
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
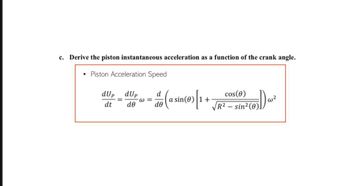
Transcribed Image Text:c. Derive the piston instantaneous acceleration as a function of the crank angle.
. Piston Acceleration Speed
dUp dUp d
de
dt dᎾ
- (a sin(0) [1.
+
=
@=
cos(0)
√R²-sin²(
Son ² (1)D) w ²
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step 1: Determine the given variables:
VIEW Step 2: Find the expression for the piston velocity with respect to the crank angle:
VIEW Step 3: Differentiate the expression with respect to θ:
VIEW Step 4: Differentiate sin(θ) and apply the chain rule to differentiate further:
VIEW Step 5: Simplify the expression:
VIEW Step 6: Combine like terms:
VIEW Step 7: Cancel out suitable terms from the numerator and denominator:
VIEW Step 8: Use the chain rule to differentiate the above expression with respect to time (t):
VIEW Solution
VIEW Step by stepSolved in 9 steps with 12 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- B W= VC = VA = rad/s A ladder is falling! The ladder has a length of 5 m. If is currently 20° and B is moving downward at 3 m/s, find the rotational speed of the ladder, the speed of the center of the ladder, and the speed of point A. m/s 1 m/s Ꮎ A CC BY UBC Engineeringarrow_forwardRequired information A model of a person's arm is used for ergonomics studies. Distances are rAB = 30 cm, BC = 28 cm, and rCD = 19 cm. NOTE: This is a multi-part question. Once an answer is submitted, you will be unable to return to this part. y D C25° 30 Determine the position vector TAD and its magnitude rAD· The position vector TAD 1i)cm and the magnitude rAD is cm.arrow_forwardpls very urgent using the formulas required in the picturearrow_forward
- pls solving this problem very urgentarrow_forwardTwo tractors leave point O at the same time and drive in the directions shown. Tractor A is traveling at a m m constant speed of 4 = 9. Tractor B is traveling at a constant speed of UB = 13 S Hint: 1. Use constant acceleration equations to find time. VA A Variable 0₁ 02 0₁ -C = y + 0₂ Values for the figure are given in the following table. Note the figure may not be to scale. Value 30 degrees 35 degrees Round your final answers to 3 significant digits/figures. V = ( m a. Determine the velocity of tractor A relative to tractor B, V4, express as a Cartesian vector. b. Determine the magnitude of the velocity of tractor A relative to tractor B, c. How long after leaving point O will the tractors be 500 m apart? VB B m Xarrow_forwardI want to solve all parts of the question using rules in the picture pls very urgentarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY