
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
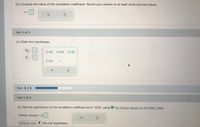
Transcribed Image Text:(b) Compute the value of the correlation coefficient. Round your answer to at least three decimal places.
Part 3 of 5
(c) State the hypotheses.
H :
O=0
ロチロ
O<O
H :
ロ>ロ
Part: 3/5
Part 4 of 5
(d) Test the significance of the correlation coefficient at a=0.05, using
The Critical Values for the PPMC Table.
Critical value(s): ±
(Choose one) v the null hypothesis.

Transcribed Image Text:Forest Fires and Acres Burned An environmentalist wants to determine the relationships between the numbers (in thousands) of forest fires over the year
and the number (in hundred thousands) of acres burned. The data for 6 recent years are shown.
Number of fires x
69 58 47 84 62 57
Number of acres burned y
42 19
26 51 15 30
Send data to Excel
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- (a) Draw a scatter diagram of the data. Compute the linear correlation coefficient. The linear correlation coefficient for the four pieces of data is (Round to three decimal places as needed.) Part 2 (b) Draw a scatter diagram of the data with the additional data point (10.3,9.3). Compute the linear correlation coefficient with the additional data point. The linear correlation coefficient for the five pieces of data is (Round to three decimal places as needed.) part 3 Comment on the effect the additional data point has on the linear correlation coefficient. Explain why correlations should always be reported with scatter diagrams.arrow_forwardThe relationship between two variables partialling out the effect that a third variable has on one of those variables can be expressed using a: a. Partial correlation O b. Point-biserial correlation Oc. Semi-partial correlation Od. Bivariate correlationarrow_forwardFind: The linear correlation coefficient is r= The critical values are r=arrow_forward
- Q1-Q5: a) Find the value of the line ar correlation coefficient r b) Find the critical values ofr from table A-6 using x= 0.05 c) Determine whether there is sufficient evidence to support a claim of a linear correlation Between the two variables. d) Find the regression equation, e) Letting the first variable be the predietor (x) variable, find the indicated predieted value. Q1. Altitude and Temperature: Altitude 3 10 14 22 28 31 33 ( thousands of feet) Temperature ( °F) 57 37 24 -5 -30 -41 -54 At 6.327 thousand feet, the author recorded the temperature. Find the best predieted temperature at that altitude. How does the result compare to the actual recorded value of 48°F?arrow_forwardDetermining significance of the correlation coefficient. Step 1: State the hypotheses. Ho: p = 0; H₁: p = 0 Step 2: Find the critical values. Two-tailed, Table F Step 3: Compute the test value. t = r freedom d.f. = n-2 Step 4: Make the decision. Step 5: Summarize the results. 54 n-2 1-2 with degrees of For each exercise, draw the scatter plot, determine if r is statistically significant, find the equation of the regression line and find the y'value for the specified xvalue. Remember that no regression should be done when ris not significant. 8.2 1. New Broadway productions and seasonal attendance are as follows. No. Of 67 62 54 61 Productions Attendance 7.4 (million) Find y' when x = 48 new productions. n(Exy) - (Ex) (Ey) √[n(Ex²) - (Ex)²][n(Ey²) — (Ey)²] CALC: STAT →Tests →LinRegTTest 7.1 r = 8.8 9.6 60 11 50 8.4 37 7.4arrow_forwardPlease finish the R code to conduct the hypothesis testing. I need the code for the p-value for the F test, tstat, and the p value for tstat. Write the conclusion to the hypothesis testing once completed. # Example 11.1# simple linear regression# H0: B=0 (there is no linear correlation)# H1: B≠0 (there is a linear correlation)data <- data.frame(estriol=c(7,9,9,12,14,16,16,14,16,16,17,19,21,24,15,16,17,25,27,15,15,15,16,19,18,17,18,20,22,25,24),birthweight=c(25,25,25,27,27,27,24,30,30,31,30,31,30,28,32,32,32,32,34,34,34,35,35,34,35,36,37,38,40,39,43))linear <- lm(birthweight~estriol, data = data)summary(linear)# This gives the results for a and b and the F statistic. # Call:# lm(formula = birthweight ~ estriol, data = data)# # Residuals:# Min 1Q Median 3Q Max # -8.1200 -2.0381 -0.0381 3.3537 6.8800 # # Coefficients:# Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|) # (Intercept) 21.5234 2.6204 8.214 4.68e-09 ***# estriol 0.6082 0.1468 4.143…arrow_forward
- You run a regression analysis on a bivariate set of data (n = 110). You obtain the regression equation y = – 3.546x 4.393 0.248 (which is significant at a = 0.01). You want to predict with a correlation coefficient of r = - what value (on average) for the explanatory variable will give you a value of 100 on the response variable. What is the predicted explanatory value? X = (Report answer accurate to one decimal place.)arrow_forwardBook Pages (x) Price (y) A 500 $7.10 B 700 7.60 C 750 9.10 D 590 6.60 E 560 7.60 F 650 7.10 G 475 5.10 (a) Develop a least squares estimated regression line. (Round your numerical values to three decimal places.) (b) Compute the coefficient of determination. (Round your answer to four decimal places.) Explain its meaning. (Give your answer as a percent. Round your answer to two decimal places.) The value of the coefficient of determination tells us that % of the variability in |--?-- ☑ has been explained by the least squares regression equation.arrow_forwardMy solution is incorrectarrow_forward
- The linear correlation coefficient is r=0.9780.978. (Round to three decimal places as needed.) Determine the null and alternative hypotheses. H0:ρ ____ ______ H1:ρ _____ _______ (Type integers or decimals. Do not round.) The test statistic is t= (Round to two decimal places as needed.) The P-value is (Round to three decimal places as needed.) Because the P-value of the linear correlation coefficient is less than or equal to: the significance level, there is: sufficient evidence to support the claim that there is a linear correlation between bill amounts and tip amounts. If everyone were to tip with the same percentage, then r= (Round to three decimal places as needed.)arrow_forwardfind the linear correlation coefficent and the critical value(s)arrow_forwardou run a regression analysis on a bivariate set of data (n=20n=20). With ¯x=44.9x¯=44.9 and ¯y=42.7y¯=42.7, you obtain the regression equationy=3.921x+57.242y=3.921x+57.242with a correlation coefficient of r=0.264r=0.264. You want to predict what value (on average) for the response variable will be obtained from a value of 140 as the explanatory variable.What is the predicted response value?y = (Report answer accurate to one decimal place.)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman