
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Students are given two spherical balls made of different materials, but of identical mass and diameter to experiment with. Each ball is dropped from an initial height, h0. The “sad ball” comes to rest without visibly bouncing when it strikes the tabletop. The “happy ball” bounces up to a final height h, where h< h0
A fellow student wants to use one of the balls in a carnival game where cups are knocked over by a thrown ball. Which ball should they use, happy or sad? Why?
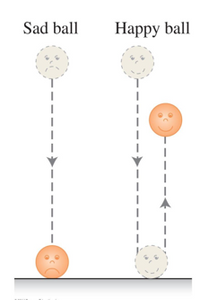
Transcribed Image Text:Sad ball
Happy ball
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A wind generator is installed. It is determined that the capacity factor of the installation is 29% over the course of a 90-day period. In that period, it produced 1566 MWh. What is the size of the installation (MW)?arrow_forwardA stringer of tennis rackets has found that the actual string tension achieved for any individual racket will vary as much as 6 pounds per square inch from the desired tension set on the stringing machine. If the stringer wishes to string at a tension lower than that specified by a customer only 5% of the time, how much above or below the customer's specified tension should the string set the stringer machinearrow_forwardDraw and discuss the FBD for the following system. • Label all forces and directions. How many unknowns are there? (Remember, an unknown does not have to be a force. It can also be a dimension, angle, etc.) • How many equilibrium equations can you create? • Is there enough information to solve for the unknowns? Explain. ● Draw pulley A as your particle. B 20° A 100 N Farrow_forward
- Only question 1 pleasearrow_forwardLooking for simple solution with correct answer.arrow_forward##L2Q3 The position of a vehicle's center of mass can be determined experimentally. To do this, it is necessary to measure the total weight of the car as well as the forces acting under the front wheels. Fig. 1 illustrates the situation in which the forces acting under the front wheels can be measured experimentally. Considering the data in the figure, determine: a) the position of the center of mass; (b) the force acting on each of the rear wheels. Consider known l, m, and Fz1. 2F C al 2F21 mgarrow_forward
- 1. You are setting up for a pool party that has a 2.5 m high slide that launches swimmers into the pool. To make it more exciting, you decide to string a steamer across the pool so that the swimmers just clear it at their maximum height after leaving the slide. The end of the slide is 0.75 m above the ground and is directed 20° above the horizontal. By watching people use the slide, you know the horizontal distance to place the streamer, so you only need to determine the maximum height. You are also curious how fast the swimmers are going when they enter the pool. In your estimates, you can assume that the swimmer starts at rest at the top of the slide and ignore friction on the slide and air resistance. 2.5 m 0.75 m streamer If the angle of the slide were different (say 15°) would either the maximum height or the speed when entering the water be different? Note: Use conservation of energy to answer these questions.arrow_forwardSolve 1st problemarrow_forward4) Calculations for the red dog food can rolling down the slope in the Rube Goldberg design are as follows (we will name it Step 1): Step 1 (calculations are given): Coefficient of friction → μ = 0.14 Mass of the object → m = 368 gm = 0.368kg Initial height of the object (red can on top of books) → h=8.89, cm = 0.0889 m Slope of the file folder → 0 = 14° Travelling Distance by the object = 11.5 inch = 0.292 m And length that the object will travel = h/sin 0 = 0.0889/ sin14° = 0.367 m So, the radius of the object → R=0.367 -0.292 = 0.075 m Initial Velocity of red can → u = 0 Velocity and Force Calculations for Step 1: -From total mechanical energy conservation: → Initial mechanical energy = final mechanical energy → mg - In case of pure rolling, the velocity of the center of mass: → V = Ro = 0.075 × 14.28 1.07 m/s. -Hence the change in force acting on the object for the travel: →F=mgsine = 0.368 × 9.81 × sin14° =0.89 N Step 2: The Selective Step (Step 2) in this design and for the…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY