
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Topic Video
Question
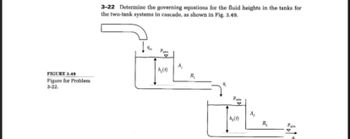
Transcribed Image Text:FIGURE 3.49
Figure for Problem
3-22.
3-22 Determine the governing equations for the fluid heights in the tanks for
the two-tank systems in cascade, as shown in Fig. 3.49.
h₂ (1)
R₁
h₂(1)
A₂
R₂
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 5 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- H.W.2/: The bottom quarter of a vertical cylindrical tank of total height 0.4 m and diameter 0.3 m is filled with a liquid (SG > 1, like glycerin) and the rest with water, as shown in the figure below. The tank is now rotated about its vertical axis at a constant angular speed of v. Determine (a) the value of the angular speed when the point P on the axis at the liquid-liquid interface touches the bottom of the tank and (b) the amount of water that would be spilled out at this angular speed? 3h h = 0.1 m D = 0.3 marrow_forwardBiotransport Phenomenaarrow_forward6. A 100 cc block of Styrofoam (density 100 kg/m³) is held by a massless string, attaching the bottom of the block to the bottom of the vat, in a vat of water (density 1 gm/cc) as shown in the diagram. В. What is the tension in the string? С. block in it), i.e. everything (vat, water, block) accelerates downwards with acceleration due to gravity, g. Now what is the tension in the string? Justify your answer. [Hint: Think carefully about how the buoyant force is derived] Now imagine you drop the whole vat of water (with the Styrofoamarrow_forward
- The Super Soaker XP30 is a marvel of hydraulic dispersion weaponry. By pumping on the handle, you charge the chamber to high pressure. The pressure is maintained until you pull the trigger at which point the water (? = 1000 kg/m3) is released at high velocity.You have charged your pressure chamber to an absolute pressure of P1 = 697500 Pascals, much higher than today's outside air pressure of 101300 Pascals. The pressure chamber is location at a height of y1 = 0.103 meters above the exit point. The exit point has a small opening with radius r = 0.0033 meters.Determine all the following:The velocity at which the water exits the Super Soaker: v2 = m/sThe mass flow rate through the exit: kg/secThe volume flow rate through the exit: m3/secNOTE: You may treat the water chamber as a "tank" and approximate the water velocity there to be zero.arrow_forwardQ.1- The water level, h (t), is controlled by an open -loop system as shown in figure below. A dc motor controlled by an armature current i turns a shaft , opening a valve. The inductance of dc motor is negligible that is, L = 0.Also the rotation friction of the motor shaft and valve is negligible .That is,C=0,The height of the water in the tank is h(t) = [(1.60(1) -h(t)) dt. The motor constant is K=10, the inertia of the motor shaft and valve is J=6x10³ Kg.m² and back e.m.f constant K, = 0.0706V/(rad/s). Determine i-The deferential equation for h(t) and V(t). ii-The transfer function H(s)/V(s). Amplifier 10:41 4.-50 07 Valve MD) 41)arrow_forwardProblem 2: Control volumes and Bernoulli's equation A large open tank of water is mounted on frictionless wheels as shown in Figure 2. The tank has one orifice on each side. The left orifice is located at a distance h from the free water surface and has a diameter d. The right orifice is located at a distance ah from the free water surface and has a diameter ẞd. αh h Bol V₂ Figure 2: Open tank on wheels. 1. Use Bernoulli's equation to calculate the exit velocities at the left and right orifices, v₁ and V2. 2. Determine an equation relating a and ẞ if the tank does not move.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY