
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Assume that the readings at freezing on a batch of thermometers are normally distributed with a mean of 0°C and a standard deviation of 1.00°C. A single thermometer is randomly selected and tested. Find the probability of obtaining a reading between -2.307°C and 2.708°C.
P(- 2.307 < Z < 2.708)=
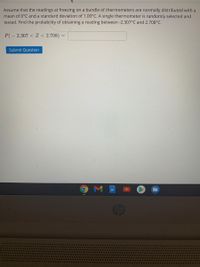
Transcribed Image Text:Assume that the readings at freezing on a bundle of thermometers are normally distributed with a
mean of 0°C and a standard deviation of 1.00°C. A single thermometer is randomly selected and
tested. Find the probability of obtaining a reading between -2.307°C and 2.708°C.
P(- 2.307 < Z < 2.708)
Submit Question
M
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, statistics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Assume that the readings on the thermometers are normally distributed with a mean of 0° and a standard deviation of 1.00°C. A thermometer is randomly selected and tested. Find the probability of each reading in degrees. (a) Between 0 and 1.48: (b) Between -1.84 and 0: (c) Between –0.0299999999999998 and 2.06: (d) Less than -0.23: (e) Greater than -0.11:arrow_forwardAssume that the readings at freezing on a batch of thermometers are normally distributed with a mean of 0°C and a standard deviation of 1.00°C. A single thermometer is randomly selected and tested. Find the probability of obtaining a reading between -2.501°C and -1.165°C.P(−2.501<Z<−1.165)arrow_forward2 C D J X A set of exam scores are approximately normally distributed with mean = 73 and standard deviation = 7. Use the Empirical Rule to determine the area of the shaded regions shown below. 1. 2. 3. 52 52 52 59 59 59 66 66 66 73 Exam Scores 73 Exam Scores 73 Exam Scores 80 80 80 87 87 87 94 Q 94 94 Qarrow_forward
- Assume that the readings at freezing on a batch of thermometers are normally distributed with a mean of 0°C and a standard deviation of 1.00°C. A single thermometer is randomly selected and tested. Find the probability of obtaining a reading between -0.915°C and -0.503°C.P(−0.915 < Z < -0.503)=arrow_forwardAssume that z-scores are normally distributed with a mean of 0 and a standard deviation of 1.If P(−b<z<b)=0.9866P(-b<z<b)=0.9866, find b.b=b=arrow_forwardAssume that the readings at freezing on a batch of thermometers are normally distributed with a mean of 0°C and a standard deviation of 1.00°C. A single thermometer is randomly selected and tested. Find the probability of obtaining a reading between -2.421°C and -2.271°C.P(−2.421<Z<−2.271)arrow_forward
- Assume that the readings at freezing on a batch of thermometers are normally distributed with a mean of 0°C and a standard deviation of 1.00°C. A single thermometer is randomly selected and tested. Find the probability of obtaining a reading between 0.609°C and 2.408°C. P(0.609 < Z < 2.408) =arrow_forwardAssume that the readings at freezing on a bundle of thermometers are normally distributed with a mean of 0°C and a standard deviation of 1.00°C. A single thermometer is randomly selected and tested. Find the probability of obtaining a reading less than -0.04°C.P(Z<−0.04)=arrow_forwardAssume that z-scores are normally distributed with a mean of 0 and a standard deviation of 1.If P(−b<z<b)=0.206P(-b<z<b)=0.206, find b.arrow_forward
- Assume that the readings at freezing on a batch of thermometers are normally distributed with a mean of 0°C and a standard deviation of 1.00°C. A single thermometer is randomly selected and tested. Find the probability of obtaining a reading between 2.857°C and 3.191°C. P(2.857 < Z < 3.191) =arrow_forwardAssume that z-scores are normally distributed with a mean of 0 and a standard deviation of 1.If P(z>c)=0.0106, find c.arrow_forwardAssume that the readings at freezing on a batch of thermometers are normally distributed with a mean of O°C and a standard deviation of 1.00°C. A single thermometer is randomly selected and tested. Find the probability of obtaining a reading between 0.346°C and 1.84°C. P(0.346 < Z < 1.84)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman