
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780134580999
Author: Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
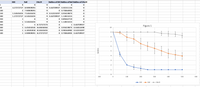
2. Based on the class data from Experiment I, generally speaking, how does
affect genetic drift?
Transcribed Image Text:3X3
9x9
19x19
StdDev of 3X3 StdDev of 9x9 StdDev of 19x19
9
9
50
4.27272727 8.90909091
9 0.46709937 0.30151134
100
150
0 0.70064905
9 0.52223297 0.93419873
2 7.90909091
1.54545455 7.54545455
200
250
9 0.46709937 1.12815215
0 0.89442719
O 1.12815215
1.27272727 6.54545455
1
9.
300
1 5.54545455
350
1
5 8.72727273
1 0.46709937
Figure 1
O 0.93419873 0.50452498
0 0.98164982 0.52223297
400
1 4.45454545 8.63636364
10
450
500
1 4.18181818 8.54545455
1 3.90909091 8.27272727
0 0.70064905 0.46709937
4
3
2
1
-100
100
200
300
400
500
600
3X3 -9
Update
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 5. Do we see logistic growth in real-world populations? If so, give an example.arrow_forward5. a. Is genetic drift a gain or loss in heterozygosity? b. What population is most effected by drift? Ne = 20 or Ne = 200. Why? c. There is a balancing act between drift and another force of evolution. What is it and why is this important?arrow_forward5. Describe the variation in the appearance among individuals in a population when a trait is single-gene controlled compared to a trait that is multiple-gene controlled. Cllarrow_forward
- 2. You have sampled a population in which you know that the percentage of the homozygous recessive genotype (a) is 26%. Using that 26%, calculate the following: A. The frequency of the "aa" genotype. B. The frequency of the "a" allele. C. The frequency of the "A" allele. D. The frequencies of the genotypes "AA" and "Aa." E. The frequencies of the two possible phenotypes if "A" is completely dominant over "aarrow_forwardI need help with Hardy-Weinberg Equilibriumarrow_forward7arrow_forward
- 1. According karacan 2014, which of the following statement is true about the level of generativity? 2.arrow_forward22. The graph shows the distribution of a trait in an animal population. mean Range of variable If the species were to undergo stabilizing selection in which extreme phenotypes were selected against, how would the graph be expected to change? A. The peak would move to the left. B. The peak would move to the right. C. The peak would become taller and narrower. D. The peak would become lower and more rounded. EducationTM Inc. Aouenberarrow_forward5) A mutant red coat color allele (Yr) arises in island B and is present in the adult population in a heterozygous individual in the population of 117 adults of year 2000. Yr is recessive to the other alleles at the Y locus. What is the probability (p) that, purely by the action of genetic drift, the allele will rise to fixation (reaching a frequency of 1.0) at some time in the future? (A) 0.0 < p < 0.2 (B) 0.2 < p < 0.4 (C) 0.4 < p < 0.6 (D) 0.6 < p < 0.8 (E) 0.8 < p < 1.05 6) For the same genetic scenario, what if the single red allele arose in the island A and was present by 1990 in a heterozygous individual, one of a population 12 individuals. Would this red mutant allele have a better or worse chance of rising to fixation relative to the island B population of problem 5? (A) red allele more likely to reach fixation in A island beginning in 1990 compared to B island beginning in…arrow_forward
- 1. Based on the class data from Experiment I, for each of the three populations, describethe effect of population size on genetic diversity over time. Your answer should touchon the magnitude of any genetic changes through time for each of the three populationsizes.arrow_forwarde. The frequencies of the genotype "Aa." f. The frequency of the recessive phenotype if "A" is completely dominant over "a." g. The frequency of the dominant phenotype if "A" is completely dominant over "a".arrow_forward11. A lecture hall of 1000 students conducts the same allele frequency simulation that we conducted in class with the A and a cards. In the beginning, everyone starts as Aa. The following data was collected; what is the most likely explanation for the results? a. natural selection against AA b. genetic drift c. mutation pogos Generation 0 1 2 %A %0 .5 9arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education

Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780134580999
Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:PEARSON

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781259398629
Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa Stouter
Publisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,

Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780815344322
Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter Walter
Publisher:W. W. Norton & Company

Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781260159363
Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, Cynthia
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.

Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9781260231700
Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael Windelspecht
Publisher:McGraw Hill Education