
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
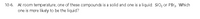
Transcribed Image Text:10-6. At room temperature, one of these compounds is a solid and one is a liquid: SiO, or PBr3. Which
one is more likely to be the liquid?

Transcribed Image Text:Answer each question and justify your answer by doing ALL of the following:
Identify the type of substance and important interpartide force(s) for both substances.
Explain how you know (substances and forces).
For each molecular substance, fully justify how you know if it is polar or nonpolar. Provide a
Lewis structure, a geometry sketch, calculation of AEN| values, and a discussion of symmetry.
Identify which of the two substances has stronger interparticle forces. If they have the same type
of interparticle force, explain how you know which is stronger.
Answer the question by connecting the property asked about to strength of interparticle forces.
Use complete sentences, write all words out (no abbreviations) and be specific and complete with
all explanations. Do not refer to any actual data.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- lodine pentoxide, I₂O5, is a white crystalline solid. It is formed by heating HIO, to about 200 °C in a stream of dry air. The reaction is shown below. 2HIO3(s) 1₂0,(s) + H₂O(g)arrow_forwardThe equation for photosynthesis is 6H2O (water) + 6CO2 (carbon dioxide) + Light Energy → C6H12O6 (glucose) + 6O2(oxygen). When first discovered, scientists were trying to decide if the oxygen in the product came from carbon dioxide or water. Which statement describes how scientists traced the path of oxygen?arrow_forwardOne day in lab, while taking apart a complicated distillation apparatus, your friend Lisa (an expert chemist) says this: "Group 2A metal hydrides react with water to produce hydroxides and hydrogen gas." Using Lisa's statement, and what you already know about chemistry, predict the products of the following reaction. Be sure your chemical equation is balanced! BaH₂(s) + H₂O(1)→arrow_forward
- Sodium hydrogen sulfate is used as a cleaning agent and as a flux (a substance that promotes the fusing of metals and prevents the formation of oxides). One of the ways in which sodium hydrogen sulfate is manufactured is by reacting sodium dichromate, Na2Cr2O7, with sulfuric acid. This process also forms water and chromium(VI) oxide, CrO3. Write a balanced equation for this reaction. (You do not need to include states.) How many kilograms of sodium dichromate, Na2Cr2O7, are necessary to produce 130.4 kg of sodium hydrogen sulfate? How many kilograms of chromium(VI) oxide are formed when 130.4 kg of sodium hydrogen sulfate is made? What is the minimum volume of 18.0 M H2SO4 solution necessary to react with 874.0 kg of sodium dichromate? What is the maximum mass of sodium hydrogen sulfate, NaHSO4, that can be formed from the reaction of 874.0 kg of sodium dichromate with 400.0 L of 18.0 M H2SO4?arrow_forwardBecause carbon and silicon are both elements in group 14 on the periodic table, we expect them to react with other elements in similar ways. To some extent, they do, but in some cases, carbon and silicon compounds that seem to have analogous structures have very different chemical characteristics. For example, carbon tetrachloride, CCl4, is very stable in the presence of water, but silicon tetrachloride, SiCl4, reacts quickly with water. The unbalanced equation for this reaction is SiCl4 + H2O → Si(OH)4 + HCl Balance this equation. Write a conversion factor that could be used to convert between moles of SiCl4 and moles of H2O. How many moles of SiCl4 react with 24 moles of water? Write a conversion factor that could be used to convert between moles of Si(OH)4 and moles of water. How many moles of Si(OH)4 form when 4.01 moles of H2O react with an excess of SiCl4?arrow_forwardModern commercial airliners are largely made of aluminum, a light and strong metal. But the fact that aluminum is cheap enough that airplanes can be made out of it is a bit of historical luck. Before the discovery of the Hall-Héroult process in 1886, aluminum was as rare and expensive as gold. What would happen if airplanes had to be made of steel? The fuselage of the Boeing 777, which can carry 305 passengers, is approximately a hollow aluminum cylinder without ends, 64.0 m long, 6.2 m wide, and 2.5 mm thick (see sketch at right). The fuselage of an airplane Suppose this fuselage was made of steel (density 7.87 g/cm³) instead of aluminum (density 2.70 g/cm³), and let's say the average passenger has a mass of 81 kg. We'll also assume the engines can't lift any greater mass than they already do. Calculate the number of passengers that the Boeing 777 could carry if its fuselage was made of steel. X Śarrow_forward
- 1. More than 2000 years ago human cultures figured out a way to produce iron metal from rocks containing iron ores. This iron could be worked by a blacksmith (repeated heating and hammering) to make iron metal pure enough for creating useful tools (even Samurai swords). This direct heating technique was common up until about 200 years ago when people found a better way to obtain iron metal. When hematite, Fe2O3(s), is strongly heated in a blast furnace in the presence of charcoal (carbon), pure iron metal is obtained. Fe2O3() 2 Fe(s) + 3/2 O2 (g) (1) C(s) + O2 (g) → CO2(g) (2) When reaction 1 is coupled to reaction 2, overall chemical equation is Fe2O3() + 3/2 C() 3/2 CO2(g) + 2 Fee) Use the thermodynamic data given below for the following calculations: AG¡ (kJ/mol) | 4H¡ (kJ/mol) | S (J/mol-K) Fe2O3(s) -742.2 -824.2 87.40 Fes) 27.28 CO2(8) -394.36 -393.51 213.74 C (6) 5.74 O2 (2) 205.14 a) Calculate the standard Gibb's free energy change for reaction 1 b) Calculate the standard Gibb’s…arrow_forwardThe titanium chloride then reacts with liquid magnesium at 900°C to givetitanium and magnesium chloride (MgCl2). Write a balanced chemicalequation for this step in the refining of titanium.arrow_forwardWhat mass of Cu(IO3)2 can be formed from 0.650 g of CuSO4 · 5H2O? What mass of KIO3 is needed to convert the copper in 0.2750 g of CUSO4 - 5H2O to Cu(IO3)2?arrow_forward
- Write the full electron configuration of Si, Si+4 and Si-4. How many valence electrons are in each of the 3 Si atoms?arrow_forwardMagnesium metal (Mg(s)) burns brightly in oxygen gas (O2(g)) to produce a whitish-grey powder, magnesium oxide (MgO(s)). Write a balanced equation for this reaction.arrow_forwardCr(s) + O2(g)→ Cr,O3(s)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY