
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
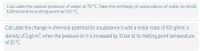
Transcribed Image Text:Calculate the vapour pressure of water at 75 °C. Take the enthalpy of vaporization of water as 40.66
kJ/mol and its boiling point as 100 °C.
Calculate the change in chemical potential for a substance X with a molar mass of 100 g/mol, a
density of 2 g/cm, when the pressure on it is increased by 10 bar at its melting point temperature
of 25 °C.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Henry's Law constant is 0.000600 mol/kg-bar and 0.00130 mol/kg.bar for N2 and O2 respectively at 25°C. What pressure of O2 is required to achieve the same solubility as 0.616 bar of N2 in units of atm? (1 bar = 0.9869 atm; 1 atm = 760 mmHg) O 1.3 atm 0.276 atm O 4.8 x 10-7 atm O 1.3 x 106 atm O 3.5 atmarrow_forwardSubject: chemistryarrow_forwardA group of students were weighing some CaCl2(s) but they forgot to record the mass. They know that they had 50 mL of water (you can assume water has a density of 1.00 g/mL) in the 1st test tube and the freezing point for the water by itself was measured to be -0.01 °C. When they added the CaCl2(s) to 50 mL water in a 2nd test tube and measured the freezing point with the same thermometer they got a freezing point of -1.868°C. The Kf value for water is 1.858 °C/m. What was the mass of CaCl2(s) that the students added to the 2nd test tube? Question 3 options: 3.09 1.09 1.87 2.03 2.63 1.61 0.86 2.24 2.87 2.40 1.25 1.42arrow_forward
- Energy to sublime Na(s) = 109.0 kJ/molElectron affinity of Cl(g) = -349.0 kJ/molFirst ionization energy of Na(g) = 495.0 kJ/molBond energy of Cl2(g) = 240.0 kJ/molΔHrxn for Na(s) + 1/2 Cl2(g) → NaCl(s) = -411.2 kJ/mol Determine the lattice energy of NaCl(s), using the data provided.arrow_forwardThe partial pressure of O2 in your lungs varies from 25 mm Hg to 40 mm Hg. What mass of O₂ can dissolve in 1.0 L of water at 25 °C if the partial pressure of O2 is 26 mm Hg? kí (O₂) = 1.3 × 10-³ Mass= g mol kg. bararrow_forward2) Calculate the vapor pressure caused by the addition of 100.0 g of nonvolatile solid naphthalene (C10H8, 128.17g/mol) into 500.0 g of benzene (C,H6, 78.11g/mol). The vapor pressure of pure benzene at this condition is 42.8 torr.arrow_forward
- Naphthalene melts at 80.2 °C and has a heat of fusion of 19.1 kJ/mol. What is its ideal solubility in liquid benzene at 37 °C?arrow_forwardA certain substance X condenses at a temperature of 111.6 C. But if a 200. g sample of X is prepared with 7.38 g of urea (NH2)2CO dissolved in it, the sample is found to have a condensation point of 111.9 C instead. Calculate the molal boiling point elevation constant Kb of X.arrow_forwardA solution is made by dissolving 38.750 g of sample of an unknown, nonelectrolyte compound in water. The mass of the solution is exactly 500.0 g. The boiling point of this solution is 100.220∘C. What is the molecular weight of the unknown compound?arrow_forward
- Please don't provide handwritten solutionarrow_forwardCalculate the solubility of oxygen in water at the top of Mt. Everest where the atmospheric pressure is 0.370 atm. The mole fraction of O2 in air is 0.209. Assume the kH of O2 is 1.30 ×× 10–3 mol/(L • atm).arrow_forwardHow to apply Raoult's law to real solutions Consider mixing a liquid with a vapor pressure of 100 torr with an equimolar amount of a liquid with a vapor pressure of 200 torr. The resulting solution would be predicted to have a vapor pressure of 150 torr if it behaved ideally. If, however, the interactions between the different components are not similar we can see positive or negative deviations from the calculated vapor pressure. An actual vapor pressure greater than that predicted by Raoult's law is said to be a positive deviation and an actual vapor pressure lower than that predicted by Raoult's law is a negative deviation.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY