
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
thumb_up100%
Transcribed Image Text:Ma
Question 14
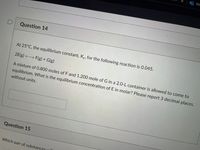
At 25°C, the equilibrium constant, Kc, for the following reaction is 0.045.
2E(g) F(g) + G(g)
A mixture of 0.800 moles of F and 1.200 mole of G in a 2.0-L container is allowed to come to
equilibrium. What is the equilibrium concentration of E in molar? Please report 3 decimal places,
without units.
Question 15
Which pair of substances will
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The equilibrium constant, Kc, for the following reaction is 55.6 at 698 K.H2 (g) + I2 (g) 2 HI (g)Calculate the equilibrium concentrations of reactants and product when 0.252 moles of H2 and 0.252 moles of I2 are introduced into a 1.00 L vessel at 698 K. [ H2 ] = M [ I2 ] = M [ HI ] = Marrow_forwardR Manipulating Equilibrium Constant Expressions equilibrium constant for the following reaction is 63.3 at 378 °C. K 63.3 at 378 °C H₂(g) + 12(g) = 2 HI(g) culate the equilibrium constant for the following reactions at 378 °C. a) 2 HI(g) = H₂(g) + I2(g) K = (b) HI(g) 1/2 H₂(g) + 1/2 I2(g) Show Approach Show Tutor Steps Submit Submit Answer Try Another Version K = [References] 4 item attempts remaining Previous Nextarrow_forwardConsider the following system at equilibrium at 698 K. 2 HI(g)→ H₂(g) + I₂ (9) Use the References to access importa When some HI(g) is removed from the equilibrium system at constant temperature, the reaction must O run in the forward direction to reestablish equilibrium. O run in the reverse direction to reestablish equilibrium. O remain the same. It is already at equilibrium. The concentration of H₂ will O increase. O decrease. O remain the same.arrow_forward
- The reaction below was allowed to react at 375 degrees Celcius until it formed an equilibrium. At equilibrium, the 16.2 L container was found to contain 1.9 mol SiF4, 1.1 mol H2O, 3.5 mol SiO2, and 2.9 mol HF. What is the Kc of the reaction at this temperature? SiF4 (g) + 2H2O (g) <--> SiO2 (s) + 4HF(g)arrow_forwardCO2 and H, are allowed to react until an equilibrium is established as follows: CO2 (g) + H, (g)H,0 (g) + CO (g) What will be the effect on the equilibriumn of removing CO from the equilibrium mixture?arrow_forwardA chemical engineer is studying the following reaction: N₂(g) + 3H₂(g) → 2 NH3(g) At the temperature the engineer picks, the equilibrium constant K for this reaction is 0.00014. The engineer charges ("fills") three reaction vessels with nitrogen and hydrogen, and lets the reaction begin. He then measures the composition of the mixture inside each vessel from time to time. His first set of measurements are shown in the table below. Predict the changes in the compositions the engineer should expect next time he measures the compositions. reaction vessel A B C compound N₂ H₂ NH3 N₂ H₂ NH₂ N₂ H₂ NH₂ pressure 32.70 atm 49.38 atm 23.45 atm 33.09 atm 50.55 atm 22.67 atm 33.10 atm 50.59 atm 22.64 atm expected change in pressure ↑ increase ↑ increase ↑ increase ↑ increase ↑ increase O ↑ increase ↑ increase ↑ increase ↑ increase decrease ↓ decrease ↓ decrease ↓ decrease ↓ decrease decrease ↓ decrease decrease decrease (no change) (no change) (no change) (no change) (no change) O (no change) (no…arrow_forward
- The formation of nitrogen monoxide from its elements has an equilibrium which favors reactants: N2 (g) + 02 (g) 2 NO (g) K, = 0.0290 at 2400°C If the initial partíal pressures of both reactant gases are 0.717 atm, what will be the equilibrium partial pressure of nitrogen monoxide? (A certain simplification is valid in solving this problem). 0.112 atm (A) (B) 0.0290 atm (C) 0.688 atm (D) 0.0563 atm (E) 0.0611 atmarrow_forwardThe equilibrium constant, Kc, for the following reaction is 55.6 at 698 K.H2 (g) + I2 (g) 2 HI (g)Calculate the equilibrium concentrations of reactants and product when 0.228 moles of H2 and 0.228 moles of I2 are introduced into a 1.00 L vessel at 698 K. [ H2 ] = M [ I2 ] = M [ HI ] = Marrow_forwardA chem ngineer is studying the following reaction: 4 HCl(g)+O,(g) – 2 H,0(g)+2Cl,(g) At the temperature the engineer picks, the equilibrium constant K, for this reaction is 0.0040. The engineer charges ("fillsf) four reaction vessels with hydrogen chloride and oxygen, and lets the reaction begin. He then measures the co mixture inside each vessel from time to time. His first set of measurements are shown in the table below. Predict the changes in the compositions the engineer should expect next time he measures the compositions. reaction compound pressure expected change in pressure vessel HCl 8.71 atm Ot increase O! decrease O (no change) 02 8.13 atm O t increase OI decrease O (no change) H,0 3.63 atm Ot increase OI decrease (no change) I decrease (no change) Cl, 1.91 atm ease I decrease (no change) 7,61 atm t increase HCI I decrease O (no change) 7,86 atm O f increase 0, I decrease O (no change) 4.18 atm t increase H,0 I decrease (no change) t increase 2.46 atm Cl, I decrease O (no…arrow_forward
- For the following reaction, K, = 0.262 at 1000°C: C(s) + 2 H2(g) = CH4(g) At equilibrium, Pa, is 1.22 atm and 1.35 g of carbon is present. What is the equilibrium partial pressure of CH4(g)? 0.390 atm 5.68 atm 0.997 atm 0.320 atm 0.624 atm None of thesearrow_forwardA chemical engineer is studying the following reaction: H₂(g) + Cl₂(g) → 2 HCl(g) At the temperature the engineer picks, the equilibrium constant K, for this reaction is 0.83. The engineer charges ("fills") three reaction vessels with hydrogen and chlorine, and lets the reaction begin. He then measures the composition of the mixture inside each vessel from time to time. His first set of measurements are shown in the table below. Predict the changes in the compositions the engineer should expect next time he measures the compositions. reaction vessel A C compound H₂ Cl₂ HCI H₂ CL₂ HCI H₂ CL₂ HCI pressure 4.00 atm 1.97 atm 3.36 atm 4.27 atm 2.82 m 3.84 atm 1.81 atm 3.69 atm expected change in pressure 1 increase O decrease decrease Of increase Of increase Ⓒ↓ decrease Of increase O decrease decrease O1 increase Ot increase O decrease Of increase O decrease Of increase O decrease decrease Of increase O (no change) (no change) O(no change) (no change) (no change) (no change) (no change) (no…arrow_forward3 A + 2 B → 1 CCalculate the equilibrium constant (K) for the following reaction at 1000. K, using this information: A and B are placed in a flask and at the beginning of the reaction [A] is 6.87 M and [B] is 6.38 M. After the reaction has reached equilibrium, [C] is 1.47 M. Unfortunately, significant figures cannot be taken into account here, so please ignorethem this time.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY