
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
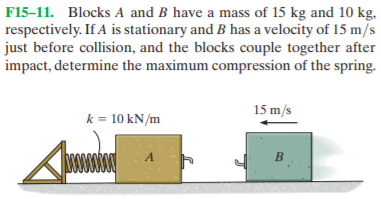
Transcribed Image Text:F15-11. Blocks A and B have a mass of 15 kg and 10 kg,
respectively. If A is stationary and B has a velocity of 15 m/s
just before collision, and the blocks couple together after
impact, determine the maximum compression of the spring.
15 m/s
k = 10 kN/m
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Follow-up Questions
Read through expert solutions to related follow-up questions below.
Follow-up Question
can I have FBD for this?
Solution
by Bartleby Expert
Follow-up Questions
Read through expert solutions to related follow-up questions below.
Follow-up Question
can I have FBD for this?
Solution
by Bartleby Expert
Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Q13. As shown in the image below, the 54 kg-crate is initially at rest, and at a distance d= 6.0 m from the top of the spring. Then it slides down the inclined plane. If the coefficient of kinetic friction between the crate and the inclined plane is uk = 0.22, determine the compression of the spring, x, when the crate momentarily stops (as the spring reaches maximum compression). The spring has spring constant k = 1.3 kN/m and initially the spring is unstretched. Please pay attention: the numbers may change since they are randomized. Your answer must include 2 places after the decimal point, and proper SI unit. Take g = 9.81 m/s². d k 45° Your Answer: Answer unitsarrow_forwardThe 10-lb block has a speed of 4 ft/s when the force of F= (8t^2) lbf is applied.Determine the velocity of the block when t= 2 s. The coefficient of kinetic friction at the surfaceis uk = 0.2arrow_forward4. The block of 2 kg travels down the slope from rest from the position shown and strikes the spring of constant k = 2 kN/m. Determine the maximum deformation of the spring after it is struck by the block. Also determine the location of the block relative to the free end of the spring when it stops after being bounced back by the spring. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and surfaces is μ = 0.25. www. 2 m 2 m 4 3arrow_forward
- 4 m M = (301²) N.m F = 15t N If the rod of negligible mass is subjected to a couple moment of M=24t² N;M where t is the time in seconds, and the engine of the car supplies a braking force F= 15t N to the wheels, determine the speed of the car at t= 10s. The car at t=0s a a speed of 9 m/s. The total mass of the car and the driver is 135 kg. Neglect the size of the car.arrow_forwardThe crate, which has a mass of 160 kg, is subjected to the action of the two forces. If it is originally at rest, determine the distance it slides in order to attain a speed of 7 m/s. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the crate and the surface is μk = 0.2.arrow_forward(25 pts) The 50-lb block rests on the smooth surface. A force F = (40+s²) lb, which s is in ft, acts on the block in the direction shown. If the spring is originally unstretched (s = 0) and the block is at rest, determine the power developed by the force the instant the block has moved s = 1.5 ft. F. 30° k = 20 lb/ft wwwwwwarrow_forward
- 15-51. The 30-Mg freight car A and 15-Mg freight car B are moving towards each other with the velocities shown. Determine the maximum compression of the spring mounted on car A. Neglect rolling resistancearrow_forward2. The 10-Ib block has a speed of 4 ft's when the force of F= (8t?) Ib is applied. Determine the velocity of the block when t= 2 s. The coefficient of kinetic friction at the surface is = 0.2. v = 4 ft/s F= (8°) lbarrow_forwardThe 20-lb box slides on the surface for which μ = 0.3. The box has a velocity v = 15 ft/s when it is 2 ft from the plate. If it strikes the smooth plate, which has a weight of 10 lb and is held in position by an unstretched spring of stiffness k = 400 lb/ft, determine the maximum compression imparted to the spring. Take e = 0.8 between the box and the plate. Assume that the plate slides smoothly. v = 15 ft/s 2 ftarrow_forward
- 5. The 8-kg smooth collar has a speed of 5 m/s when it is at s = 0. Determine the maximum distance s it travels before it stops momentarily. The spring has an unstretched length of 2 m. -1.5 m- -3 m/s k = 100 N/marrow_forwardThe 0.31-kg mass slides on a frictionless wire that lies in the vertical plane. The spring attached to the mass has a free length of 80 mm and stiffness of 0.13 N/mm. Calculate the smallest value of the distance b so that the mass will reach the end of the wire at B after being released from rest at A.arrow_forwardIf A is stationary and B has a velocity of 15 m/s just before collision, and the blocks couple together after impact, determine the maximum compression of the spring. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY