
Principles of Cost Accounting
17th Edition
ISBN: 9781305087408
Author: Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. Mitchell
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
kk.
Subject :- Accounting
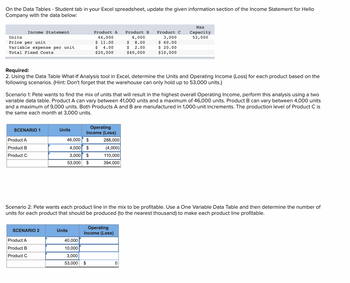
Transcribed Image Text:On the Data Tables - Student tab in your Excel spreadsheet, update the given information section of the Income Statement for Hello
Company with the data below:
Units
Price per unit.
Variable expense per unit
Total Fixed Costs
Income Statement
SCENARIO 1
Product A
Product B
Product C
Required:
2. Using the Data Table What-lf Analysis tool in Excel, determine the Units and Operating Income (Loss) for each product based on the
following scenarios. (Hint: Don't forget that the warehouse can only hold up to 53,000 units.)
Scenario 1: Pete wants to find the mix of units that will result in the highest overall Operating Income, perform this analysis using a two
variable data table. Product A can vary between 41,000 units and a maximum of 46,000 units. Product B can vary between 4,000 units
and a maximum of 9,000 units. Both Products A and B are manufactured in 1,000-unit increments. The production level of Product C is
the same each month at 3,000 units.
SCENARIO 2
Product A
Product B
Product C
Units
Product A
44,000
$ 11.00
$ 4.00
$20,000
46,000 $
4,000 $
3,000 $
53,000 $
Units
Operating
Income (Loss)
40,000
10,000
3,000
53,000 $
288,000
(4,000)
110,000
394,000
Scenario 2: Pete wants each product line in the mix to be profitable. Use a One Variable Data Table and then determine the number of
units for each product that should be produced (to the nearest thousand) to make each product line profitable.
Product B
6,000
$ 8.00
$ 2.00
$40,000
Operating
Income (Loss)
Product C
3,000
$ 60.00
$ 20.00
$10,000
Max
Capacity
53,000
0
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- On the Data Tables - Student tab in your Excel spreadsheet, update the given information section of the Income Statement for Hello Company with the data below: Units Price per unit Variable expense per unit Total Fixed Costs Income Statement SCENARIO 1 Product A Product B Product C Required: 2. Using the Data Table What-if Analysis tool in Excel, determine the Units and Operating Income (Loss) for each product based on the following scenarios. (Hint: Don't forget that the warehouse can only hold up to 45,000 units.) Scenario 1: Pete wants to find the mix of units that will result in the highest overall Operating Income, perform this analysis using a two variable data table. Product A can vary between 32,000 units and a maximum of 37.000 units. Product B can vary between 5,000 units and a maximum of 10,000 units. Both Products A and B are manufactured in 1,000-unit increments. The production level of Product C is the same each month at 3,000 units. SCENARIO 2 Product A Product B Product…arrow_forwardplease help me number it from 1-5arrow_forwardUsing the data in P4-2 and Microsoft Excel: 1. Separate the variable and fixed elements. 2. Determine the cost to be charged to the product for the year. 3. Determine the cost to be charged to factory overhead for the year. 4. Determine the plotted data points using Chart Wizard. 5. Determine R2. 6. How do these solutions compare to the solutions in P4-2 and P4-3? 7. What does R2 tell you about this cost model?arrow_forward
- Using the table below, create a line chart in which profit or loss is plotted on the Y-axis and sales volume is plotted on the X-axis. This is commonly called a profit/volume chart. Although sales volume can be expressed in either units or dollars, use units for your chart. Complete the Chart Tickler Data Table to include a column for profits. Use this table as a basis for preparing the chart. Cost-Volume-Profit Analysis Data Section Income Statement in a Contribution Margin Fixed Variable Particulars Amounts Production costs Projected unit sales 120,000 Direct materials $2.30 Selling price per unit $16.00 Direct labor 4.70 Less Vairable Cost Factory overhead $225,000 3.00 Direct materials $2.30 Selling expenses Direct labor 4.70 Sales salaries & commissions 97,000 0.75 Factory overhead…arrow_forwardPlease help with questionarrow_forwardplease fill out this chartarrow_forward
- Direction: Read carefully and answer the questions below. Encircle the letter of the correct answer. 1. Which of the following is an example of a variable cost? а. interest b. ingredients с. insurance d. lease 2. What type of cost varies depending on the quantity of products being produced? а. fixed b. net sales с. total d. variable 3. Which among the following concepts is usually seen on the top item in an income statement from which all costs and expenses is subtracted to arrive at net income? a. fixed cost b. net sales с. total cost d. variable cost 4. When do we obtain the break-even point? When the fixed cost is equal to the total cost When the total cost is equal to the variable cost When the variable cost is equal to the fixed cost d. When the number of units of goods sold covers the all the costs а. b. с. 5. Which of the following is NOT true? а. The fixed cost does not vary over time. b. The total cost is the sum of the fixed cost and the variable cost. с. The total cost is…arrow_forwardanswer in text form please (without image)arrow_forwardAnswer full question.arrow_forward
- Fill in the missing amounts in each of the following eight case situations. Treat each case independently. (Hint: One way to find the missing amounts would be to prepare a contribution margin income statement for each case, enter the known data, and then compute the missing items.) a. Assume that only one product is being sold in each of the following four case situations: (Negatlve omounts should be Indicated by a mlnus sign. Enter your contributlon margln answers as per unlt dollor values. Enter your answers rounded to the nearest whole number.) Fixed Еxpenses Net Income (Loss) Variable Contribution Case Units Sold Sales Expenses Margin 14,000 196,000 $9 per unit 46.000 1 106,600 $16 per unit 40% 31,500 59,400 15 10,000 3. 9,900 282,000 $31 per unit 104,000 (8,000) 4 b. Assume that more than one product is being sold in each of the following four case situations: (Negative omounts should be Indicated by a mlnus sign.) Average Contribution Margin (percentage) Variable Fixed Net Income…arrow_forwardplease answer within the format by providing formula the detailed workingPlease provide answer in text (Without image)Please provide answer in text (Without image)Please provide answer in text (Without image)arrow_forwardUse the following information about sales and costs to prepare a scatter diagram. Draw a cost line that reflects the behavior displayed by this cost. Determine whether the cost is variable, step-wise, fixed, mixed, or curvilinear. Period Sales Costs Period Sales Costs $760 $590 9. $580 $390 2. 800 560 10. 320 240 3. 200 230 II. 240 230 4 400 400 12. 720 550 5 480 390 13 280 260 6 620 550 14. 440 410 7 680 590 15 380 260 8 540 430arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning Excel Applications for Accounting PrinciplesAccountingISBN:9781111581565Author:Gaylord N. SmithPublisher:Cengage LearningCentury 21 Accounting Multicolumn JournalAccountingISBN:9781337679503Author:GilbertsonPublisher:Cengage
Excel Applications for Accounting PrinciplesAccountingISBN:9781111581565Author:Gaylord N. SmithPublisher:Cengage LearningCentury 21 Accounting Multicolumn JournalAccountingISBN:9781337679503Author:GilbertsonPublisher:Cengage Essentials Of Business AnalyticsStatisticsISBN:9781285187273Author:Camm, Jeff.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Essentials Of Business AnalyticsStatisticsISBN:9781285187273Author:Camm, Jeff.Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Principles of Cost Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781305087408
Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. Mitchell
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Accounting Volume 2
Accounting
ISBN:9781947172609
Author:OpenStax
Publisher:OpenStax College

Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And Analysis
Accounting
ISBN:9781337788281
Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald Pagach
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Excel Applications for Accounting Principles
Accounting
ISBN:9781111581565
Author:Gaylord N. Smith
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Century 21 Accounting Multicolumn Journal
Accounting
ISBN:9781337679503
Author:Gilbertson
Publisher:Cengage

Essentials Of Business Analytics
Statistics
ISBN:9781285187273
Author:Camm, Jeff.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,