
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Referring to Figure 10.11, suppose you have some lizards that
are at 16°C and have been living at that temperature for 5 weeks.
What is their resting metabolic rate? If the lizards are suddenly
shifted to a room at 33°C, trace on the graph how their metabolic
rate will change from the moment they are placed in the new
room until 5 weeks have passed. According to the graph, will
they exhibit compensation?
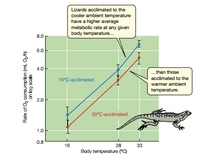
Transcribed Image Text:**Graph Title: Effect of Acclimation Temperature on Metabolic Rate in Lizards**
**Y-Axis: Rate of O₂ consumption (mL O₂/h) on log scale**
- The Y-axis measures the rate of oxygen consumption, represented on a logarithmic scale from 0.8 to 8.0 mL O₂/h.
**X-Axis: Body temperature (°C)**
- The X-axis indicates the body temperature, ranging from 16°C to 33°C.
**Data Series:**
- **16°C-acclimated (Blue Line):** Represents lizards acclimated to a cooler ambient temperature.
- Data Points:
- ~1.0 mL O₂/h at 16°C
- ~2.5 mL O₂/h at 28°C
- ~6.0 mL O₂/h at 33°C
- **33°C-acclimated (Red Line):** Represents lizards acclimated to a warmer ambient temperature.
- Data Points:
- ~0.9 mL O₂/h at 16°C
- ~2.0 mL O₂/h at 28°C
- ~4.5 mL O₂/h at 33°C
**Key Observations:**
- Lizards acclimated to a cooler ambient temperature exhibit a higher average metabolic rate at any given body temperature compared to those acclimated to a warmer ambient temperature.
**Text Boxes:**
- **Top Box:** "Lizards acclimated to the cooler ambient temperature have a higher average metabolic rate at any given body temperature..."
- **Bottom Box:** "...than those acclimated to the warmer ambient temperature."
**Illustration:**
- An image of a lizard is present, emphasizing the subject of the study.
**Background:**
- The graph has a light green background, aiding in the differentiation of the data points and lines.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Please explain and answerarrow_forwardHeat Transfer question In order to cool down a hot steel sphere (its diameter is 5 cm), CO2 gas is blown over it through a pipe with a diameter of 10 cm. The CO2 gas is kept at atmospheric pressure while moving through a smooth pipe at a speed of 6 m/sec. The gas temperature entering the pipe is 300K and exiting the pipe is 340 K. The pipe temperature at the entrance is 350K and at the exit is 550K. The sphere is located just about the pipe exit. Find the convective heat transfer coefficient of the gas moving in the pipe, the heat transfer rate at the pipe and the pipe length. What is the surface temperature of the sphere if the heat transfer rate between the sphere and the gas is 7W and its surface temperature is higher than the gas?arrow_forwardMATCH THE ANSWER WITH THE QUESTION Path Function Choose. Choose. Isobaric Process Pressure is constant Нeat Intensive property No work done Pressure Adiabatic Process Volume No transfer of heatarrow_forward
- Your house has an electric water heater. Several friends are visiting you over the weekend and they are taking consecutive showers. Assume that at the maximum heating level, the heater uses 50 kW of electricity. The water use rate is a continuous 4 gallons per minute with the new water saving showerhead you recently installed. Your very old showerhead had used 7 gallons per minute. You replaced the showerhead because you learned that heating water was the second highest energy use in your home. By slowing the flow of water through the heater, the water temperature should increase to a higher temperature. (a) What is the change in temperature (T) for the old showerhead? (b) What is the change in temperature (T) for the new showerhead? Assume the system is at steady sate, and all of the 50 kW energy used is heating the water.arrow_forwardConduction Heat Transfer X material (a) material (b) . both (a) and (b) have the same thermal conductivity the temperature distribution is independent of thermal conductivity it's not that simple 9. Fin efficiency is defined as: • tanh (mL) (hP/k Ac)1/2 (heat transfer with fin) / (heat transfer without fin) (actual heat transfer through fin) / (heat transfer assuming all fin is at T = Tb) (Tx=L-Tf)/(Tb-Tf) 10. For an infinite fin, the temperature distribution is given by: (T-Tf)/(Tb-Tf)= e-mx. The heat flow through the fin is therefore given by: k (Tb-Tf)/L ● zero, because the fin is infinite ● infinite because the fin is infinite ● (Tb-Tf) (hP/k Ac)1/2 ● (Tb – Tf) (h P / k Ac)1/2 tanh (mL) 11. The Biot number, Bi, is defined as: • Bi=hk/L • Bi=hL/k • Bi= k/LH • Bi=qL/k • Bi=p UL/k 12. For a plate of length L, thickness, t, and width, W, subjected to convection on the two faces of area L x W. What is the correct length scale for use in the Biot number? . L ● W ● t • t/2 • L/2 13. If Bi…arrow_forwardAn electric hot water heater consumes 3.1 kilowatts of electricity and converts it to heat. How long will it take the water heater to heat a 67 gallon tank of water from 10 degrees Celsius to 50 degrees Celsius? (1 kilogram of water is 0.37 gallons, 1 Calorie = 4200 J). It may be helpful to refer back to the weekly handout for guidance on this problem. Your final answer should be in minutes (rounded to the nearest 10 minutes).arrow_forward
- A 370-g sample of an unknown (nongaseous) material experiences a 24.0°C increase in temperature after absorbing 1.24 x 103) of energy. (a) What is the specific heat of this material? 3400 Your response differs significantly from the correct answer. Rework your solution from the beginning and check each step carefully. J/(kg. °C)arrow_forwardplease i need solution in 20 mins help me . i will give positive feedbackarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY