
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780134580999
Author: Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
thumb_up100%
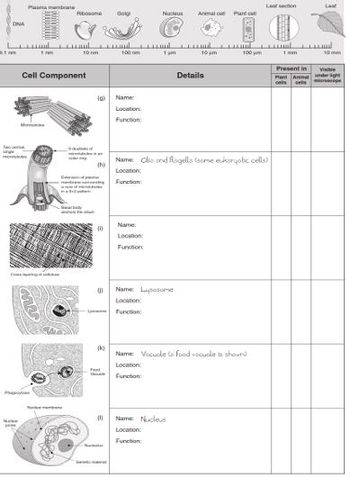
Transcribed Image Text:Ot
DNA
unge
Hu
p
Pasma memban
MU
t.m
www.w
400
Cell Component
(0)
Rbosome dolg
C
10m
(h)
Re
(0)
(1)
(k)
Food
SKLER
(1)
100 m
Name
Locations
Function:
Nukus
Name:
Location:
Function
1pm
Name: Lysosome
Location:
Function:
Animal
10m
Name Nucleus
Location:
Function:
Details
Pantall
Name: Clia and Ragella (some eukaryotic cells)
Location:
Function
100 μm
Name Vacuole to food vecuole is shown
Location:
Function:
Letton
1mm
Lauf
10 mm
Presentin
Visible
Par Animal g
cells
Gips
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1
A prokaryotic cell doesn't have any membrane organelles such as mitochondria, Endoplasmic reticulum. An eukaryotes have membrane bound organelles such as nucleus, Endoplasmic reticulum etc.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Protein processing pathway Match each description with the appropriate step in protein secretion. Labels The vesicle may travel to the plasma membrane releasing its contents to the extracellular environment. The proteins are modified and packaged into vesicles for transport 0 Drop Zones 34 Reser All Prev 11 of 14 Nocleus Next > SUSASTICarrow_forward31arrow_forwardPlease match the junction type with the cytoskeletal component it is associated with Desmosome Tight junction Adherens junction Focal adhesion Hemidesmosome ✓ [Choose ] microtubule none intermediate filament actin [Choose ] [Choose ] [Choose ]arrow_forward
- The cytoplasm of a certain cell is composed of a solution that is 98% water, 2% solutes. Consider the solution shown in the beaker in this picture: FOOE OOS Foor solution. [Select] Cytoplasm is 98% water, 2% solutes. The solution in the beaker would be considered when compared to [Select] The plasma membrane is impermeable to solutes. Beaker solution is 98% water, 2% solutes the cell. We would expect that the cell would [Select] if it was placed in the would account for whatever changes might occur to the volume of the cytoplasm of the cell when it is placed in the solution.arrow_forwardLabel and define the following termsarrow_forwardpleas write a one page essay on stroke. what some of the condition is and why it happens and how we can treat it and the best way to avoid it.arrow_forward
- Calculate the free energy changes at 20°C for the transmembrane movement of Na and K ions using the conditions presented Figure 9.1. Assume the membrane potential is -70 mV. Use 3 significant figures. AG (Na) - AG (K) = kJ. mol ¹ kJ mol2 Aarrow_forward1a. Describe three types of cytoskeletal filaments. What functions do they serve in the cell? What is a motor protein? Name two motor proteins, and give examples of their cellular roles. 1b. Draw a picture showing the path a secreted protein takes from synthesis until it exits the cell.arrow_forwardCan you please help me matchingarrow_forward
- Match each organelle with its corresponding structure/function. [Each choice will be used exactly once.] DOD Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum Golgi Complex Lysosome Ribosome Nucleus 1. Made of rRNA and protein. A single membrane that is continuous with the Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum. Large spherical structure surrounded by 2 membranes that are spanned by pores. Resembles a stack of pita bread; where each pita is a flattened membranous sac. Small spherical sac filled with hydrolytic enzymes. 2. 3. 4. 5.arrow_forwardthe structure of the plasma membrane is best described as: two layers of phospholipids stacked on top of each other, with proteins embedded in the phospholipids Oa single layer of proteins and polysachharides mixed together two layers of proteins stacked on top of each other O many sheets of peptidoglycan stacked on top of each other O one layer of triglycerides on top of a layer of proteinsarrow_forwardIf you did a classic Pulse-Chase experiment to follow the path of a secreted protein, and you forgot to do the Chase, which of the following would you observe? No radioactivity would be seen in any of the structures. Radioactivity would increase first in rough ER, then Golgi Complex, then secretory vesicles, but it would remain high in all, never decreasing. Nothing would change Radioactivity would increase in all 3 structures simultaneously and stay high.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education

Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780134580999
Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:PEARSON

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781259398629
Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa Stouter
Publisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,

Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780815344322
Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter Walter
Publisher:W. W. Norton & Company

Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781260159363
Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, Cynthia
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.

Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9781260231700
Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael Windelspecht
Publisher:McGraw Hill Education