
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
block of mass m= 5 Kg is sent sliding up a large plane inclined at 0 = 37° while a
horizontal force of magnitude 50 Newton acts on it. The coefficient of kinetic friction
between the block and the plane is u= 0.3, and the coefficient of static friction is us=
0.35.
g
5
The blocks initial speed is 4 m/s
If the block reaches a highest point, does it remain at rest or slides back down the plane?
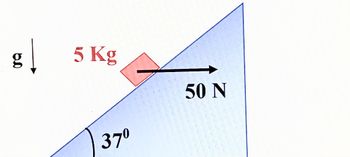
Transcribed Image Text:gļ
5 Kg
37⁰
50 N
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- time = 0 time = t -10 kinetic friction A block slides on a horizontal plane. The initial speed is vo = 2.5 m/s. - V The block slows down because of friction; the coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.100. At time t the speed is vo/2. What is t? (in s) OA: 1.089 OB: 1.274 OC: 1.491 OD: 1.744 OE: 2.041 OF: 2.388 OG: 2.794 OH: 3.269arrow_forwardA0.28-kg rock is thrown vertically upward from the top of a cliff that is 31 m high. When it hits the ground at the base of the cliff, the rock has a speed of 30 m/s . You may want to review (Pages 234 -241) - Part A Assuming that air resistance can be ignored, find the initial speed of the rock. Express your answer using two significant figures. ? m/s Submit Requeet Answer Part B Find the greatest height of the rock as measured from the base of the cliff. Express your answer using two significant figures. Hmar = Submit Requeet Anewerarrow_forwardHelparrow_forward
- Bicýcle Down and Up Hill Example Wa. A Otros 1 of 20 Cons, of E E; = Es Giveni V; -10 mls Y; = 7m Part A A 63 kg person starts traveling from rest down a waterslide 7.0 m above the ground. At the bottom of the waterslide, it then curves upwards by 1.0 m above the ground such that the person is consequently launched into the air. Ignoring friction, how fast is the person moving upon leaving the waterslide? Express your answer with the appropriate units. Value Units Submit Request Answer Mostrar todos Págin Lab_Work Ener..docx a V Lab_Conserv.docx MacBook Air F10 吕口 F5 SC * & %arrow_forwardYou want the final speed at the bottom of your roller coaster hill to be 25 m/s. What is the height (h) of the hill to achieve this? Use g = 9.8 m/s2arrow_forward1. Sam, whose mass is 75 kg, takes off across level snow on his jet-powered skis. The skis have a thrust of 200 N and a coefficient of kinetic friction on snow of 0.10. Unfortunately, the skis run out of fuel after only 10 s. A. What is Sam’s top speed? B. How far has Sam traveled when he finally coasts to a stop?arrow_forward
- Forces: A 7.60×103 kg transport truck is approaching a 20.0° icy hill that has a bridge at the top that is out of service. The driver immediately slams on the brakes and begins to skid up the hill. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the tires and the hill is 0.350. If there is only 131 m from the bottom of the hill to the bridge what maximum speed can the truck initially be going and still avoid an accident?arrow_forwardAnswer Saved Suppose the roller skating woman has a mass of 41.3 kg. Her roller blades have a coefficient of kinetic friction 4g = 0.0306 with respect to the street. She approaches the car, slowing to a speed of v = 6.23 m/s when she touches the car. If the average force she exerts to slow herself down has a magnitude of F = 68.3 N how long does it take for her to come to a stop?arrow_forwardAn object released from rest slides down a frictionless ramp that makes an angle 0j of 60.0° with the horizontal. The object begins at a height Hj of 12.0 m above the base of the ramp. The bottom end of the ramp merges smoothly with a H second frictionless ramp that rises at angle 02 of 39.0°. H2 What distance d does the object slide along the second ramp before coming to a momentary stop? d = m When the object is on its way back down the second ramp, what is its speed vr at the moment that it is at a height H2 of 7.00 m above the base of the ramp? Uf = m/sarrow_forward
- "roblem 8.54 Part A Determine a formula for the maximum height h that a rocket will reach if launched vertically from the Earth's surface with speed vo(< vesc). Express in terms of vn, TE, ME, and G. Express your answer in terms of the variable vo and constants rE, ME, and G. h = Submit Request Answer Part B How high does a rocket go if 8.45 km/s ? Ignore air resistance and the Earth's rotation. ? h = m Submit Request Answer Provide Feedback P Type here to search lyparrow_forwardInthe figure, a 3.9 kg block slides along a track from one level to a higher level after passing through an intermediate valley. The track is frictionless until the block reaches the higher level. There a frictional force stops the block in a distance d. The block's initial speed is vo = 6.8 m/s, the height difference is h = 1.1m, and A. = 0.589. Find d. -0- He Number Unitsarrow_forward5. Two identical blocks, each with mass m, both at rest initially, are connected, as shown. The surface is rough with the coefficient of kinetic friction 4. If the initial height is h, what are the speeds of the blocks once the hanging block hits the ground? harrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON