
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question

Transcribed Image Text:Luna Corporation was established in 2021. The company authorized 15,000 shares of Preferred
Stock; the par value is $100.00
per share and 5% cumulative stock. Common stock was authorized at 100,000 shares with a par
value of $5.00 per share. Prepare the following transactions in the proper journal entry form.
Calculate the number of outstanding shares of Common Stock Luna Company has as of June 30.
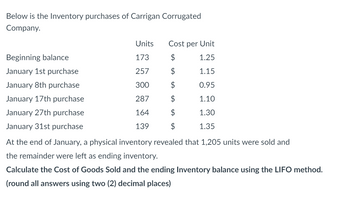
Transcribed Image Text:Below is the Inventory purchases of Carrigan Corrugated
Company.
Beginning balance
January 1st purchase
January 8th purchase
January 17th purchase
January 27th purchase
January 31st purchase
Units
173
257
300
287
164
139
Cost per Unit
$
1.25
$
1.15
$
0.95
$
1.10
$
1.30
$
1.35
At the end of January, a physical inventory revealed that 1,205 units were sold and
the remainder were left as ending inventory.
Calculate the Cost of Goods Sold and the ending Inventory balance using the LIFO method.
(round all answers using two (2) decimal places)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Co.'s purchases and sales of a particular product during the year are shown below: Jan. 1 Beginning Inventory Jan. 18 Purchase 1,500 units @ $ 10 1,250 units @ $ 12 1,500 units @ $ 20 1,750 units @ $ 14 1,750 units @ $ 25 500 units @ $ 15 Jan 20 Sold Jan. 25 Purchase Jan. 27 Sold Jan. 29 Purchase Assuming that company uses perpetual inventory system, determine the cost of goods sold and compute the ending inventory as of Jan. 31 and make the journal entry for Jan. 27 transaction inventory subsidiary ledger for LIF0 cost flow assumption. by using DATE IN OUT BALANCE Quantity Price Total Quantity Price Total Quantity Price Total Jan 1 Jan 18 Jan 20 Jan 25 Jan 27 Jan 29arrow_forwardplease help mearrow_forwardThe records of Alaska Company provide the following information for the year ended December 31. At Cost $ 473,050 2,771,405 At Retail $928,850 6,281,050 5,512,700 46,300 Beginning inventory, January 1 Cost of goods purchased Sales Sales returns Required: 1. Use the retail inventory method to estimate the company's year-end inventory at cost. 2. A year-end physical inventory at retail prices yields a total inventory of $1,692,800. Prepare a calculation showing the company's loss from shrinkage at cost and at retail. Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Required 1 Re ired 2 A year-end physical inventory at retail prices yields a total inventory of $1,692,800. Prepare a calculation showing the company's loss from shrinkage at cost and at retail. Note: Round your ratio calculations to 2 decimal places. (i.e. 10.15%) ALASKA COMPANY Inventory Shortage December 31 At Cost Estimated inventory Physical inventory Inventory shortage Required 1 1. Use the retail…arrow_forward
- Assume ShoeFanatic.com began March with 10 units of inventory that cost a total of $170. During March, ShoeFanatic.com purchased and sold goods as follows: EE (Click the icon to view the purchases and sales.) Under the FIFO inventory costing method and the perpetual inventory system, how much is ShoeFanatic.com's cost of goods sold for the sale on March 14? 'O A. $450 B. $900 OC. $440 O.D. $710arrow_forwardInventory records for Capetown, Incorporated revealed the following: Number of Date April 1 April 20 Transaction Units Unit Cost Beginning Inventory Purchase 460 310 $ 2.39 2.51 Capetown sold 630 units of inventory during the month. Cost of goods sold assuming LIFO would be: (Do not round your intermediate calculations. Round your answer to the nearest dollar amount.)arrow_forwardThe following inventory transactions apply to Green Company for Year 2. January 1 Purchased 240 units @ $10 April 1 Sold 120 units @ $19 August 1 Purchased 420 units @ $11 December 1 Sold 525 units @ $20 The beginning inventory consisted of 165 units at $11 per unit. All transactions are cash transactions. Required Record these transactions in general journal format assuming Green uses the FIFO cost flow assumption and keeps perpetual records. Compute cost of goods sold for Year 2.arrow_forward
- Skysong, Inc. has the following inventory data: July 1 Beginning inventory 33 units at $16 $528 7 Purchases 115 units at $17 1955 22 Purchases 16 units at $18 288 $2771 A physical count of merchandise inventory on July 30 reveals that there are 41 units on hand. Using the LIFO inventory method, the amount allocated to cost of goods sold for July isarrow_forwardThe units of an item available for sale during the year were as follows: Jan. 1 Inventory 850 units at $ 43 Mar. 10 Purchase 1090 units at $ 46 Aug. 30 Purchase 902 units at $ 49 Dec. 12 Purchase 870 units at $ 55 There are 950 units of the item in the physical inventory at December 31. The periodic inventory system is used. Determine the inventory cost and the cost of merchandise sold by the following three methods, presenting your answers in the following form: Cost of Merchandise Merchandise Inventory method Inventory Sold a. First-in, first-out $ $ b. Last-in, first-out c. Weighted average cost Show your calculationsarrow_forwardAkira Company had the following transactions for the month. Number Total of Units Cost Beginning inventory 150 $1,500 Purchased Mar. 31 160 1,920 Purchased Oct. 15 130 1,950 Total goods available for sale 440 5,370 Ending inventory 60 ? Calculate the gross margin for the period for each of the following cost allocation methods, using periodic inventory updating. Assume that all units were sold for $28 each. Round your intermediate calculations to 2 decimal places and final answers to the nearest dollar amount. Gross Margin A. First-in, First-out (FIFO) $ B. Last-in, First-out (LIFO) C. Weighted Average (AVG) %$4 %24 %24 %24arrow_forward
- Sunland Company's inventory records show the following data for the month of September: Units Unit Cost Inventory, September 1 200 $5.00 Purchases: September 8 900 6.00 September 18 900 7.00 A physical inventory on September 30 shows 520 units on hand. Calculate the value of ending inventory and cost of goods sold if the company uses LIFO inventory costing and a periodic inventory system. Ending inventory $ Cost of goods sold $ +Aarrow_forwardCarla Vista Lighting had a beginning inventory of 29 units at a cost of $7 per unit on August 1. During the month, the following purchases and sales were made. August 5 34 units at $8 August 11 44 units at $9 August 23 39 units at $10 Purchases 1. 2. Ending inventory Cost of goods sold $ Sales Carla Vista uses a periodic inventory system. Determine ending inventory and cost of goods sold under: 1. FIFO and 2. LIFO. $ August 2 August 10 August 19 August 21 24 units FIFO 29 units 59 units 29 units $ LIFOarrow_forwardShellhammer Company's inventory records show the following data for the month of September: Inventory, September 1 100 Purchases: September 8 Units September 18 350 Ending inventory 450 Cost of goods sold Unit Cost $3.34 3.50 A physical inventory on September 30 shows 200 units on hand. Calculate the value of ending inventory and cost of goods sold if the company uses FIFO inventory costing and a periodic inventory system. 3.70arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education