
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780134580999
Author: Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
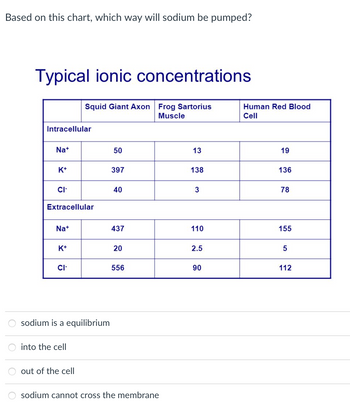
Transcribed Image Text:### Typical Ionic Concentrations
**Question:**
Based on this chart, which way will sodium be pumped?
**Table: Ionic Concentrations**
| | Squid Giant Axon | Frog Sartorius Muscle | Human Red Blood Cell |
|---------------------|-------------------|------------------------|----------------------|
| **Intracellular** | | | |
| Na⁺ (Sodium) | 50 | 13 | 19 |
| K⁺ (Potassium) | 397 | 138 | 136 |
| Cl⁻ (Chloride) | 40 | 3 | 78 |
| **Extracellular** | | | |
| Na⁺ (Sodium) | 437 | 110 | 155 |
| K⁺ (Potassium) | 20 | 2.5 | 5 |
| Cl⁻ (Chloride) | 556 | 90 | 112 |
**Options:**
- Sodium is at equilibrium
- Into the cell
- Out of the cell
- Sodium cannot cross the membrane
**Explanation:**
The table shows the concentrations of three types of ions: Sodium (Na⁺), Potassium (K⁺), and Chloride (Cl⁻), both intracellularly and extracellularly across three different cell types: Squid Giant Axon, Frog Sartorius Muscle, and Human Red Blood Cell. The concentrations are measured in typical units and can help determine the direction of ion movement based on concentration gradients.
For instance, sodium concentrations are higher extracellularly than intracellularly across all three cell types, suggesting that sodium will be pumped out of the cell against its concentration gradient.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- How can you apply the Michaelis-Menten dynamics to explain what happens in plasma concentration of a solute reaches Tm and the effect that has on the Clearance of the solute?arrow_forwardBlood plasma has an osmolarity of about Group of answer choices: 100 mOsm/L. 900 mOsm/L. 1200 mOsm/L. 300 mOsm/L. 30 mOsm/L.arrow_forwardwhich 2 of the following are characteristics of the sodium potassium pump. sel - structure - transporter - enzyme - proteinarrow_forward
- what would the membrane potential be if the membrane became 10X more permeable to both sodium and chloridearrow_forward2% urea is therefore (select all that apply): hyperosmotic isotonic hypotonic hypertonic hypo-osmotic iso-osmoticarrow_forwardWhat effect does digitalis have on the Na and K gradients? Why?arrow_forward
- Which of the following best describes the changes between dilute (osmolarity 50mOsm/Kg) andconcentrated urine (osmolarity 1200mOsm/Kg)? a. Concentrated urine has more water than NaCl moleculesb. Concentrated urine has less water than NaCl moleculesc. Dilute urine has more NaCl than water moleculesd. Dilute urine has less water than NaCl moleculesarrow_forwardCountercurrent exchange in the fish gill helps to maximise [Blank]. Question 20 options: diffusion osmosis active transport blood pressurearrow_forwardThe statement that the majority of sodium is contained outside cells tells us that: A. The amount of sodium in extracellular compartment is more than the intracellular one OB. The osmolarity is higher outside cells than inside cells O C. The volume of ECF is more than the ICF D. All of the abovearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education

Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780134580999
Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:PEARSON

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781259398629
Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa Stouter
Publisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,

Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780815344322
Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter Walter
Publisher:W. W. Norton & Company

Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781260159363
Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, Cynthia
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.

Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9781260231700
Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael Windelspecht
Publisher:McGraw Hill Education