
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Transcribed Image Text:As solute is dissolved in a solvent, the vapor
pressure of the solution changes according to
Raoult's law
Psoln Psolv X Xsolv
where Psoln is the vapor pressure of the solution,
Psolv is the vapor pressure of the pure solvent, and
Xsolv is the mole fraction of the solvent. If the
solute dissociates into ions, the term Xsolv must be
modified to take into consideration the total number
of moles of particles in the solution, both ions and
molecules. When a solution contains two volatile
components, A and B, the total pressure of the
solution is equal to the sum of the individual vapor
pressures according to Dalton's law as follows:
Ptotal PAX XA +PB X XB
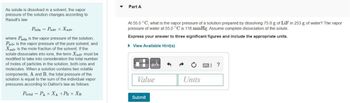
Part A
At 55.0 °C, what is the vapor pressure of a solution prepared by dissolving 75.8 g of LiF in 253 g of water? The vapor
pressure of water at 55.0 °C is 118 mmHg. Assume complete dissociation of the solute.
Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units.
► View Available Hint(s)
μA
Value
Submit
Units
?
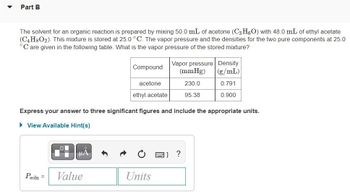
Transcribed Image Text:Part B
The solvent for an organic reaction is prepared by mixing 50.0 mL of acetone (C3H6O) with 48.0 mL of ethyl acetate
(C4H8O2). This mixture is stored at 25.0 °C. The vapor pressure and the densities for the two pure components at 25.0
°C are given in the following table. What is the vapor pressure of the stored mixture?
Psoln =
μA
Compound
Value
acetone
Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units.
View Available Hint(s)
ethyl acetate
Vapor pressure Density
(mmHg)
(g/mL)
230.0
0.791
95.38
0.900
Units
?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Calculate the vapor pressure above a solution prepared by dissolving 2.00 g of aspirin (C9H8O4) in 50.0 g of methanol (CH3OH) at 21.2 °C. Pure methanol has a vapor pressure of 101 torr at 21.2 °C.arrow_forwardHow many grams of pentane, CH3(CH2)3CH3, must be mixed with 64.18 g of hexane, CH3(CH2)4CH3, at 25.00 °C to produce a solution with a vapor pressure above the solution of 273.5 torr? The vapor pressures of pure pentane and hexane at 25.00 °C are 511.0 torr and 150.0 torr, respectively. These compounds form nearly ideal solutions when mixed together.arrow_forwardMolality A solution contains 22.5 g of methanol, CH3OH, dissolved in sufficient water to give a total mass of 105.3 g. The molar mass of CH3OH is 32.4 g/mol. What is the molality of the aqueous methanol solution?arrow_forward
- What is the mole fraction of acetone, C3H6O, in the vapor phase from a solution consisting of a mixture of acetone and ethyl acetate, CH3COOCH2CH3, at 30.00 °C, if the total pressure above the solution is 202.2 torr? The vapor pressures of pure acetone and NaN at 30.00 °C are 285.0 torr and 118.0 torr, respectively.arrow_forwardThe vapor pressure of diethyl ether (ether) is 463.57 mm Hg at 25 °C. A nonvolatile, nonelectrolyte that dissolves in diethyl ether is aspirin.Calculate the vapor pressure of the solution at 25 °C when 10.17 grams of aspirin, C9H8O4 (180.1 g/mol), are dissolved in 151.7 grams of diethyl ether.diethyl ether = CH3CH2OCH2CH3 = 74.12 g/mol. The vapor pressure of diethyl ether (ether) is 463.57 mm Hg at 25°C.How many grams of estrogen (estradiol), C18H24O2, a nonvolatile, nonelectrolyte (MW = 272.4 g/mol), must be added to 192.1 grams of diethyl ether to reduce the vapor pressure to 452.63 mm Hg ?diethyl ether = CH3CH2OCH2CH3 = 74.12 g/mol.arrow_forwardThe vapor pressure of diethyl ether (ether) is 463.57 mm Hg at 25 °C. A nonvolatile, nonelectrolyte that dissolves in diethyl ether is aspirin.Calculate the vapor pressure of the solution at 25 °C when 10.17 grams of aspirin, C9H8O4 (180.1 g/mol), are dissolved in 151.7 grams of diethyl ether.diethyl ether = CH3CH2OCH2CH3 = 74.12 g/mol. The vapor pressure of diethyl ether (ether) is 463.57 mm Hg at 25°C.How many grams of estrogen (estradiol), C18H24O2, a nonvolatile, nonelectrolyte (MW = 272.4 g/mol), must be added to 192.1 grams of diethyl ether to reduce the vapor pressure to 452.63 mm Hg ?diethyl ether = CH3CH2OCH2CH3 = 74.12 g/mol.arrow_forward
- If 57.22 mg of Na2SO4 (formula mass = 142.02 g/mol) is dissolved in 36.64 mL. What is the osmotic pressure of this solution at 29.21 °C. Assume any salt is completely ionic!arrow_forwardThe vapor pressure of chloroform is 173.11 mm Hg at 25 °C. A nonvolatile, nonelectrolyte that dissolves in chloroform is aspirin.Calculate the vapor pressure of the solution at 25 °C when 13.35 grams of aspirin, C9H8O4 (180.1 g/mol), are dissolved in 238.1 grams of chloroform.chloroform = CHCl3 = 119.40 g/mol.VP(solution) = __________mm Hgarrow_forward5. The vapor pressure of benzene is 73.03 mm Hg at 25 °C. A nonvolatile, nonelectrolyte that dissolves in benzene is TNT. Calculate the vapor pressure of the solution at 25 °C when 12.12 grams of TNT, C,H;N;Os (227.1 g/mol), are dissolved in 155.7 grams of benzene. benzene = CHs = 78.12 g/mol.arrow_forward
- At 25.0 °C, 100.0 mL of an aqueous solution containing 45.2 mg of a molecular solute has an osmotic pressure of 18.4 Torr. The molar mass of the solute is ___ g/mol.arrow_forwardA 2.20 g sample of a non-electrolyte is dissolved in 51.1 g of water. The solution freezes at −1.23℃ . Calculate the molar mass of the solute.arrow_forwardThe vapor pressure of diethyl ether (ether) is 463.57 mm Hg at 25 °C. A nonvolatile, nonelectrolyte that dissolves in diethyl ether is aspirin.Calculate the vapor pressure of the solution at 25 °C when 10.18 grams of aspirin, C9H8O4 (180.1 g/mol), are dissolved in 239.0 grams of diethyl ether.diethyl ether = CH3CH2OCH2CH3 = 74.12 g/mol.VP(solution) = mm Hgarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY