O, as the molar mass.) * Liters of Gas (at STP) 22 4 Liters 1 mole Divide by Multiply by 22.4 Liters 22.4 Liters 1 mole 22.4 Liters Multiply by Molar Mass Moles Divide by Molar Mass 1 mole (6.02 x 10^23) 6.02 x 10 atoms or molecules 1 mole Multiply by (6.02 x 10^23) Divide by Particles Molar Mass 6.02 x 10 atoms or molecules (Atoms or Molecules) Weight in 1 mole grams 1 mole Molar Massarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning

Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079250
Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed Peters
Publisher:Cengage Learning


Chemistry: Matter and Change
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078746376
Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl Wistrom
Publisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co


Introductory Chemistry: A Foundation
Chemistry
ISBN:9781337399425
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning