
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
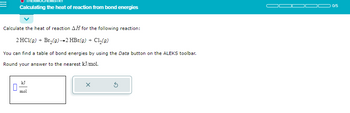
Transcribed Image Text:Calculating the heat of reaction from bond energies
Calculate the heat of reaction AH for the following reaction:
2 HC1(g) + Br₂(g) →2 HBr(g) + C1₂(g)
You can find a table of bond energies by using the Data button on the ALEKS toolbar.
Round your answer to the nearest kJ/mol.
mol
X
0/5
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Consider these reactions: Reaction 1: H2(g)+Cl2(g)⟶2HCl(g)ΔH=−184.6 kJ Reaction 2: 2OF2(g)⟶O2(g)+2 F2(g)ΔH=−49.4 kJ Reaction 3: N2(g)+2O2(g)⟶2NO2(g)ΔH=+66.4 kJ Use Reaction 2. How much energy (in kJ) is released when 79.0 g of oxygen difluoride decomposes?arrow_forwardCalculate the heat of reaction AH for the following reaction: CH4(g) + 202(g) →CO2(g) + 2H2O(g) You can find a table of bond energies by using the Data button on the ALEKS toolbar. Round your answer to the nearest kJ/mol. mol Garrow_forwardCalculate the heat of reaction forarrow_forward
- An important reaction in the production of sulfuric acid is SO2 (g) + ¿O2 (g) → SO3 (g) Calculate the enthalpy change for this reaction. Determine whether the reaction is endothermic or exothermic. -99 kJ, exothermic -99 kJ, endothermic 99 kJ, exothermic 99 kJ, endothermicarrow_forwardConsider an endothermic reaction that takes place in 303 mL of solution. If the reaction requires 4,468 J of energy and the initial temperature of the solution is 26.7, what will the final solution temperature be? (3 sf) The density of solution is 1.00 g/mL and the specific heat of the solution is the same as that of water.arrow_forwardCalculate the enthalpy of reaction for the combustion reaction (in kJ/mol) shown below. Enter your answer without units. ннно: •. Н-С-С—С—С-Ӧ—Н + 50=0 4 0=c=o° + 4 Н—0—Н ннн Average Bond Energy Bond (kJ/mol) H-H 436 H-C 414 H-O 464 C-C 347 C=C 611 C-0 360 C=O 799 0-0 142 O=0 498 If you cannot see the images above,then click herearrow_forward
- When 3.8 g A are reacted with 8.5 g D, according to the balanced chemical equation below, 33 kJ of energy are released. Please calculate the enthalpy for this reaction when 3 moles of G are produced. 2A + 3D = 2Z + 3G given molar masses: A = 141.8 g/mole D = 63.996 g/ mole Z = 4.032 g/ mole G = 56.028 g/ molearrow_forwardFor the reaction below ΔH = -296 kJ per mole of SO2 formed. S(s) + O2(g) → SO2(g) (c) What quantity of energy is required to break up exactly 2 mol of SO2(g) into its constituent elements?arrow_forwarda) Using standard enthalpies of formation (in Appendix G in your text), calculate the standard enthalpy change (AH°) for the following reaction shown below. (Show all work.) b) Based on your calculation, is the reaction exothermic or endothermic? 2 H2S(g) + SO2(g) --> 3/8 S8(s) + 2 H20(g)arrow_forward
- Calculating the heat of reaction from bond energies Calculate the heat of reaction AH for the following reaction: 2 H₂(g) + O₂(g) → 2 H₂O(g) You can find a table of bond energies by using the Data button on the ALEKS toolbar. Round your answer to the nearest kJ/mol. kJ mol X 1/5arrow_forwardUse the bond energies provided for the questionarrow_forwardGive Detailed Solution (don't give Handwritten answer)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY