
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Beam cross section is shown below. If a resultant shear force, V acting at the beam cross section is 40 kN,
(a) Determine the shear stress due to bending at points C
(b) Sketch the shear stress distribution over the beam cross section and describe the shear stress pattern at the interface between flange and web.
Given I NA = 301.3 x 10-6 m4
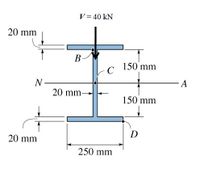
Transcribed Image Text:V= 40 kN
20 mm
В
150 mm
C
N-
20 mm-
A
150 mm
D
20 mm
250 mm
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 6 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The beam shown below is subjected to an applied moment of 8kNm and a uniformly distributed load of 2kN/m, and is supported at A by a pinned connection and at B by a roller connection. Identify the corresponding shear force diagram from the options given below. 2kN/m 8kNm A C 5m 2m 2m (a) (b) A D A в B (c) (d)arrow_forwardDetermine the shear force acting at each of the following locations:(a) x = 0+ ft (i.e., just to the right of support A)(b) x = 9 ft(c) x = 12.333333333333 ftWhen entering your answers, use the shear force sign convention.Answer:(a) V = kips.(b) V = kips.(c) V = kips. The shear-force diagram crosses the V = 0 axis between points A and B. Determine the location x where V = 0 kips.Answer: x = Enter your answer in accordance to the question statement ft. Determine the maximum bending moment that acts anywhere in the beam. When entering your answer, use the bending moment sign convention.Answer: Mmax = Enter your answer in accordance to the question statement kip-ft. Use the graphical method to determine the bending moment acting at each of the following locations:(a) x = 3.3 ft(b) x = 9 ft(c) x = 12.6 ftWhen entering your answers, use the bending moment sign convention.Answers:(a) M = kip-ft.(b) M = kip-ft.(c) M = kip-ft.arrow_forwardA wide flange beam as shown below is subjected to a shear force V. Using the dimensions of the cross section, determine the following quantities: a. τmax in the webb. τmin in the webc. τmax/ τaverage of the webarrow_forward
- The internal shear force V at a certain section of an aluminum beam is 8.7 kN. If the beam has the cross section shown (assume a=44 mm, b=87 mm, tw=t=4 mm, d=88 mm), determine: (a) the shear stress ty at point H, which is located 44 mm above the bottom surface of the tee shape. (b) the maximum horizontal shear stress Tmax in the tee shape. bf H a Answers: (а) тн — i MPa. (Б) тmах — i MРа.arrow_forwardThe figure shows the cross-section of a beam that is composed of a wide-flanged structural profile, whose specification is indicated in the figure, and two steel plates, joined by means of screws, placed in pairs with a longitudinal separation of 20 cm . If the beam is subjected to a vertical shear force of 25 KN, determine the shear stress supported by each bolt in the topsheet. Please add the free diagram body.arrow_forwardAT OVERHANG( NEED NEAT HANDWRITTEN SOLUTION ONLY OTHERWISE DOWNVOTE).arrow_forward
- Mechanics of materials IIarrow_forwardIf the internal moment acting on the cross-section is 800 N.m, determine the maximum tensile and compressive bending stresses acting in the beam. Sketch the stress-distribution acting on the cross-section.arrow_forwardI have gotten this question wrong twice, so the answer isn't 3.43 or .413 kN/m.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY