
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
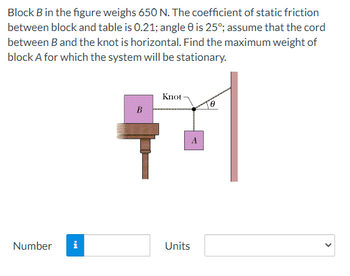
Transcribed Image Text:Block B in the figure weighs 650 N. The coefficient of static friction
between block and table is 0.21; angle 0 is 25°; assume that the cord
between B and the knot is horizontal. Find the maximum weight of
block A for which the system will be stationary.
Number
Knot
B
+
Units
0
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- PROBLEM SET 06: Interacting Objects, Tension, Pulleys OPEN a T₁= B Find the magnitude of the tension in each of the three cables supporting the traffic light if it weights w=335 N and a = 20°, 8=83. You may click the image to enlarge. Help on how to format answers: units. T₁= T- Turned in automatically when due Instructions Aarrow_forwardA setup similar to the one shown in the figure below is often used in hospitals to support and apply a horizontal traction force to an injured leg. (Let m = 5.25 kg and 8 = 75.0°.) (a) Determine the force of tension in the rope supporting the leg. N (b) What is the traction force exerted to the right on the leg? Additional Materials еВookarrow_forward(a) A block of mass m = 3.10 kg is suspended as shown in the diagram below. Assume the pulley to be frictionless and the mass of the strings to be negligible. If the system is in equilibrium, what will be the reading of the spring scale in newtons? Spring Scale m (b) Two blocks each of mass m = 3.10 kg are connected as shown in the diagram below. Assume the pulley to be frictionless and the mass of the strings to be negligible. If the system is in equilibrium, what will be the reading of the spring scale in newtons? Spring Scale (c) A block of mass m = 3.10 kg is in equilibrium on an incline plane of angle e = 34.0° when connected as shown in the diagram below. Assume the mass of the strings to be negligible. If the system is in equilibrium, what will be the reading of the spring scale in newtons? Spring Scale marrow_forward
- It is known that the 10 kg pipe will roll up the ramp and not slide on the ramp when P becomes sufficiently large. Using the rolling assumption, find the minimum P required to cause impending motion of the 10 kg pipe up the ramp. Note that the coefficients of friction for the block/ramp, the pipe/ramp and the pipe/block contacts are each 0.30. 18 kg block 35° 10 kg pipe B μg 0.30 for all contactsarrow_forwardThe block shown in (Figure 1) has a mass of m = 75 kg, a height H = 1.1 m, and width L = 1.6 m. It is resting on a ramp that makes an angle 0 = 34° with the horizontal. A force P is applied parallel to the surface of the ramp at the top of the block. What is the maximum force that can be applied without causing the block to move? The coefficient of static friction is μs = 0.42, and the center of mass of the block is at the center of the rectangle. What is the maximum magnitude of P that can be applied before tipping would occur, assuming the block does not slip? Express your answer to three significant figures with appropriate units. Ptip = 649 N Submit Previous Answers Correct Figure W H F x 2 of 2 Part F What is the maximum magnitude of P that does not cause motion of the block? Express your answer to three significant figures with appropriate units. ☐ μÅ Pmax = |667.611 N Submit Previous Answers Request Answer × Incorrect; Try Again; 5 attempts remaining Provide Feedback ? Review…arrow_forwardInclude a free body diagram please.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON