
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
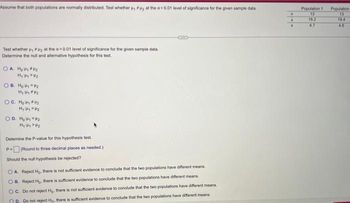
Transcribed Image Text:Assume that both populations are normally distributed. Test whether , #uy at the a=0.01 level of significance for the given sample data
Test whether i, at the a 0.01 level of significance for the given sample data.
Determine the null and alternative hypothesis for this test.
О. А. Нощина
H₁4/2
OB. Hoy #2
H₁ H2
OC. H₂₁*₂
H₂₂
OD. H₂₁ P₂
H₁ HP₂
Determine the P-value for this hypothesis test.
P=(Round to three decimal places as needed.)
Should the null hypothesis be rejected?
OA Reject H₂, there is not sufficient evidence to conclude that the two populations have different means
OB. Reject H₂. there is sufficient evidence to conclude that the two populations have different means
OC. Do not reject Hg, there is not sufficient evidence to conclude that the two populations have different means
P. Do not reject Ho. there is sufficient evidence to conclude that the two populations have different means
n
Population 1
13
16.2
4.7
Population
13
19.4
4.6
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- From the data please state the intervals and what this tells us about the silver content between coins 1 and 2arrow_forwardFind test statistic and P value And state conclusion for the testarrow_forwardDo men have a higher body temperature than women? Test the indicated claim about the means of two populations. Assume that the two samples are randomly selected, independent, the population standard deviations are not know and not considered equal. The table shows results from a study of body temperatures of men and women. At the 0.05 significance level, test the claim that men have a higher body temperature than women. Men Women n1 = 13 n2 = 16 xˉx̄1 = 97 °F xˉx̄2 = 95.17 °F s1 = 0.26 °F s2 = 0.57 °F What are the correct hypotheses? (Select the correct symbols and use decimal values not percentages.)H0: Select an answer x̄₂ μ₁ p p₂ μ₂ μ μ(men) p̂₁ x̄₁ σ₁² p₁ s₁² ? > < ≥ ≠ ≤ = Select an answer p̂₁ p₁ μ μ₁ p x̄₁ μ₂ s₁² x̄₂ μ(women) σ₁² p₂ H1: Select an answer σ₂² μ p̂₂ p₁ p p₂ x̄₁ μ(men) x̄₂ μ₂ μ₁ s₂² ? = ≤ > < ≥ ≠ Select an answer s₁² x̄₁ μ₂ μ p̂₁ x̄₂ σ₁² μ(women) p₁ p p₂ μ₁ Original Claim = Select an answer H₀ H₁ df = Based on the hypotheses, find…arrow_forward
- Use a y-test to test the claim o 35 H, o35 hir winga H, o>35 Identify the test statistic. 18.652 (Round to three decimal places as needed.) me Identify the critical value(s). nts (Round to three decimal places as needed. Use a comma to separate answers as needed.) t: C k Contents edia Library View an example Get more help - Clear all Check answer Help me solve this Plan ior SucceSE 72°F A a a 99+ P Type here to search 10/05/17 Delete PrtSc Insert F12 E11arrow_forwardSuppose you want to test the claim that u, > H,. Two samples are randomly selected from normal populations. The sample statistics are given below. Assume that o #o5. At a level of significance of a = 0.01, when should you reject Ho? n, = 18, n2 =13, x, = 470, x2 = 455, s, = 40, s2 = 25 %3D O A. Reject H, if the standardized test statistic is greater than 2.681. B. Reject Ho if the standardized test statistic is greater than 1.699. O C. Reject H, if the standardized test statistic is greater than 3.055. D. Reject H, if the standardized test statistic is greater than 2.179.arrow_forwardTest the research hypothesis that there is a difference in weights between the two groups at the 0.05 significance level? Assume the equality of variance, adequate sample size, and normal distribution for both the groups to test the hypothesis. X1 = 200 X2 = 198 n1 = 17 n2 = 17 s1 = 2.45 s2 = 2.35 Please show all the necessary steps of hypothesis testing to answer this question.arrow_forward
- Identify the two samples as either independent or dependent. 1. Two samples comparing pre and post semester scores for students in a class 2. A sample of air quality measurements taken in the spring and a sample of air quality measurements taken in the fall. 3. A survey comparing couples political beliefs 4. Sample exam means comparing two different classes 5. Before and after comparison of 500 meter run times, when comparing two different exercise programs Write the null and alternative hypothesis for each claim. Remember to use the difference notation D. 1. A statistics instructor claims his teaching can improve your exam scores 2. Using before and after rounds of golf, a coach claims that she can improve your golf game Listed below are heights in inches of fathers and their first sons. 72 73 Father Son Difference 1. Complete the table and find the differences 2. Use a 5% level of significance to test the claim there is no difference in heights between fathers and first sons. Before…arrow_forwardHW10Q9arrow_forwardSuppose that we have disjoint normal populations A and B and we want to find the standard error estimate for estimating the difference in their means. We have an IRS from A of size 9 and an IRS from B of size 4. The POOLED variance is 18.72. What is the MARGIN OF ERROR for the 99 percent confidence interval for the difference of population means if we assume both populations have the same population variance? Group of answer choicesarrow_forward
- Use a y-test to test the claim o = 0.48 at the a = 0.01 significance level using sample statistics s = 0.466 and n = 15. Assume the population is normally distributed. Identify the null and alternative hypotheses. YA. Ho: o? = 0.48 O B. Ho: o 20.48 H:o +0.48 H,: o 0.48 Identify the test statistic. (Round to two decimal places as needed.)arrow_forwardPlease sir or ma’am, please help me with hypothesis, critical region, and t statistic.arrow_forward7. A study was conducted to compare the amount of salt in potato chips. Random samples of recorded. Assume the populations are normally distributed with equal variances. The 7 A study was conducted to compare the amount of salt in potato chips. Random sampies o. three varieties were obtained and the amount of salt in each 1-Oz portion of potato chp recorded. Assume the populations are normally distributed with equal variances. results are given here: BBQ Cheese- Amount of salt (in mg of sodium) 338, 159, 240, 190 235, 251, 233, 255, 260 Variety flavored Olestra-based 164, 150, 149, 170 a) Identify the explanatory variable. b) Identify the response variable. c) State the appropriate hypotheses to test for a difference in means. d) The appropriate analysis to test for a difference in means would be: a. One-way ANOVA b. Two-way ANOVA c. Three-way ANOVA d. Two-Sample t-testarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman