
Fundamentals Of Analytical Chemistry
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781285640686
Author: Skoog
Publisher: Cengage
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
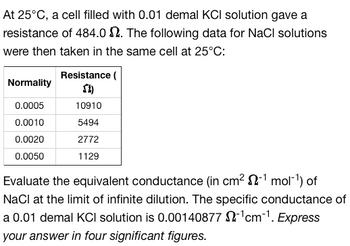
Transcribed Image Text:At 25°C, a cell filled with 0.01 demal KCI solution gave a
resistance of 484.02. The following data for NaCl solutions
were then taken in the same cell at 25°C:
Normality
0.0005
0.0010
0.0020
0.0050
Resistance (
SI)
10910
5494
2772
1129
Evaluate the equivalent conductance (in cm² 2-¹ mol-¹) of
NaCl at the limit of infinite dilution. The specific conductance of
a 0.01 demal KCI solution is 0.00140877 $2¹cm-¹. Express
your answer in four significant figures.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Use the following data to calculate the enthalpy of solution of sodium perchlorate, NaClO4: fH(s)=382.9kJ/mol and fH(aq,1m)=369.5kJ/molarrow_forwardThe conductivity of a 0.0312 M solution of a weak base is 1.53 x 104 Scm'. If the sum of the limiting ionic conductances for BH* and OH-' is 237.0 Scm²mol·' what is the value of the base constant K6? 4.5 x 10s mol.dm (i) 2.3 x 103 mol.dm (iii) 2.89 x 10 mol.dm3 (ii) 1.37 x 10-5 mol.dm3 (iv) (v) 4.78 x 103 mol.dm3arrow_forwardA conductivity cell filled with a 0.01 M KCl solution was found to have a resistance of 189 ohms at 25oC. When filled with 0.01 M HCl solution, the cell gave a resistance of 64.8 ohms at the same temperature. At 25oC, the conductivity of 0.01 M KCl solution was 1.4088 x 10-3 S cm-1. Calculate (a) the cell constant and (b) the conductivity of the HCl solution. answer is [0.266; 4.105 x 10-3] please explain. thank you!arrow_forward
- The mean activity coefficient of a 0.010 m H2SO4 solution is 0.544. What is its mean activity?arrow_forwardConsider the following cell. Pt | H2(1 bar) | HCI(m) | AgCI(s) | Ag At 25.0°C, the emf values at various molalities are given by the following. m/(mol-kg-1) 0.122 0.0548 0.0260 0.0136 0.00927 0.00553 0.00317 E/V 0.342 0.381 0.418 0.450 0.468 0.494 0.521 (a) Determine the value of E° graphically. Compare your value of E° with that listed in the table. E° from graph .2387 X V E° from table 4.0 .8 X V (b) Calculate the mean activity coefficient (Y+) for HCl at 0.122 m. (Use the E° value from the table.) 4.0 .0011arrow_forwardNonearrow_forward
- Calculate the ionic strength of a solution that is 0.040 mol kg−1 in K3[Fe(CN)6](aq), 0.030 mol kg−1 in KCl(aq), and 0.050 mol kg−1 in NaBr(aq).arrow_forwardRequired: Normality of Iodinearrow_forwardThe cell constant of a conductance cell is 388.1 m-1. At 25oC the resistance of a 4.8 x 10-4 mol dm-3 aqueous solution of sodium chloride is 6.4 x 104 and that of a sample of water is 7.4 x 106 . Calculate the molar conductivity of the NaCl in solution at that concentration if the conductance of the NaCl solution is a sum of the conductance of NaCl and that of waterarrow_forward
- b) Determine the standard enthalpy change and std. Gibbs free energy change of reaction at 400 k for the reaction СO(g) +2H2(g) — CHОН (g) At 298.15 K, AH.co (0)= -26.41 kcal/mol, AH AG.co (9)= -32.8079 kcal/mol, AG cH,oh(9)= -38.69 kcal/mol, °.CH20H(9)= -48.08 kcal/mol, The standard heat capacity of various components is given by, CO = a + bT + cT² + dT³, where C, is in cal/mol-K and T is in K b x10² с х105 d x10° Соmponent CH3OH а 4.55 2.186 -0.291 -1.92 CO 6.726 0.04 0.1283 -0.5307 H2 6.952 -0.0457 0.09563 -0.2079arrow_forwardCalculate the cell potential at 25°C for the reaction Fe(s)|Fe^3+ (aq,0.0952 M)|| C12(g,7.62 atm) Cl-(aq,0.0577 M)|Pt(s). Eᵒcell= 1.396 V. 3 sig figs in answer.arrow_forwardThe Nernst-Planck equation (shown below) describes the motion of a charged chemical species in a fluid. dC; z,FC; dv J; = - D; dx RT dx' What are the units for the ion flux J, where: zis the valence state of the ion (unitless) C is the concentration (mol/m³) Fis the Faraday constant (Coulomb/mol) Ris the ideal gas constant (kg m²/(s² mol °K)) Tis the temperature (K) dCi/dx is the concentration gradient (mol/m*) dV/dx is the electric potential gradient (V/m) D; is the diffusion coefficient (m²/s) Note that Coulomb is a unit of charge and V is volts where 1 V= 1 Joule/Coulomb)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning


Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:9781285199047
Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:9781337399074
Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:9781133949640
Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:Cengage Learning