
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
![**Boiling Point Elevation/Freezing Point Depression**
\[\Delta T = m \cdot K\]
where, for freezing point depression:
\[\Delta T = T(\text{pure solvent}) - T(\text{solution})\]
and for boiling point elevation:
\[\Delta T = T(\text{solution}) - T(\text{pure solvent})\]
- \(m\) = (# moles solute / Kg solvent)
- \(K_b\) = boiling point elevation constant.
- \(K_f\) = freezing point depression constant.
\(K_b\) and \(K_f\) depend only on the SOLVENT. Below are some common values. Use these values for the calculations that follow.
| Solvent | Formula | \(K_b\)(°C / m) | \(K_f\)(°C / m) |
|--------------|---------------|------------------|------------------|
| Water | H₂O | 0.512 | 1.86 |
| Ethanol | CH₃CH₂OH | 1.22 | 1.99 |
| Chloroform | CHCl₃ | 3.67 | |
| Benzene | C₆H₆ | 2.53 | 5.12 |
| Diethyl ether| CH₃CH₂OCH₂CH₃ | 2.02 | |](https://content.bartleby.com/qna-images/question/5e64e050-9cb6-467e-8132-ec94d7497579/9fcd55e6-0a7d-47e6-a812-23ebabb72a78/96d158_thumbnail.png)
Transcribed Image Text:**Boiling Point Elevation/Freezing Point Depression**
\[\Delta T = m \cdot K\]
where, for freezing point depression:
\[\Delta T = T(\text{pure solvent}) - T(\text{solution})\]
and for boiling point elevation:
\[\Delta T = T(\text{solution}) - T(\text{pure solvent})\]
- \(m\) = (# moles solute / Kg solvent)
- \(K_b\) = boiling point elevation constant.
- \(K_f\) = freezing point depression constant.
\(K_b\) and \(K_f\) depend only on the SOLVENT. Below are some common values. Use these values for the calculations that follow.
| Solvent | Formula | \(K_b\)(°C / m) | \(K_f\)(°C / m) |
|--------------|---------------|------------------|------------------|
| Water | H₂O | 0.512 | 1.86 |
| Ethanol | CH₃CH₂OH | 1.22 | 1.99 |
| Chloroform | CHCl₃ | 3.67 | |
| Benzene | C₆H₆ | 2.53 | 5.12 |
| Diethyl ether| CH₃CH₂OCH₂CH₃ | 2.02 | |
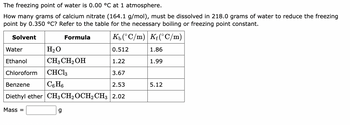
Transcribed Image Text:The freezing point of water is 0.00 °C at 1 atmosphere.
*Problem Statement:*
How many grams of calcium nitrate (164.1 g/mol) must be dissolved in 218.0 grams of water to reduce the freezing point by 0.350 °C? Refer to the table for the necessary boiling or freezing point constant.
*Data Table:*
- **Solvent:** Different solvents and their properties
- **Formula:** Chemical formula of each solvent
- \( K_b \) \((\degree C/m)\): The boiling point elevation constant for each solvent
- \( K_f \) \((\degree C/m)\): The freezing point depression constant for each solvent
| Solvent | Formula | \( K_b \) \((\degree C/m)\) | \( K_f \) \((\degree C/m)\) |
|----------------|--------------------|-----------------------------|-----------------------------|
| Water | \( \text{H}_2\text{O} \) | 0.512 | 1.86 |
| Ethanol | \( \text{CH}_3\text{CH}_2\text{OH} \) | 1.22 | 1.99 |
| Chloroform | \( \text{CHCl}_3 \) | 3.67 | |
| Benzene | \( \text{C}_6\text{H}_6 \) | 2.53 | 5.12 |
| Diethyl ether | \( \text{CH}_3\text{CH}_2\text{OCH}_2\text{CH}_3 \) | 2.02 | |
The task is to calculate the mass of calcium nitrate needed using the properties of water from this table: \( K_f = 1.86 \degree C/m \).
**Mass = \(\boxed{\phantom{g}}\)**
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1

Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- We can calculate the amount of freezing point depression that will occur using the following equation: ΔT = ikfm where ΔT is the amount of the change in the freezing point, i is the number of particles dissolved, kf is a constant (different for each solvent), and m is the concentration of dissolved material. This concentration has units of mol per kg solvent. With this in mind, lets calculate the amount of depression that will occur when 5 g of sodium chloride is dissolved into 0.250 kg of water. Remember when sodium chloride dissolves in water it breaks into two particles. The kf for water is 0.512 0C/m. Report you answer with two decimal points and no units.arrow_forwardThe vapor pressure of methane chloride @ 24 degrees C is 400mmHg and the vapor pressureof formic acid @ 24 degrees C is 40.0mmHg. If a liquid solution consist of 0.250 mole fraction methane chloride and .750 mole fraction formic acid @ 24 degrees C. What is the total vapor pressure in (mmHg) in the above solution?arrow_forwardIf a 0.750 ? aqueous solution freezes at −3.70 ∘C, what is the van't Hoff factor, ?, of the solute? Consult the table of Kf values.arrow_forward
- Determine the number of solute particles in solution, i, for a im NaCl solution with a freezing point lowering value of 3.7°C. Round to the neare whole number. Recall: AT= (KJ(m)(i), where K = -1.86 °C/m U a. 5 b. 2 c. с. 4 O d. 3 11: 70°F Partly cloudy ^ ) 9/22 P Type here to search DELLarrow_forwardplease answer must be to 1 sig figarrow_forwardA solution of hexane and heptane at 30 C with hexane mole fraction of 0.305 has a vapor pressure of 95.0 torr and a vapor-phase hexane mole fraction of 0.555. Fine the vapor pressures of pure hexane and heptane at 30 C.arrow_forward
- Please don't provide handwritten solution .....arrow_forwardis this correct ? i think something doesnt make sense Please solve correctly with explanation.arrow_forward4) The molality of naphthalene in a solution of naphthalene (C10H8, MW= 128.18 g/mol) and cyclohexane (C6H12, MW = 84.16 g/mol) is my = 0.438 mol/kg. Using the information given below (given at p = 1.00 atm) find the normal melting point and normal boiling point of the solution T* = 6.6 °C (normal freezing point for cyclohexane) Kr=20.0 kg °C/mol (freezing point depression constant for cyclohexane) Tb* = 80.7 °C (normal boiling point for cyclohexane) Kb = 2.79 kg °C/mol (boiling point depression constant for cyclohexane)arrow_forward
- The experimental data in the table was collected during a freezing point depression study where BHT (butylated hydroxytoluene) was the solvent. Mass of BHT Mass of unknown Freezing point of pure BHT Freezing point of BHT and unknown solution Kf for BHT 7.709 g7.709 g 1.252 g1.252 g 74.17 ∘C74.17 ∘C 70.91 ∘C70.91 ∘C 6.83 ∘C/?6.83 ∘C/m Use this data to calculate the molar mass of the unknown solute. molar mass =arrow_forwardThe boiling point of an aqueous solution is 102.46 degrees Celcius. What is the freezing point? Consult the table of colligative constants.arrow_forwardWhat is the vapor pressure if the solution is ideal, and what is the composition of acetone and chloroform in the vapor phase?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY