
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
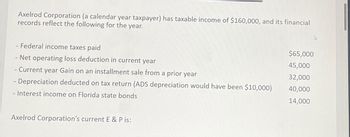
Transcribed Image Text:Axelrod Corporation (a calendar year taxpayer) has taxable income of $160,000, and its financial
records reflect the following for the year.
- Federal income taxes paid
- Net operating loss deduction in current year
$65,000
45,000
- Current year Gain on an installment sale from a prior year
32,000
- Depreciation deducted on tax return (ADS depreciation would have been $10,000)
40,000
- Interest income on Florida state bonds
14,000
Axelrod Corporation's current E & P is:
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Lolo Inc. had pre-tax accounting income of P900,000 in 2020, its first year of operations. During 2020 the company had the following transactions: • Received rent from Mama, Co. for year 2021- P32,000 • Government bonds interest income- P40,000 • Depreciation for tax purposes in excess of book depreciation- • Installment sales revenue to be collected in 2021-P54,000 . P20,000 At the end of 2020, which of the following deferred tax accounts and balances is reported on Papa, Inc.'s statement of financial position? (assume income tax rate of 40%) A.Deferred tax liability- P20,800B.Deferred tax liability- P12.800C.Deferred tax asset- P12,800D.Deferred tax asset- P20,800arrow_forwardEFG, a calendar year, accrual basis corporation, reported $479,900 net income after tax on its financial statements prepared in accordance with GAAP. The corporation’s financial records reveal the following information: EFG earned $10,700 on an investment in tax-exempt municipal bonds. EFG’s allowance for bad debts as of January 1 was $21,000. Write-offs for the year totaled $4,400, while the addition to the allowance was $3,700. The allowance as of December 31 was $20,300. On August 7, EFG paid a $6,000 fine to a municipal government for a violation of a local zoning ordinance. EFG’s depreciation expense per books was $44,200, and its MACRS depreciation deduction was $31,000. This is EFG’s second taxable year. In its first taxable year, it recognized an $8,800 net capital loss. This year, it recognized a $31,000 Section 1231 gain on the sale of equipment. This was EFG’s only disposition of noninventory assets. In its first taxable year, EFG capitalized $6,900 organizational costs…arrow_forwardOn its year 1 financial statements, Seatax Corporation, an accrual-method taxpayer, reported federal income tax expense of $570,000. On its year 1 tax return, it reported a tax liability of $650,000. During year 1, Seatax made estimated tax payments of $700,000. What book-tax difference, if any, associated with its federal income tax expense should Seatax have reported when computing its year 1 taxable income? Is the difference favorable or unfavorable? Is it temporary or permanent? Year 1 Book-tax Difference Favorable or Unfavorable Temporary or Permanentarrow_forward
- For the year ended December 31, 2019, Nelson Co.’s income statement showed income of $425,000 before income tax expense. To compute taxable income, the following differences were noted: Income from tax-exempt municipal bonds $60,000 Depreciation deducted for tax purposes in excess of depreciation recorded on the books 130,000 Proceeds received from life insurance on death of an insured employee 100,000 Corporate tax rate for 2019 30% Enacted tax rate for future periods 35% Required: 1. Calculate taxable income and tax payable for tax purposes. 2. Prepare Nelson’s income tax journal entry at the end of 2019.arrow_forwardBluth, Inc. reported the following financial information: Taxable income for current year $200,000 Deferred tax liability, beginning of year 46,000 Deferred tax liability, end of year 57,000 Deferred tax asset, beginning of year 12,000 Deferred tax asset, end of year 18,000 Current and future years' tax rate 21% The current year's income tax expense is what amount?arrow_forwardAt the end of the year, Falabella Co. has pretax financialincome of $550,000. Included in the $550,000 is $70,000interest income on municipal bonds, $25,000 fine fordumping hazardous waste, and depreciation of $60,000.Depreciation for tax purposes is $45,000. Compute incometaxes payable, assuming the tax rate is 30% for all periods.arrow_forward
- LNS Corporation reports book income of $2,940,000. Included in the $2,940,000 is $17,500 of tax-exempt interest income. LNS reports $2,560,000 in ordinary and necessary business expenses. What is LNS Corporation's taxable income for the year? Answer is complete but not entirely correct. $ 640,000 Taxable incomearrow_forwardGrand Corporation reported pretax book income of $639,000. Tax depreciation exceeded book depreciation by $426,000. In addition, the company received $319,500 of tax-exempt municipal bond interest. The company's prior-year tax return showed taxable income of $53,250. Compute the company's current income tax expense or benefit. (Leave no answer blank. Enter N/A or zero.) Current income tax Deferred income tax N/A benefit $ 22,365arrow_forwardSunland Corporation began operations in 2020 and reported pretax financial income of $212,000 for the year. Sunland’s tax depreciation exceeded its book depreciation by $33,000. Sunland’s tax rate for 2020 and years thereafter is 30%. Assume this is the only difference between Sunland’s pretax financial income and taxable income.Prepare the journal entry to record the income tax expense, deferred income taxes, and income taxes payable. Show how the deferred tax liability will be classified on the December 31, 2020, balance sheet. Deferred tax liability should be classified as a a) current asset b) current liability c) non current asset or d) non current liability on the December 31, 2020, balance sheet.arrow_forward
- LNS Corporation reports book income of $2,890,000. Included in the $2,890,000 is $32,750 of tax-exempt interest income. LNS reports $2,597,500 in ordinary and necessary business expenses. What is LNS Corporation's taxable income for the year? Taxable incomearrow_forwardAt the end of the year, the deferred tax asset account had a balance of $12 million attributable to a cumulative temporary difference of $30 million in a liability for estimated expenses. Taxable income is $35 million. No temporary differences existed at the beginning of the year, and the tax rate is 40%. Prepare the journal entry(s) to record income taxes assuming it is more likely than not that one-fourth of the deferred tax asset will not ultimately be realized.arrow_forwardHopkins Co. at the end of 2021, its first year of operations, prepared a reconciliation between pretax financial income and taxable income as follows: Pretax financial Income 3,000,000 Estimated litigation expense 4,000,000 Extra depreciation for taxes (6,000,000) Taxable Income $1,000,000 The tax rate is 20% Instructions: Calculate the income tax expense and income tax payable for 2021.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education