
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
thumb_up100%
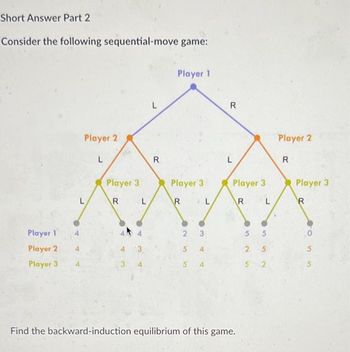
Transcribed Image Text:Short Answer Part 2
Consider the following sequential-move game:
Player 1
Player 2
Player 3
Player 2
L
Player 3
R
3
L
L
R
Player 1
Player 3
R
2
3
5
4
5 4
L
R
L
Player 3
R
Find the backward-induction equilibrium of this game.
L
5 5
2. 5
5 2
Player 2
R
Player 3
R
20
0
5
5
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Thank you for helping on this!arrow_forwardFor each of the following games, identify the backwards induction equilibrium and the equilibrium strategy for each player. 5. b. (1,1) (0,2) (2.2) (0,1) (1,) (1.0)arrow_forward1. Consider the following game matrix. Player A Answer: Top Bottom Left a, b e, f Player B Right c, d g, h (a) If top and left are strictly dominant strategies, then what do we know the relationship of the parameters? (b) If (top, left) is a Nash equilibrium, then what do we know the relationship of the parameters? Answer: (c) If top and left are strictly dominant strategies, will (top, left) be a Nash equilibrium? Why? Answer: (d) If (top, left) is a Nash equilibrium, must the strategies be strictly dominant strategies? Why? Answer:arrow_forward
- Use the following game table to answer the question: Player 2 Y 6, 3 1, 3 A 10, 5 0,0 Player 1 B 2,6 0,0 3,5 3, 4 3, 3 Is the Nash equilibrium of this game for Player 1 to choose A and Player 2 to choose X? Why or why not? O It is; if Player 2 chose B or C they would get less than 10, and if Player 1 chose Y or Z they would get less than 5. It is not; Player 2 could get 6, instead of 5, if they chose B. O It is; if Player 1 chose B or C they would get less than 10, and if Player 2 chose Y or Z they would get less than 5. It is; if Player 2 chose B or C they would get less than 5, and if Player 1 chose Y or Z they would get less than 10. It is not; Player 1 could get 6, instead of 5, if they chose B.arrow_forwardExplain the nature of game theory. What current issue could this be applied to?arrow_forward3. Consider the following game in normal form. Player 1 is the "row" player with strate- gies a, b, c, d and Player 2 is the "column" player with strategies w, x, y, z. The game is presented in the following matrix: W x y Z 2,1 0,2 2,1 a 3,3 b 1,1 1,2 1,0 1,4 c 0,0 1,0 3,2 1,1 d 0,0 0,5 0,2 3,1 Find all the Nash equilibria in the game in pure strategies.arrow_forward
- Question 5 Consider following extensive form game Keep Prices (8,2) Advertise Lower Prices (4,6) O Advertise; Lower Prices Firm 1 O Advertise; Keep Prices Firm 2 O Not Advertise; Keep Prices Not Advertise The subgame perfect Nash-equilibrium is O Not Advertise; Lower Prices Keep Prices (6,10) O Lower Prices (3,7) 5 ptsarrow_forward3. Consider the following game: K Out 2 2 1 9 Player 1 Player 1 X In A Y Player 2 0 2 B 5 5 a) Does the game have perfect information? Why/why not? b) Circle the subgames. c) Find all backward induction solutions. d) Below are written five strategy profiles. One of them is a subgame perfect equilibrium; circle it! One of them is not a Nash equilibrium; write "X" across it! ((Out, X), A) ((Out, Y), A) ((In, Y),B) ((Out, Y), B) ((In, X),B)arrow_forwardThe hand written is not allowed.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education