
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
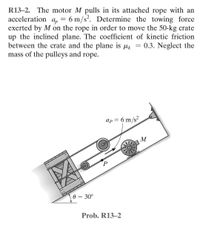
Transcribed Image Text:R13-2. The motor M pulls in its attached rope with an
acceleration q = 6 m/s². Determine the towing force
ар
exerted by M on the rope in order to move the 50-kg crate
up the inclined plane. The coefficient of kinetic friction
between the crate and the plane is k 0.3. Neglect the
mass of the pulleys and rope.
=
ap = 6 m/s²
0 = 30°
Prob. R13-2
M
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A brake mechanism is used to lower body A with a constant velocity of 3.0 m/s. The coefficient of friction between the brake and drum D is 0.40. Neglect the weight of the brake. Determine the mass of body A and the power dissipated by the brake. (hint: the normal force between the brake the and disk is not 1200 N)arrow_forwardThe conveyor belt is moving downward at 5 m/s. If the coefficient of static friction between the conveyor and the 12-kg package B is uk = 0.71, determine the shortest time the belt can stop so that the package does not slide on the belt.arrow_forwarda 7.4 lb block has a speed of v-2.4 ft/s to the left when the force of F=3.6t^3 lb is applied to the right. determine the velocity and position of the block when t= 0.2 seconds. the coefficient of friction at the surface is uk= 0.2. provide both a free body diagram and a kinetic diagram. the force is being applied in the opposite direction to the velocity of the block.arrow_forward
- The 40-kg disk is rotating at e = 100 rad/s. When the force Pis applied to the brake as indicated by the graph. If the cocfficient of kinetic friction at B is pe= 0.3, determine the time t needed to stay the disk from rotating. Neglect the thickness of the brake.arrow_forward14-1. The 20-kg crate is subjected to a force having a constant direction and a magnitude F = 100 N. When s = 15 m, the crate is moving to the right with a speed of 8 m/s. Determine its speed when s = 25 m. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the crate and the ground is µ, = 0.25. 30°arrow_forwardAssume that a driver (car modeled as a point mass) is negotiating a circular turn with a radius of 160 ft. The car and driver have a mass of 3800 lb and the coefficient of friction between the car and road is µ1 = 0.85. What is the maximum constant speed for which the car can travel at the given radius? r= 160 ftarrow_forward
- The motor winds in the cable with a constant acceleration, such that the 20-kg crate moves a distance s = 6 m in 3 s, starting from rest. Determine acceleration. what is the normal force (N) at point A. Determine the tension developed in the cable. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the crate and the plane is u= 0.3.arrow_forwardThe 925-kg motorized unit A is designed to raise and lower the 615-kg bucket B of concrete. Determine the average force R which supports unit A during the 5.9 seconds required to slow the descent of the bucket from 4.6 m/s to 0.9 m/s. Analyze the entire system as a unit without finding the tension in the cable. Answer: R = i kNarrow_forwardDetermine the speed v which the 690-kg four-man bobsled must have in order to negotiate the turn without reliance on friction. Also find the net normal force N exerted on the bobsled by the track. 23° Answers: V= i N = i -p=58 m m/s kNarrow_forward
- Pls. specify the procedurearrow_forward*13–16. The 75-kg man pushes on the 150-kg crate with a horizontal force F. If the coefficients of static and kinetic friction between the crate and the surface are µ, = 0.3 and Hi = 0.2, and the coefficient of static friction between the man's shoes and the surface is µ, = 0.8, show that the man is able to move the crate. What is the greatest acceleration the man can give the crate?arrow_forward1. The 40-kg crate is pulled by the constant force P. If the crate starts from rest and achieves a speed of 10 m/s in 9 s, determine the magnitude of P. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the crate and the ground is 0.15. 30°arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY