
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Draw the product and complete mechanism for the following reaction including initiation, propagation and 1 example of termination.
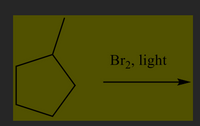
Transcribed Image Text:### Alkane Halogenation Reaction
**Chemical Reaction:**
The image depicts the halogenation of a methylcyclopentane using bromine (\( \text{Br}_2 \)) under light conditions (photochemical reaction).
1. **Reactant:** Methylcyclopentane
- Structure: A cyclopentane ring (five-membered carbon ring) with a single methyl group (\( \text{CH}_3 \)) attached.
2. **Reaction Conditions:**
- Reagent: \(\text{Br}_2\) (Bromine)
- Catalyst: Light (often UV light is used to initiate the reaction)
**Process Explanation:**
- The presence of light initiates the homolytic cleavage of the bromine (\(\text{Br}_2\)) bond, generating bromine radicals.
- These bromine radicals abstract hydrogen atoms from the methyl group, leading to the formation of alkyl radicals.
- The alkyl radical then reacts with another bromine molecule to form bromomethylcyclopentane, a substitution product where hydrogen is replaced by bromine.
**Purpose in Education:**
This reaction is an example of free radical halogenation, often discussed in organic chemistry to illustrate mechanisms involving free radicals and the role of light in promoting chemical reactivity.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- NH2 For the reaction shown here, draw the complete, detailed mechanism and major product. 1. CH3I (excess) 2. Ag,0 3. Aarrow_forwardPlease answer the following question to the fullest and be extremely sure that it is correct and double check. Thank youarrow_forwardShow the rate determining step for each an E1 and an E2 reaction including intermidiates / transition sites.arrow_forward
- Problem attachedarrow_forward6. Consider the following E1 reaction. OH H3O+ reflux + H₂O a. Draw the complete, detailed mechanism (curved arrows) for this reaction. b. Draw a reaction free energy diagram that agrees with the mechanism, labeling overall reactants, overall products, all transition states, and all intermediates.arrow_forwarda) Draw the complete mechanism for this reaction Cackmor b) With reference to your mechanism, explain why the reaction takes place at position A rather than B HOarrow_forward
- Give detailed Solution with explanation needed..no need handwritten answer,,arrow_forwardFollow the curved arrows and draw the product of this reaction. Ph • You do not have to consider stereochemistry.arrow_forwardThe crossed aldol reaction shown here can be carried out using a weak base such as pyridine. (a) Draw the complete, detailed mechanism for this reaction. (b) Explain why a relatively weak base can be used. EtO OEt H EtO OEt H. Diethyl malonatearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY