
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
b. Calculate the
| Tolerable misstatement | $ | 15,000 | |
| Expected misstatement | $ | 6,000 | |
| Desired confidence level | 95 | % | |
| Recorded amount of accounts receivable | $ | 300,000 | |
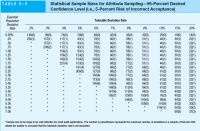
Transcribed Image Text:**Statistical Sample Sizes for Attribute Sampling — 95-Percent Desired Confidence Level (i.e., 5-Percent Risk of Incorrect Acceptance)**
**Table 8-5**
This table provides statistical sample sizes necessary for attribute sampling under various conditions, specifically with a 95% desired confidence level (equating to a 5% risk of incorrect acceptance). It is used in auditing and quality control environments to determine the number of samples that need to be tested to make reliable inferences about a population.
**Headers:**
- **Expected Population Deviation Rate**: The anticipated rate of deviation within the population.
- **Tolerable Deviation Rate**: The rate of deviation that the auditor is willing to accept.
**Columns:**
- **Expected Population Deviation Rate**: Ranges from 0.00% to 7.00%.
- **Tolerable Deviation Rate**: Varies from 2% to 20%.
Each cell within the table contains two values:
- First value: Indicates the required sample size.
- Value in parentheses: Indicates the maximum number of deviations allowable in the sample for the auditor to conclude that the tolerable deviation rate is not exceeded.
**Important Notes:**
- An asterisk (*) indicates that the sample size required is too large to be cost-effective for most audit purposes.
- The number in parentheses is crucial as it represents the maximum tolerable deviations in the sample size.
For example:
- For an **Expected Population Deviation Rate** of 0.00% and a **Tolerable Deviation Rate** of 2%, the required sample size is 149, and 0 deviations are acceptable.
- Conversely, for the same deviation rate expectation and a tolerable deviation rate of 20%, the required sample size significantly decreases to 14 with 0 deviations acceptable.
**Practical Application:**
Auditors can use this table to determine the number of items to sample when assessing control procedures. If an auditor expects a 1% population deviation and can tolerate a 5% deviation rate, they would need a sample size of 93, accepting up to 1 deviation (see the intersection between the 1.00% row and the 5% column).
**Conclusion:**
This table is a critical resource for ensuring that audits are both effective and efficient, helping auditors to balance between the necessary level of assurance and practical constraints like time and cost.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, statistics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Please answer the following questions on sampling. 1. Define, and differentiate between, non statistical (judgmental) sampling and statistical sampling. I need at least four sentences for this answer. 2. List and explain up to three advantages of applying statistical sampling techniques to audit testing. I need at least five sentences for this answer. Please help me as soon as possible.arrow_forwardDetermine the sample size for the estimate of ufor the following. E = 3.0, o = 15.45, confidence level= 99%. Round your answer to the nearest integer. n = iarrow_forwardA. Find the sample meanB. Find the sample standard deviation C. Construct a 98% confidence interval for the population mean(please show what numbers you are putting into the formula for part b)arrow_forward
- Refer to the sample of body temperatures (degrees Fahrenheit) in the table below. Given these temperatures, what issue can be addressed by conducting a statistical analysis of the data? Subject 2 3 4 5 1 97.0 98.5 97.6 97.7 98.7 8 AM 12 AM 97.6 97.8 98.0 98.4 98.4 Choose the correct answer below. OA. The data can be used to address the issue of whether there is a correlation between body temperatures at 8 AM and at 12 AM. OB. The data can be used to address the issue of whether there is a difference between average body temperature for males and for females. OC. The data can be used to address the issue of whether there is a correlation between average body temperature and a person's exposure to sunlight. OD. The data can be used to find the percentage of people whose body temperature increases with illness. DELLarrow_forwardThe fill size for a small bag of peanuts distributed by a popular airline is 50 grams. The producer wishes to set up a set of control charts for this process and collects the data shown in the table. Item #1 Sample 1 54.5 2 50.6 3 51.1 4 52.7 5 51.7 6 51.1 7 54.0 8 53.2 9 51.9 What is the sample size? a. 4 Ob.9 c. 13 d. 45 Item #2 54.3 53.5 54.3 52.1 51.2 51.5 52.3 50.4 50.2 Item #3 53.8 53.2 50.4 51.3 54.7 54.7 54.7 53.4 50.2 Item #4 50.4 54.9 50.7 51.0 54.3 50.4 51.4 51.4 52.9arrow_forward7 Answer: Calculate the median of the following sample data: 8 10 7 14 53 22 5 5 5 22 Answer: O E hoarrow_forward
- Refer to the table of sample values in Section 8.2 Exercise 6 of the text.Find the values of the UCL and LCL used in the p chart for this data, and round your answers to 5 places after the decimal point.Hint: Make sure that you use the EXACT value of (p-bar) in your calculations. a. UCL = 0.69914LCL = -0.21164 b. UCL = 0.69955LCL = -0.21155 c. UCL = 0.69955LCL = 0 d. UCL = 0.69914LCL = 0arrow_forwardConsider the following sets of sample data: A: 2.6, 3.8, 2.6, 4.0, 1.9, 1.8, 4.3, 2.2, 1.9, 2.0, 4.4, 4.4, 3.0, 3.8 B: $2.64, $2.18, $1.92, $2.31, $2.64, $1.40, $1.82, $1.68, $2.51, $1.29, $2.34 Step 1 of 2: For each of the above sets of sample data, calculate the coefficient of variation, CV. Round to one decimal place. Answer How to enter your answer (opens in new window) TV for Data Set A: CV for Data Set B: % %arrow_forwardSamuel F.B. Morse (1791-1872), the creator of the Morse Code, claimed that 12 % of all letters used in English language were "e"s. Suppose random samples of 196 letters are selected from a book. Use this information to answer question below.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman