
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
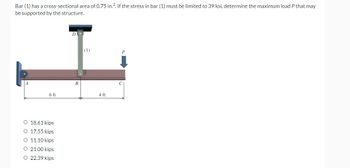
Transcribed Image Text:Bar (1) has a cross-sectional area of 0.75 in.2. If the stress in bar (1) must be limited to 39 ksi, determine the maximum load P that may
be supported by the structure.
D
A
6 ft
O 18.61 kips
O 17.55 kips
O 11.10 kips
O 21.00 kips
O 22.39 kips
B
(1)
4 ft
C
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A simple pin connected truss is loaded and supported as shown. The truss is constructed from three aluminum members, each having a cross sectional area of A = 1220 mm ^2. Assume a = 1.4 m, b = 8.9 m, and c = 3.6m. If P = 60kN and Q = 80kN determine the normal stress in each member.arrow_forward2. A replacement disc consists of the tube Cwith larger diameter of 4 cm, the cylindrical core B with the diameter of 2 cm and two relatively rigid discs on both ends. The disc replacement placed between vertebrae is under compressive force of 400N. The corresponding moduli of elasticity are Ec=10MPA and EB=20MPa. Determine the stress in the tube A and the core B. F Rigid parts 1cm C 2om 4cm F (Answer: OB = 509.3KPA, oc = 254.6KPA) 254.6KРа) %3Darrow_forwardTwo solid cylindrical rods (1) and (2) are joined together at flange B and loaded as shown. If F₁ = 13 kips, F₂ = 34 kips, and the normal stress in each rod must be limited to 22 ksi, determine the minimum diameter d₁ required for rod (1). A (2) d₁ F₂ B C O 1.087 in. O 0.823 in. O 0.541 in. O 0.867 in. O 1.003 in. d₂arrow_forward
- Two aluminum plates, each having a width of b = 8.0 in. and a thickness of t = 0.750 in., are welded together as shown. Assume a = 4.0 in. For a load of P = 75 kips, determine (a) the normal stress that acts perpendicular to the weld and (b) the magnitude of the shear stress that acts parallel to the weld. Answer: O= P T = 1 i 1 ksi ksi b Parrow_forwardPHILPS 2 Concepts EA/Documents/Week12 Compatibility 21-22-1%20(1).pdf 30 / 31 100% PROBLEM 2.35 The 1.35 m concrete post is reinforced with six steel bars, each with a 28 mm diameter. 450 mm Knowing that E, = 200 GPa and E, = 29 GPa, determine the normal stresses in the 1.35 m steel and in the concrete when a 1560 kN axial centric force P is applied to the post. [Ans. o = -59.5 MPa; o̟ = -8.63 MPa] Fig. P2.35 Seašon's Greetínas ·arrow_forwardi need the answer quicklyarrow_forward
- The timber member has a cross-sectional area of 1850 mm? and its modulus of elasticity is 12 GPa. What is the normal stress in member AB? 40 kN 35 kN 20 kN D A B +1.5 m→ - 3 m - - 3 m · Select one: O a. 8.11 MPa b. 10.81 MPa с. 13.51 MPа d. 21.62 MPaarrow_forwardRank the normal stress in each section of the bar. Rank the values of normal stress from largest (largest tensile stress) to smallest (largest compressive stress). Use AB for segment AB, BC for segment BC, and CD for segment CD.arrow_forwardDetermine the compressive force (in Ib) in the bars shown after a temperature rise of 149°F if d = 0.012 in. Round off the final answer to five decimal places. d ... L M Use the following data: Bronze Aluminum A = 2.24 sq. in A = 2.73 sq. in E = 14930924 psi L = 13.4 in E = 10543748 psi L= 16 in a = 11.76 x 10-6/ °F a = 12.54 x 10-6/°Farrow_forward
- 1200 N 2. For the bone shown to the left, assume the cross-section at C can be approximated as annular, with an outer diameter of 25mm. When the 1200 N forces are applied, the average normal stress in the bone at point C is determined to be 3.80 MPa. Determine the inner diameter of the bone cross section at C. Ans: d; = 14.93 mm 4 in. P 3 in. B 1200 N "UI 8arrow_forward1.85 helparrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY