
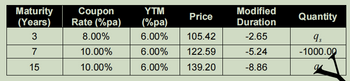
Question 2 Assume the yield curve is flat shown as following table. A cash and $duration-neutral butterfly is to be constructed by selling one thousand 7-year coupon paying bonds and purchasing qs and ql coupon paying bonds with maturities 3 and 15 years respectively. More information on the bonds to be used in the strategy is given
Note that we are assuming all bonds pay interest semi-annually.
(a) Explain how to interpret the modified duration of -8.86 corresponding to the 15-year maturity bond.
(b) Write down the system of equations that needs to be solved in order to find qs and ql and verify that the solution to this system is qs = 679.32 and ql =366.23.
(c) Find the profit from this strategy if yield curve moves: (i) up to 8% pa and (ii) down to 5% pa.
(d) Explain why in practice it may be difficult to profit from the cash and $duration neutral butterfly.
(e) Explain the major differences between the 50-50 butterfly strategy and the cash and $duration neutral butterfly.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 10 images

- Question 1 Assume the yield curve is flat at 6% pa nominal. Today’s date is 18/7/2011. Suppose we have a liability of $100,000 due in exactly 5 year’s time. We want to immunize the liability by investing in a combination of 3 year coupon-paying bonds paying 10% annual coupons and 7 year zero coupon bonds. (a) Assuming annual compounding for all bonds and that each bond has a face value of $100, show that the immunization portfolio consists of 317.62 coupon-paying bonds with three years to maturity and 594.95 zero-coupon bonds with 7 year to maturity. Note: You only have to derive a system of equations and then show that the solution given above satisfies both equations. (b) Explain carefully what further transactions are needed, if any, to ensure the liability can be met on the due date. In your answer, refer to interest rate risk, reinvestment risk and rebalancing and any other relevant concepts.arrow_forwardPlease answer yield to maturity?arrow_forward9arrow_forward
- Conceptual Overview: Explore the value of fixed-interest coupon bonds of different terms. This graph shows the value of 10% coupon bonds of different terms across differing market interest rates. Each bond pays INT = $100 at the end of each year and returns M = $1,000 at maturity. For comparison, the blue line depicts the value of a one-year bond. The term of the other bond in years may be changed using the slider. Drag on the graph to change the current market interest rate (rd) at which the bond (orange curve) is evaluated. ∑ t = 1 Y r s I N T ( 1 + r d ) + M ( 1 + r d ) = ∑ t = 1 1 5 $ 1 0 0 ( 1 + 0 . 1 0 0 ) + $ 1 0 0 0 ( 1 + 0 . 1 0 0 ) = 1 , 0 0 0 ∑ t=1 Yrs (1+r d ) t INT + (1+r d ) Yrs M =∑ t=1 15 (1+0.100) t $100 + (1+0.100) 15 $1000 =1,000 ∑t=1Yrs(1+rd)tINT+(1+rd)YrsM=∑t=115(1+0.000)t$100+(1+0.000)15$1000=2,500. 1. What is the value of a 15-year 10% $1,000 coupon bond when the market interest rate is 15%? $421$708$1,000$1,5192. What is the value of a 12-year 10% $1,000…arrow_forwardExploring Finance: Coupon Bonds. Coupon Bonds Conceptual Overview: Explore the value of fixed-interest coupon bonds of different terms. This graph shows the value of 10% coupon bonds of different terms across differing market interest rates. Each bond pays INT = $100 at the end of each year and returns M = $1,000 at maturity. For comparison, the blue line depicts the value of a one-year bond. The term of the other bond in years may be changed using the slider. Drag on the graph to change the current market interest rate (rd) at which the bond (orange curve) is evaluated. 5. For a 10%, $1,000 coupon bond, a longer term bond (say, 15 years) is: less affected by changes in the market rate than a 1-year bond. affected the same by changes in the market rate than a 1-year bond. more affected by changes in the market rate than a 1-year bond. Cannot be determined.arrow_forwardPlease use this information to help me determine the correct Realized rate of returnarrow_forward
- Can you please walk me through this? Problem 6-11 DEFAULT RISK PREMIUM A company’s 5-year bonds are yielding 7.75% per year. Treasury bonds with the same maturity are yielding 5 2% per year, and the real risk-free rate (r*) is 2.3%. The average inflation premium is 2 5%; and the maturity risk premium is estimated to be 0.1 x (t 1) %, where t = number of years to maturity. If the liquidity premium is 1%, what is the default risk premium on the corporate bonds?arrow_forwardPlease show step by solutions. do not skip stepsarrow_forwardOnly by excel please or else skip itarrow_forward
 Essentials Of InvestmentsFinanceISBN:9781260013924Author:Bodie, Zvi, Kane, Alex, MARCUS, Alan J.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Essentials Of InvestmentsFinanceISBN:9781260013924Author:Bodie, Zvi, Kane, Alex, MARCUS, Alan J.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

 Foundations Of FinanceFinanceISBN:9780134897264Author:KEOWN, Arthur J., Martin, John D., PETTY, J. WilliamPublisher:Pearson,
Foundations Of FinanceFinanceISBN:9780134897264Author:KEOWN, Arthur J., Martin, John D., PETTY, J. WilliamPublisher:Pearson, Fundamentals of Financial Management (MindTap Cou...FinanceISBN:9781337395250Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Fundamentals of Financial Management (MindTap Cou...FinanceISBN:9781337395250Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning Corporate Finance (The Mcgraw-hill/Irwin Series i...FinanceISBN:9780077861759Author:Stephen A. Ross Franco Modigliani Professor of Financial Economics Professor, Randolph W Westerfield Robert R. Dockson Deans Chair in Bus. Admin., Jeffrey Jaffe, Bradford D Jordan ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Corporate Finance (The Mcgraw-hill/Irwin Series i...FinanceISBN:9780077861759Author:Stephen A. Ross Franco Modigliani Professor of Financial Economics Professor, Randolph W Westerfield Robert R. Dockson Deans Chair in Bus. Admin., Jeffrey Jaffe, Bradford D Jordan ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





