
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Block A has a weight of 10 lb., and block B has a weight of 30 lb. Determine the speed of block B
after it moves down a distance of 2 ft, starting from rest. The coefficient of kinetic friction between
block A and the horizontal plane is µk = 0.2. Neglect the mass of the cord and pulleys.
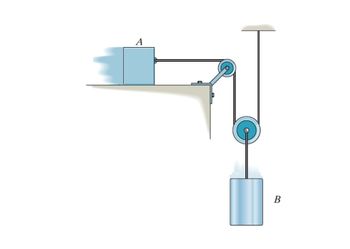
Transcribed Image Text:A
B
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The 10-lb block has a speed of 4 ft/s when the force of F= (8t^2) lbf is applied.Determine the velocity of the block when t= 2 s. The coefficient of kinetic friction at the surfaceis uk = 0.2arrow_forwardThe 2-lb collar starts from rest at A and is lifted by applying a constant vertical force F to the cord. The rod is smooth. h=9-ft. 3 ft В h F A Determine the Force required for the collar speed to be 5 ft.s at B ofarrow_forward4. The block of 2 kg travels down the slope from rest from the position shown and strikes the spring of constant k = 2 kN/m. Determine the maximum deformation of the spring after it is struck by the block. Also determine the location of the block relative to the free end of the spring when it stops after being bounced back by the spring. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and surfaces is μ = 0.25. www. 2 m 2 m 4 3arrow_forward
- 6. At a given instant the 12-lb block A is moving downward with a speed of 6 ft/s. Determine its speed 2 s later. Block B has a weight of 4 Ib, and the coefficient of kinetic friction between it and the horizontal plane is µg = 0.25. Neglect the mass of the cord and pulleys. B Aarrow_forwardThe 81-kg crate is subjected to the forces shown. If it is originally at rest, determine the distance it slides in order to attain a speed of v = 8 m/s. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the crate and the surface is uk = 0.27. Forces with respect to 45° and 30° are 611 N and 398 N, respectivelyarrow_forward2. Initially the 5-kg block is moving with a constant speed of 2 m/s around the circular path centered at 0 on the smooth horizontal plane. If a constant tangential force F = 5 N is applied to the block, determine its speed when t = 3 s. Neglect the size of the block. 1.5 m F = 5 N 2 m/sarrow_forward
- The block has a mass of 40 kg and rests on the surface of the cart having a mass of 78 kg If the spring which is attached to the cart and not the block is compressed 0.2 m and the system is released from rest, determine the speed of the block with respect to the cart after the spring becomes undeformed. Neglect the mass of the wheels and the spring in the calculation. Also neglect friction. Take k = 310 N/marrow_forward2. The 50 kg crate is subjected to the forces shown. If it is originally at rest, determine the distance it slides in order to attain a speed of v= 10 m/s. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the crate and the surface is 0.3. 300 N 600 N 40° 300arrow_forwardIf the force exerted on cable AB by the motor is F = ( 110 t 3/2 ) N, where tt is in seconds, determine the 55-kg crate's velocity when ttt = 5 s . The coefficients of static and kinetic friction between the crate and the ground are μs = 0.37 and μk = 0.29, respectively. Initially the crate is at rest. (Figure 1)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY