
Concept explainers
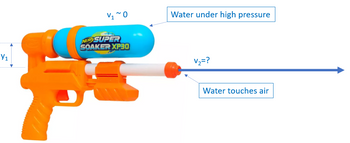
The Super Soaker XP30 is a marvel of hydraulic dispersion weaponry. By pumping on the handle, you charge the chamber to high pressure. The pressure is maintained until you pull the trigger at which point the water (? = 1000 kg/m3) is released at high velocity. You have charged your pressure chamber to an absolute pressure of P1 = 675500 Pascals, much higher than today's outside air pressure of 101300 Pascals. The pressure chamber is location at a height of y1 = 0.117 meters above the exit point. The exit point has a small opening with radius r = 0.0038 meters.
Determine all the following:
a) The velocity at which the water exits the Super Soaker: v2 = m/s
b) The mass flow rate through the exit: kg/sec
c) The volume flow rate through the exit: m3/sec
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

- if air is at pressure of 2200 lb/ft^3, and at a temperature of 800°R, what is the specific volume?arrow_forwardA pump is cavitating at its inlet (i.e., on the suction side). The fluid is water at 120°F. The atmosphericpressure is 0.9 bar. What is the gage pressure of the water in units of kPa?arrow_forwardSuppose a gas-filled incandescent light bulb is manufactured so that the gas inside the bulb is at atmospheric pressure (1 atm = 1.013 × 105 Pa) when the bulb has a temperature of 20.0 °C. Find the gauge pressure inside such a bulb when it is hot, assuming its average hot temperature is 75.0 °C. gauge pressure when hot: 1.87 X104 Incorrect The actual final pressure of the light bulb will be different than calculated in the first question because the glass bulb will expand. What will the final actual gauge pressure be, taking this into account? The volume expansion coefficient for glass is ß = 2.700 x 10-5 °C-1. final gauge pressure, accounting for glass expansion: 1.20 ×105 Pa Incorrect Paarrow_forward
- The Super Soaker XP30 is a marvel of hydraulic dispersion weaponry. By pumping on the handle, you charge the chamber to high pressure. The pressure is maintained until you pull the trigger at which point the water (? = 1000 kg/m3) is released at high velocity.You have charged your pressure chamber to an absolute pressure of P1 = 697500 Pascals, much higher than today's outside air pressure of 101300 Pascals. The pressure chamber is location at a height of y1 = 0.103 meters above the exit point. The exit point has a small opening with radius r = 0.0033 meters.Determine all the following:The velocity at which the water exits the Super Soaker: v2 = m/sThe mass flow rate through the exit: kg/secThe volume flow rate through the exit: m3/secNOTE: You may treat the water chamber as a "tank" and approximate the water velocity there to be zero.arrow_forwardWe would like to calculate the minimum pressure required to force plasma from the heart to the top of the head. For this analysis we will assume blood is a Newtonian, incompressible fluid. The distance from the heart to the top of the head is 0.5m. Assume the density of plasma to be 1065 kg/m3. The vein diameter is 0.95 mm. Assume friction can be neglected.arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





