
Essentials Of Investments
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781260013924
Author: Bodie, Zvi, Kane, Alex, MARCUS, Alan J.
Publisher: Mcgraw-hill Education,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
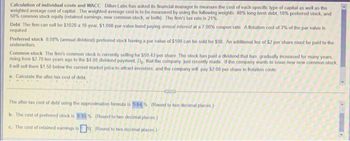
Transcribed Image Text:Calculation of individual costs and WACC Dillon Labs has asked its financial manager to measure the cost of each specific type of capital as well as the
weighted average cost of capital. The weighted average cost is to be measured by using the following weights: 40% long-term debt, 10% preferred stock, and
50% common stock equity (retained eamings, new common stock, or both). The firm's tax rate is 21%
Debt The firm can sell for $1020 a 10-year, $1,000-par-value bond paying annual interest at a 7.00% coupon rate: A flotation cost of 3% of the par value is
required.
Preferred stock 8.00% (annual dividend) preferred stock having a par value of $100 can be sold for $98. An additional fee of $2 per share must be paid to the
underwriters
Common stock The firm's common stock is currently selling for 559 43 per share. The stock has paid a dividend that has gradually increased for many years,
rising from $2.70 ten years ago to the $4.00 dividend payment, Do, that the company just recently made. If the company wants to issue new new common stock,
it will sell them $1.50 below the current market price to attract investors, and the company will pay $2.00 per share in Botation costs
a. Calculate the after-tax cost of debt
AY
The after-tax cost of debt using the approximation formula is 5.64% (Round to two decimal places.)
b. The cost of prefem
tock is 8 33% (Round to two decimal places)
c. The cost of retained earnings is
(Round to two decimal places)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, finance and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- WACCarrow_forwardHamada equation Original % debt in capital structure, wd Original % common equity in capital structure, wc Risk-free rate, TRF Market risk premium, RPM Tax rate, T Firm's cost of equity, rs Calculation of firm's current beta: Firm's current beta, b Calculation of firm's unlevered beta: Firm's unlevered beta, bu New % of debt in capital structure, Wd New New % of common equity in capital structure, Wc New Calculation of firm's new beta: Firm's new beta, bL New Calculation of firm's new cost of equity: Firm's new cost of equity, rs New 30.00% 70.00% 5.00% 7.00% 40.00% 14.00% 50.00% 50.00% Formulas #N/A #N/A #N/A #N/Aarrow_forwardK Calculation of individual costs and WACC Dillon Labs has asked its financial manager to measure the cost of each specific type of capital as well as the weighted average cost of capital. The weighted average cost is to be measured by using the following weights: 35% long-term debt, 15% preferred stock, and 50% common stock equity (retained earnings, new common stock, or both). The firm's tax rate is 29%. Debt The firm can sell for $1025 a 12-year, $1,000-par-value bond paying annual interest at a 7.00% coupon rate. A flotation cost of 2.5% of the par value is required. Preferred stock 9.00% (annual dividend) preferred stock having a par value of $100 can be sold for $96. An additional fee of $5 per share must be paid to the underwriters. Common stock The firm's common stock is currently selling for $60 per share. The stock has paid a dividend that has gradually increased for many years, rising from $2.70 ten years ago to the $4.40 dividend payment, Do, that the company just recently…arrow_forward
- You would like to estimate the weighted average cost of capital for a new airine business. Based on its industry asset beta, you have already estimated an unlevered cost of capital for the firm of 8%. However, the new business will be 23% debt financed, and you anticipate its debt cost of capital will be 5%. If its corporate tax rate is 30%, what is your estimate of its WACC? The equity cost of capital is. (Round to two decimal places.)arrow_forwardNonearrow_forwarda) Calculate the after-tax cost of debt for each capital structure.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Essentials Of InvestmentsFinanceISBN:9781260013924Author:Bodie, Zvi, Kane, Alex, MARCUS, Alan J.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Essentials Of InvestmentsFinanceISBN:9781260013924Author:Bodie, Zvi, Kane, Alex, MARCUS, Alan J.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

 Foundations Of FinanceFinanceISBN:9780134897264Author:KEOWN, Arthur J., Martin, John D., PETTY, J. WilliamPublisher:Pearson,
Foundations Of FinanceFinanceISBN:9780134897264Author:KEOWN, Arthur J., Martin, John D., PETTY, J. WilliamPublisher:Pearson, Fundamentals of Financial Management (MindTap Cou...FinanceISBN:9781337395250Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Fundamentals of Financial Management (MindTap Cou...FinanceISBN:9781337395250Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning Corporate Finance (The Mcgraw-hill/Irwin Series i...FinanceISBN:9780077861759Author:Stephen A. Ross Franco Modigliani Professor of Financial Economics Professor, Randolph W Westerfield Robert R. Dockson Deans Chair in Bus. Admin., Jeffrey Jaffe, Bradford D Jordan ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Corporate Finance (The Mcgraw-hill/Irwin Series i...FinanceISBN:9780077861759Author:Stephen A. Ross Franco Modigliani Professor of Financial Economics Professor, Randolph W Westerfield Robert R. Dockson Deans Chair in Bus. Admin., Jeffrey Jaffe, Bradford D Jordan ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Essentials Of Investments
Finance
ISBN:9781260013924
Author:Bodie, Zvi, Kane, Alex, MARCUS, Alan J.
Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,



Foundations Of Finance
Finance
ISBN:9780134897264
Author:KEOWN, Arthur J., Martin, John D., PETTY, J. William
Publisher:Pearson,

Fundamentals of Financial Management (MindTap Cou...
Finance
ISBN:9781337395250
Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. Houston
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Corporate Finance (The Mcgraw-hill/Irwin Series i...
Finance
ISBN:9780077861759
Author:Stephen A. Ross Franco Modigliani Professor of Financial Economics Professor, Randolph W Westerfield Robert R. Dockson Deans Chair in Bus. Admin., Jeffrey Jaffe, Bradford D Jordan Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education