
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
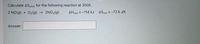
Transcribed Image Text:Calculate ASuniv for the following reaction at 300K.
2 NO(g)
O2(g)
2NO2(g)
AHrxn = -114 kJ
ASrxn = -72.6 J/K
+
Answer:
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- What is AS° for the following reaction? 2CI2(g) + SO2(g) → SOCI2(g) + Cl2O(g) Substance: Cl2g) SO23) SOCI23) Cl20(g) S°U/K • mol): 223.0 248.1 309.8 266.1 1270.0 J/K mol -104.8 J/K • mol 118.2J/K mol 104.8 J/K • mol -118.2 J/K • molarrow_forwardCalculate AS°, in J/K for the following reaction at 373K. (rxn) CO(g) + H2O(g) → CO2(g) + H2(g) ΔΗ ο (rxn) = -4.1 x 104 J AS univ = 56 J/Karrow_forwardWithout doing any calculations, match the following thermodynamic properties with their appropriate numerical sign for the following exothermic reaction. C,H4(g) + H20(g) →CH3CH,OH(g) Clear All > 0 AHrxn 0 low T, 0 high T Previous Nextarrow_forward
- Be sure to answer all parts. For the gaseous reaction of carbon monoxide and chlorine to form phosgene (COCl₂), perform the following calculations. (a) Calculate the AS at 298 K (AH° = −220. kJ/mol and AG° = −206 kJ/mol). kJ/mol K (b) Assuming that AS and AH change little with temperature, calculate AG at 450. K. kJ/molarrow_forwardHint: No calculations are required. For the reaction 2HBr(g) + Cl2(g)- >2HCI(g) + Br2(g) AH° = -81.1 kJ and AS° =-1.20 J/K At standard conditions, this reaction would be product favored O at all temperatures. O at relatively high temperatures. O at no temperature. O at relatively low temperatures.arrow_forward18arrow_forward
- Determine the AU°reaction at 25 °C (in kJ/mol) for the following reaction: 2NO(g) + O2(g)→2NO2(g) Appendix D kJ/molarrow_forwardUse the data shown below, to calculate AH°rxn and AS°rxn at 25°C for the following reaction: 3 H₂(g) + Fe₂O₂(s) → 2 Fe(s) + 3 H₂O(g) What is the value of AGᵒrxn at 25°C? Substance: H₂(g) AHof (kJ.mol-¹) 0 So (J.K-¹.mol-¹) 130.7 Fe₂O3(s) -824.2 87.40 Fe(s) 0 27.28 H₂O(g) -241.8 188.8arrow_forwardA chemical engineer is studying the two reactions shown in the table below. In each case, he fills a reaction vessel with some mixture of the reactants and products at a constant temperature of 74.0 °C and constant total pressure. Then, he measures the reaction enthalpy AH and reaction entropy AS of the first reaction, and the reaction enthalpy AH and reaction free energy AG of the second reaction. The results of his measurements are shown in the table. Complete the table. That is, calculate AG for the first reaction and AS for the second. (Round your answer to zero decimal places.) Then, decide whether, under the conditions the engineer has set up, the reaction is spontaneous, the reverse reaction is spontaneous, or neither forward nor reverse reaction is spontaneous because the system is at equilibrium. AH = 181. kJ AS = -499. K ? 2NO(g) N, (g) + 0, (g) AG = kJ Which is spontaneous? this reaction the reverse reaction neitherarrow_forward
- Given the following information, calculate AGO for the reaction below at 27 °C. Ni(s) + 1/2O₂(g) → NIO(s) ΔΗ, = -401.7 kJ and AS° = -94.6 J/K KJarrow_forwardCalculate G for the reaction of iron (III) oxide with carbon monoxide to give elemental iron and carbon dioxide. í G₁ (kJ/mol) Fe(s) 0 CO₂(g) -394.4 Fe₂O3(s) -741.0 CO(g) -137.3arrow_forwardGiven the information below: 3M(g) = K.=6.88 × 10~3 27(g) 2Z(g) = 3Q(g)+6X(g) K,=3.12 × 102arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY