
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Calcuate Bending From Point A to Point B and Point A to Point C, Calcuate torsion From Point A to Point C. Draw a FBD from point A to point B and another for point A to C indicating what stresses are been calculate. Use the stress tensor and stress cube to Indicate what forces are acting at point A.
Force apply at point B is 70lb
Distacen from Point A to B is 12 in or 1 feet long
Distacen from Point A to C is 3 in
Handle diameter 0.625 in
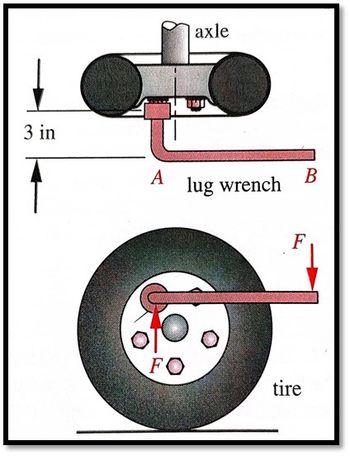
Transcribed Image Text:3 in
A
FO
axle
lug wrench
B
F
tire
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1: Given data
For the solution refer below images.
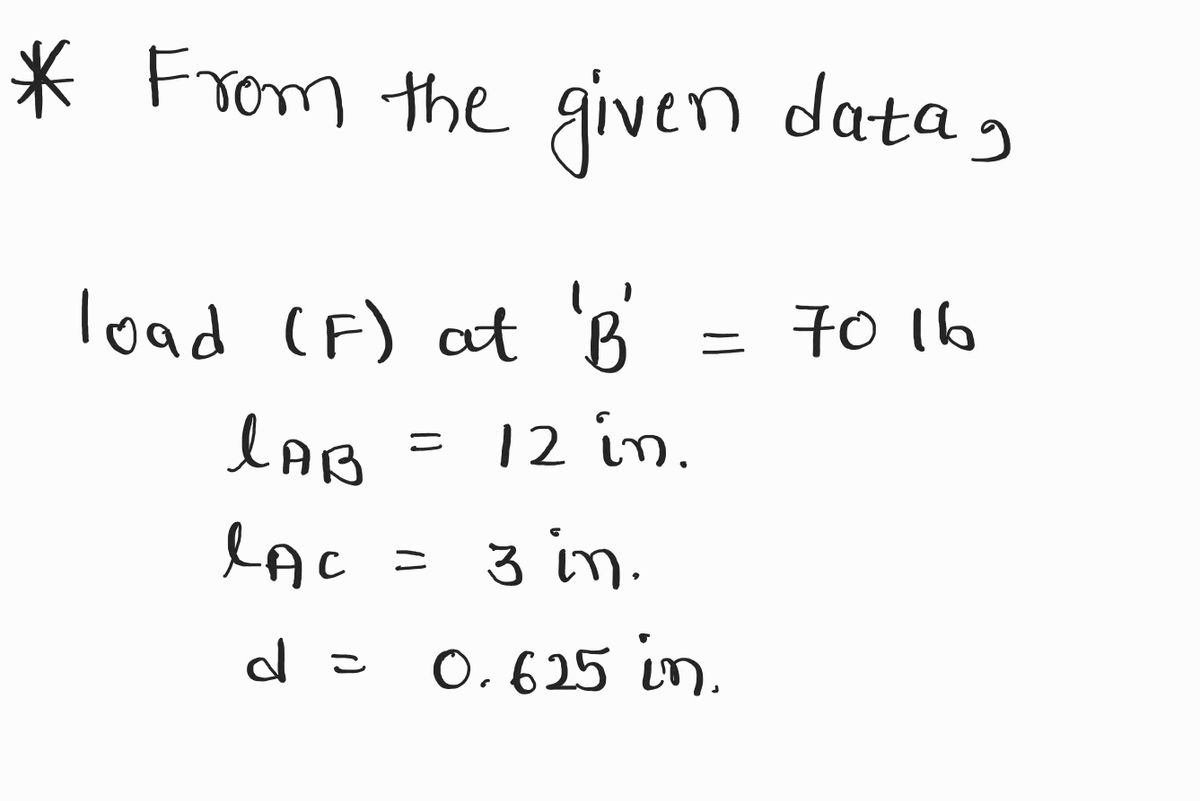
- Find F.B.D. and shear and bending diagrams for portions AB and BC.
- Find stress tensor at A.
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps with 7 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Calcuate Bending From Point A to Point B and Point A to Point C.Calcuate Torsion From Point A to Point C (point C is where is connect it to the lug nut). Draw a FBD from point A to point B and another for point A to C indicating what stresses are been calculate. Use the stress tensor and stress cube to Indicate what forces are acting at point A. All the information need it is given Force apply at point B is 70lb Distacen from Point A to B is 12 in or 1 feet long Distacen from Point A to C is 3 in Handle diameter 0.625 in Modulus of elasticity for steel is 300000000 psiarrow_forwardCalculate the forces, in Newtons, for the following: (d) member FG (e) pin H (f) hydraulic cylinder AB 400 G E H 100 175 a 800 200 LBE C D 150 400 E 175 8 B 900 150 200 Dimensions in millimeters 150arrow_forward11:11 A The wood beam has an allowable shear stress of Tallow = 9.6 MPa. d3 d3 Variable d₁ d₂ d1 d3 d4 d5 wamap.org Value d2 V Values for the figure are given in the following table. Note the figure may not be to scale. 0.05 m 0.125 m 0.05 m 0.225 m P 0.1125 m d1 d5 a. Determine the Q at point P. b. Determine the moment of inertia, I. d4 c. Determine the magnitude of the max shear force that can be applied to the cross-section at point P, Vmax.arrow_forward
- PLEASE ANSWER ASAP THANK YOUarrow_forwardCalcuate torsion From Point A to Point C, Calcuate Bending From Point A to Point B and Point A to Point C. Draw a FBD from point A to point B and another for point A to C indicating what stresses are been calculate. Use the stress tensor and stress cube to Indicate what forces are acting at point A. Force apply at point B is 70lb Distacen from Point A to B is 12 in or 1 feet long Distacen from Point A to C is 3 in Handle diameter 0.625 inarrow_forwardQuestion 2 For the stresses of plane stress state is ox = -8 MPa , Oy = 7 MPa and Txy = -6 MPa Draw a Mohr's circle diagram. Draw stress element for the given stresses Find the principal normal and shear stresses, and determine the angle from the x axis to ơ1 Draw the stress element for the principle stress. Using stress transformation, find the principle stresses and the angle of o, Determine the stress transformation for the angle Ø = 25°arrow_forward
- As a way to check my workarrow_forwardQUESTION 4 Figure 3 below shows a vertical rod under its own weight. Find the displacement at A and stress distribution. Use E-100 MPa and weight per unit volume 0.06 N/cm³. Solve using two elements and comment on the stress distribution. 1.6 m 1m A Area = 2500 cm² 8 B Area = 1500 cm²arrow_forwardThe beam is supported by a fixed support at point A. There are 2 distributed loads applied to the beam. Neglect the weight and thickness of the beam. Take the origin for all functions to be at A. , i.e. start at the left and go right. Must use positive sign convention for V and M. W1 A W2 d1 Values for the figure are given in the following table. Note the figure may not be to scale. Variable Value di 3 m W1 6 (kN)/m W2 3 (kN)/m a. For the interval 0 < x < 3 m, determine the equation for the Shear Force as a function of x, V(x). b. For the interval 0 < x < 3 m, Use integrals to determine the equation for the Moment as a function of X, M(x). o Enter the coefficient of the x term as a fraction and the rest as decimals. for example, x4 1.4x c. Determine the magnitude of the max shear on the beam,Vmax d. Determine the magnitude of the max bending moment on the beam, Mn maxarrow_forward
- Calcuate Bending From Point A to Point B and Point A to Point C also Torsion from Point A to Point C. Draw a FBD from point A to point B and another for point A to C indicating what stresses are been calculate. Use the stress tensor and stress cube to Indicate what forces are acting at point A. Force apply at point B is 70lb Distacen from Point A to B is 12 in or 1 feet long Distacen from Point A to C is 3 in Handle diameter 0.625 inarrow_forwardThe state of stress at a point on an element of material is shown. Let sigmaX= 49.0 ksi, sigmaY= 17.0 ksi, and Txy= 11.0 ksi. Use this information to represent the principle state of stress and maximum in plane shear stress. Plot the mohr circle and state sigmaX' and sigmaY' and Tx'y' with unit. Also draw the state of stress on the rotated element.arrow_forwardFrom 3 forces, 2 bending moments and 1 toque acting on B, which ones are non zero, and the direction they are acting. Then indicate if they make shear or normal stress Draw 3-d stress state cust above plane aarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY