
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
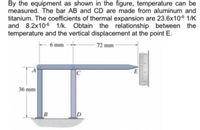
Transcribed Image Text:By the equipment as shown in the figure, temperature can be
measured. The bar AB and CD are made from aluminum and
titanium. The coefficients of thermal expansion are 23.6x106 1/K
and 8.2x106 1/k. Obtain the relationship between the
temperature and the vertical displacement at the point E.
6 mm
72 mm
36 mm
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 50 mm PROBLEM 2.55 Brass 37.5 mm A brass link (E, = 105 GPa, a, = 20.9x10/°C) and a steel rod (E, = 200 GPa, a =11.7x10/°C) have the dimensions shown at a temperature of 20°C. The steel rod is cooled until it fits freely into the link. The temperature of the whole assembly is then raised to 45°C. Determine (a) the final stress in the steel rod, (b) the final length of the steel rod. 37.5 mm 0.12 mm -250 mm 30-mm diameter Steel A Section A-A 0, =-36.8 MPa L, = 250.147 mm %3Darrow_forwardA square bar subjected to a tensile load of 100KN having a gauge length of 200mm, extends to a length of 0.19mm. Given the tensile strength as 200 MPa, determine, (i) Side of the bar (express in mm) (ii) Final length (express in mm) (ii) Modulus of elasticity (express in GPa)arrow_forwardA long metal plate (E = 210 GPa) with some cutouts in it is mounted between two rigid plates at 6 am. By noon, the temperature has risen by 20°C. The structure is made from aluminium with a coefficient of thermal expansion of a = 23 x 10-6/°C. Please use the stress concentration chart shown below for any relevant calculations. a10 h L b O Use the following values in your working out: K 3.2 3.0 2.8 2.6 2.4 2.2 2.0 L = 13 m 0 0.1 P 0.2 W W Javg 0.3 2r P (w2r)t 0.4 P ▬▬▬▬▬▬▬ 0.5 h = 5.3 m a = 0.8 m b = 1.6 m a) What is the average normal stress throughout the plate at noon? b) What is the maximum stress at any point in the structure? c) The material the plate is made from has a tensile yield stress of 416 MPa and a compressive yield stress of 200 MPa. Using these values, do you expect the plate to yield at/before noon?arrow_forward
- shows two tubes, one of copper and another of steel of equal length and rigidly connected at their ends so that under all conditions they are of equal length. The copper tube has internal and external diameters of 100 mm and 125 mm respectively whilst the internal and external diameters of the steel tube are 75 mm and 100 mm respectively. If the original length of the tubes was 375 mm, for a temperature rise of 22o C calculate: 1 The stress set up in each tube; 2 The final length of the tubes. Assume: α copper = 18,7 x 10-6/ 0 C; E copper = 82 GPa α steel = 12,6 x 10-6/ 0 C; E steel = 207 GPaarrow_forwardll ? The rod BD is made of material with G1= 135 GPa has a diameter 16 mm is bonded to the tube CA at point B, the tube made of material with G2=230o GPa has an outer diameter 37 mm and wall thickness of 7 mm. li T1=803 N.m and T2=1445 N.m, answer the following questions: B T2 Nm 04 m 0.1 m 0.3 m TI N-m The polar moment of inertia of the rod BD is Your answer The polar moment of inertia of the tube CA isarrow_forwardDetermine the equivalent stiffness constant of the ff.arrow_forward
- Current Attempt in Progress A solid prismatic rod is L; = 330 mm long and has a circular cross section with a diameter of d = 24 mm. After the temperature of the unconstrained rod is increased, its final length is measured as L₁= 330.265 mm. Determine the change in the rod's diameter after the temperature increase. Answer: Ad = i mmarrow_forward1.6-7 A wire of length L = 2.5 m and diameter d = 1.6 mm is stretched by tensile forces P = 600 N. The wire is made of a copper alloy having a stress- strain relationship that may be described mathemat- ically by 124,020ɛ 0 s8s 0.03 (o = MPa) 1+ 300ɛ in which e is nondimensional and o has units of MPa. (a) Construct a stress-strain diagram for the material. (b) Determine the elongation of the wire due to the forces P. (c) If the forces are removed, what is the permanent set of the bar? (d) If the forces are applied again, what is the proportional limit?arrow_forwardThe rod BD is made of materia with G1= 124 GPa has a diameter 34 mm is bonded to the tube CA at point B, the tube made of material with G2=211 GPa has an outer diameter 73 mm and wall thickness of 10 mm. If T1=579 N.m and T2=1042 N.m, answer the following questions: A B T2 N-m 0.4 m 0.1 m 0.3 m T1 N-m The polar moment of inertia of the rod BD is The maximum shear stress of the tube CA is The maximum shear stress of the assembly isarrow_forward
- FN = 50arrow_forwardA pushrod in the valve mechanism of an automotive engine has a nominal length of 203 mm. If the rod is made of SAE 4140 steel, compute the elongation due to a temperature change from -20°C to 140°C. TABLE 3-4 Coefficients of thermal expansion, a, for some t nd concrretearrow_forwardBy the equipment as shown in the figure, temperature can be measured. The bar AB and CD are made from aluminum and titanium. The coefficients of thermal expansion are 23.6x106 1/K and 8.2x10-6 1/k. Obtain the relationship between the temperature and the vertical displacement at the point E. 6 mm 72 mm 36 mm Darrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY